Externally Induced Thermal Actuation of Polymer Nanocomposites
Ying Hu
i-Lab, Suzhou Institute of Nano-Tech and Nano-Bionics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Suzhou 215125, Jiangsu, P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Wei Chen
i-Lab, Suzhou Institute of Nano-Tech and Nano-Bionics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Suzhou 215125, Jiangsu, P. R. China
i-Lab, Suzhou Institute of Nano-Tech and Nano-Bionics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Suzhou 215125, Jiangsu, P. R. China.Search for more papers by this authorYing Hu
i-Lab, Suzhou Institute of Nano-Tech and Nano-Bionics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Suzhou 215125, Jiangsu, P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Wei Chen
i-Lab, Suzhou Institute of Nano-Tech and Nano-Bionics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Suzhou 215125, Jiangsu, P. R. China
i-Lab, Suzhou Institute of Nano-Tech and Nano-Bionics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Suzhou 215125, Jiangsu, P. R. China.Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
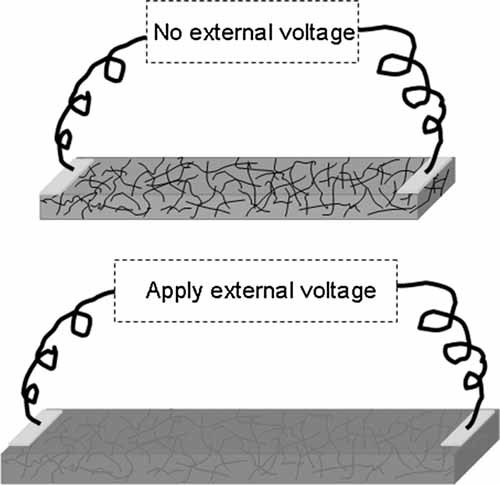
Among the stimuli responsive polymers, thermally active polymers have attracted great attention because of the accessible and effective characteristics of thermal stimulation. Nanomaterials with their unique properties could serve as “nanoantennas” and “nanoheaters” for harvesting external energy such as electrical, optical, and magnetic, and then convert them into useful thermal energy. With a uniform mixture of the nanomaterials, an external stimulus which has no impact on the thermally responsive polymers could effectively induce the mechanical actuation of polymer nanocomposites. Hence, the trend article aims to present a brief overview of recent progress on the externally induced thermal actuation of polymer nanocomposites as well as provide a summary of the thermal actuation mechanisms. Examples are introduced to highlight the influence of embedded nanomaterials during the actuation progress.
References
- 1 P. Brochu, Q. Pei, Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2010, 31, 10.
- 2 E. Smela, Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 481.
- 3 R. Yoshida, Curr. Org. Chem. 2005, 9, 1617.
- 4 D. J. Beebe, J. S. Moore, J. M. Bauer, Q. Yu, R. H. Liu, C. Devadoss, B. H. Jo, Nature 2000, 404, 588.
- 5 V. H. Ebron, Z. Yang, D. J. Seyer, M. E. Kozlov, J. Oh, H. Xie, J. Razal, L. J. Hall, J. P. Ferraris, A. G. MacDiarmid, R. H. Baughman, Science 2006, 311, 1580.
- 6 A. Pelah, R. Seemann, T. M. Jovin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 468.
- 7 E. Du, S. Manoochehri, J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104, 064902.
- 8
Y. Bar-Cohen,
Electroactive Polymer (EAP) Actuator as Artificial Muscles: Reality, Potential and Challenges,
SPIE Press,
Belingham, Washington
2004.
10.1117/3.547465 Google Scholar
- 9 W. T. S. Huck, Mater. Today 2008, 11, 24.
- 10 S. K. Ahn, R. M. Kasi, S. C. Kim, N. Sharma, Y. X. Zhou, Soft Matter 2008, 4, 1151.
- 11 S. V. Ahir, E. M. Terentjev, Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 491.
- 12 H. Koerner, G. Price, N. A. Pearce, M. Alexander, R. A. Vaia, Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 115.
- 13 T. Xie, Nature 2010, 464, 267.
- 14 G. M. Spinks, L. Liu, G. G. Wallace, D. Zhou, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2002, 12, 427.
- 15 K. Hiraoka, W. Sagano, T. Nose, H. Finkelmann, Macromolecules 2005, 38, 7352.
- 16 T. Mirfakhrai, J. D. W. Madden, R. H. Baughman, Mater. Today 2007, 10, 30.
- 17 R. Shankar, T. K. Ghosh, R. J. Spontak, Soft Matter 2007, 3, 1116.
- 18 D. L. Thomsen III, G. Bush, P. Keller, R. G. Bryant, Proc. SPIE 2002, 4695, 435.
- 19 P. T. Mather, Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 93.
- 20 E. S. Gil, S. M. Hudson, Prog. Polym. Sci. 2004, 29, 1173.
