Liposomal Drug Deposits in Poly(Dopamine) Coatings: Effect of Their Composition, Cell Type, Uptake Pathway Considerations, and Shear Stress
Martin E. Lynge
iNANO, Aarhus University, Gustav Wieds Vej 14, Aarhus, 8000 Denmark
Search for more papers by this authorMarina Fernandez-Medina
iNANO, Aarhus University, Gustav Wieds Vej 14, Aarhus, 8000 Denmark
Search for more papers by this authorAlmar Postma
CSIRO Materials Science and Engineering, Ian Wark Laboratory, Bayview Ave, Clayton, Victoria, 3168 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Brigitte Städler
iNANO, Aarhus University, Gustav Wieds Vej 14, Aarhus, 8000 Denmark
Search for more papers by this authorMartin E. Lynge
iNANO, Aarhus University, Gustav Wieds Vej 14, Aarhus, 8000 Denmark
Search for more papers by this authorMarina Fernandez-Medina
iNANO, Aarhus University, Gustav Wieds Vej 14, Aarhus, 8000 Denmark
Search for more papers by this authorAlmar Postma
CSIRO Materials Science and Engineering, Ian Wark Laboratory, Bayview Ave, Clayton, Victoria, 3168 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Brigitte Städler
iNANO, Aarhus University, Gustav Wieds Vej 14, Aarhus, 8000 Denmark
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
Implantable devices equipped with coatings which have the ability to carry and deliver active compounds are of great interest. We report the assembly of liposome-containing poly(dopamine) films, and their interaction with adhering cells. The liposome composition is varied by adding lipophilic dopamine-conjugates and charged lipids. The cell mean fluorescence (CMF) of adhering cells due to the internalization of fluorescent cargo is found to be similar for coatings with the lipophilic-dopamine conjugates, while the charge affects the amount and location of the internalized cargo. The uptake mechanism for cargo by myoblasts using chemical inhibitors is found to be dependent on the used type of liposome. The CMF is significantly reduced for endothelial cells adhering to coatings with applied shear stress.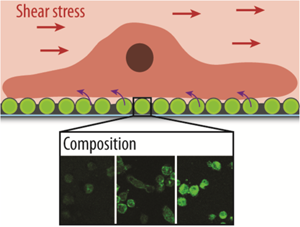
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| mabi201400350-sm-0001-SuppFig-S1.docx10.3 MB |
Figure S1. a) Dissipation changes ΔD of crystals upon exposure to Mzw, Mzw/OL1(25), Mzw/ST1(25), Mzw/PL1(5,10), Mzwp, or Mzw/PL1(5,10) for 70 min changing the solution after 35 min. (ϕ: The solution was not changed within the 70 min.) b) Frequency change Δf of a crystal upon coating with PLL and Mzw/PL10 including the buffer washing steps. c) Dissipation changes ΔD of crystals upon exposure to Mzw/ST25 using different DA concentrations in the mixture for 70 min. Figure S2. a) Representative brightfield microscopy images of myoblasts adhering to Mzw, Mzw/ST25 and Mzw/PL10 for 24 h. Scale bars are 10 µm. b) Photograph of the well plate containing the glass slides after coating with Mzw, Mzw/ST25 and Mzw/OL25, showing that the solution in the last case aggregated within the coating time. Figure S3. Charged liposomes: Change in dissipation ΔD of crystals upon exposure to Mzw, Mn1(2), Mp1(2) and Mp1(2)/ST25 using 2.5 mg/mL DA. Adsorption onto PLL was measured for Mzw, Mn, and onto PLL, PLL/PMA and PLL/PMAc for Mp. Figure S4. A photograph of solutions containing freshly extruded Lp2/ST25 (left) and Lp1/ST25 (right). A pinkish color is observed, which is more pronounced for higher content of positively charges lipids in the liposomes. Figure S5. Representative bright field images of macrophages adhered for 3 h to substrates coated with Mzw, Mn1(2), or Mp1(2). Scale bars are 25 µm. Figure S6. Representative bright field images of hepatocytes adhered 3 h to substrates coated with Mzw, Mn1(2), or Mp1(2). Scale bars are 25 µm. Figure S7. Representative