- 21 R. Yoshida, K. Uchida, Y. Kaneko, K. Sakai, A. Kikuchi, Y. Sakurai, T. Okano, Nature 1995, 374, 240.
- 22 L. M. Geever, C. M. Minguez, D. M. Devine, M. J. D. Nugent, J. E. Kennedy, J. G. Lyons, A. Hanley, S. Devery, P. T. Tomkin, C. L. Higginbotham, J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 4136.
- 23 W. M. Huang, B. Yang, Y. Zhao, Z. Ding, J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 3367.
- 24 Z. Q. Yang, W. T. S. Huck, S. M. Clarke, A. Tajbakhsh, E. M. Terentjev, Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 486.
- 25 Y. Osada, A. Matsuda, Nature 1995, 376, 219.
- 26 C. Liu, H. Qin, P. T. Mather, J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 1543.
- 27 F. Yang, E. Wornyo, K. Gall, W. P. King, Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 285302.
- 28 Y. Hirokawa, T. Tanaka, J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 81, 6379.
- 29 H. Kawasaki, S. Sasaki, H. Maeda, Langmuir 1998, 14, 773.
- 30 A. R. Tajbakhsh, E. M. Terentjev, Eur. Phys. J. E 2001, 6, 181.
- 31 R. I. Shakoor, S. A. Bazaz, M. Kraft, Y. Lai, M. M. Hassan, Sensors 2009, 9, 2389.
- 32 C. Li, T. Thostenson, T.-W. Chou, Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 1227.
- 33 S. R. Sershen, G. A. Mensing, M. Ng, N. J. Halas, D. J. Beebe, J. L. West, Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 1366.
- 34 W. Suwanwatana, S. Yarlagadda, J. W. Gillespie, Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 2825.
- 35 Y. Hu, W. Chen, L. H. Lu, J. H. Liu, C. R. Chang, ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3498.
- 36 M. Behl, M. Y. Razzaq, A. Lendlein, Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 3388.
- 37 M. Behl, A. Lendlein, Soft Matter 2007, 3, 58.
- 38 J. Zotzmann, M. Behl, D. Hofmann, A. Lendlein, Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 3424.
- 39 N. Jawad, S. Amritha, J. Hong, N. Nikolay, K. Patrick, R. R. Banahalli, Macromolecules 2003, 36, 8499.
- 40 H. Kawasaki, S. Sasaki, H. Maeda, Langmuir 1998, 14, 773.
- 41 H. Dautzenberg, Y. Gao, M. Hahn, Langmuir 2000, 16, 9070.
- 42 Paul. A. Tipler, Gene. Mosca, Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Sixth Edition, Worth Publishers, New York 2008, Vol. 1, pp. 666– 670.
- 43 M. C. LeMieux, M. E. McConney, Y.-H. Lin, S. Singamaneni, H. Jiang, T. J. Bunning, V. V. Tsukruk, Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 730.
- 44 G. Jordan, A. M. Lyons, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2007, 19, 212.
- 45 M. K. Shin, J. Oh, M. Lima, M. E. Kozlov, S. J. Kim, R. H. Baughman, Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2663.
- 46 Y. L. Liu, W. H. Chen, Y. H. Chang, Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 76, 232.
- 47 P. R. Thakre, Y. Bisrat, D. C. Lagoudas, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 191.
- 48 M. Kato, M. Ishibashi, J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2008, 127, 012003.
- 49 L. Z. Chen, C. H. Liu, C. H. Hu, S. S. Fan, Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 263104.
- 50 A. T. Sellinger, D. H. Wang, L. Tan, R. A. Vaia, Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 3430.
- 51 H. Koerner, G. Price, N. A. Pearce, M. Alexander, R. A. Vaia, Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 115.
- 52 J. W. Cho, J. W. Kim, Y. C. Jung, N. S. Goo, Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2005, 26, 412.
- 53 X. Luo, P. T. Mather, Soft Matter 2010, 6, 2146.
- 54 T. Fujigaya, T. Morimoto, Y. Niidome, N. Nakashima, Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 3610.
- 55 S. Lu, B. Panchapakesan, Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2548.
- 56 S. V. Ahir, E. M. Terentjev, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 133902.
- 57 J. J. Liang, Y. F. Xu, Y. Huang, L. Zhang, Y. Wang, Y. F. Ma, F. F. Li, T. Y. Guo, Y. S. Chen, J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 9921.
- 58 S. X. Lu, B. Panchapakesan, Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 305502.
- 59 C. M. Yakacki, N. S. Satarkar, K. Gall, R. Likos, J. Z. Hilt, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 112, 3166.
- 60 A. M. Schmidt, Colloid Polym. Sci. 2007, 285, 953.
- 61 R. Mohr, K. Kratz, T. Weigel, M. Lucka-Gabor, M. Moneke, A. Lendlein, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3540.
- 62 B. J. Adzima, C. J. Kloxin, C. N. Bowman, Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2784.
- 63 H. Huang, S. Delikanli, H. Zeng, D. M. Ferkey, A. Pralle, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 602.