bright field microscopy images of myoblasts cells adhered 3 h to substrates coated with Mzw, Mn1(2), or Mp1(2). Scale bars are 25 µm Figure S8. Representative bright field images of endothelial cells adhered for 3 h to substrates coated with Mzw, Mn1 (2), or Mp1 (2). Scale bars are 25 µm. Figure S9. Representative CLSM images of macrophages adhered for 3 h to substrates coated with Mzw, Mn1(2), or Mp1(2). Scale bars are 50 µm. Figure S10. Representative CLSM images of hepatocytes adhered for 3 h to substrates coated with Mzw, Mn1(2), or Mp1(2). Scale bars are 50 µm. Figure S11. Representative CLSM images of myoblasts adhered for 3 h to substrates coated with Mzw, Mn1(2), or Mp1(2). Scale bars are 50 µm. Figure S12. Representative CLSM images of endothelial cells adhered for 3 h to substrates coated with Mn1(2). Scale bars are 50 µm. Figure S13. Cell viability of cells incubated for 3 h in the presence of inhibitors with concentrations 1x, 2x and 4x. Amil: Amiloride (x: 50 µM), Cp: Chlorpromazine (x: 10 µM), Fil: Filipin (x: 1 µg/mL) Figure S14. Uptake pathway: CMF of myoblasts exposed to Ln2 for 3 h in the presence of different chemical inhibitors (Ami: Amiloride (200 µg/ml), Cp: chlorpromazine (10 µg/mL), Fil: filipin complex (1 µM)) for specific endocytosis uptake pathways are shown. Control experiments using untreated cells (C), cells with PBS (P) or PBS and DMSO (D) but without inhibitors are shown for comparison. Figure S15. Mass spectra data of PL-DA (a) and ST-DA (b). Table S1. Diameter and PDI of liposomes containing different lipophilic DA-conjugates. Table S2. Diameter and PDI of liposomes containing different charged lipids and/or lipophilic DA-conjugates. |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 a) V. Gribova, R. Auzely-Velty, C. Picart, Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 854; b) A. N. Zelikin, ACS Nano 2010, 4, 2494.
- 2 H. Lee, S. M. Dellatore, W. M. Miller, P. B. Messersmith, Science 2007, 318, 426.
- 3 Y. Liu, K. Ai, L. Lu, Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5057.
- 4 M. E. Lynge, R. van der Westen, A. Postma, B. Städler, Nanoscale 2011, 3, 4916.
- 5 S. H. Ku, J. Ryu, S. K. Hong, H. Lee, C. B. Park, Biomaterials 2010, 31, 2535.
- 6 L. Hosta-Rigau, B. E. B. Jensen, K. S. Fjeldsø, A. Postma, G. Li, K. N. Goldie, F. Albericio, A. N. Zelikin, B. Städler, Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2012, 1, 791.
- 7 a) D. R. Dreyer, D. J. Miller, B. D. Freeman, D. R. Paul, C. W. Bielawski, Langmuir 2012, 28, 6428; b) S. Hong, Y. S. Na, S. Choi, I. T. Song, W. Y. Kim, H. Lee, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 4711; c) N. F. Della Vecchia, R. Avolio, M. Alfè, M. E. Errico, A. Napolitano, M. d'Ischia, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 1331; d) J. Liebscher, R. Mrowczynski, H. A. Scheidt, C. Filip, N. D. Hadade, Langmuir 2013, 29, 10539.
- 8 H. Lee, J. Rho, P. B. Messersmith, Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 431.
- 9 a) Y. Zhang, B. Thingholm, K. N. Goldie, R. Ogaki, B. Städler, Langmuir 2012, 28, 17585; b) Y. Zhang, B. M. Teo, A. Postma, F. Ercole, R. Ogaki, M. Zhu, B. Städler, J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 10504; c) W.-B. Tsai, C.-Y. Chien, H. Thissen, J.-Y. Lai, Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 2518; d) S. M. Kang, N. S. Hwang, J. Yeom, S. Y. Park, P. B. Messersmith, I. S. Choi, R. Langer, D. G. Anderson, H. Lee, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 2949; e) Y. Zhang, K. Panneerselvam, R. Ogaki, L. Hosta-Rigau, R. van der Westen, B. E. B. Jensen, B. M. Teo, M. Zhu, B. Städler, Langmuir 2013, 29, 10213.
- 10 a) J. H. An, N. T. Huynh, Y. Sil Jeon, J.-H. Kim, Polym. Int. 2011, 60, 1581; b) C. J. Ochs, T. Hong, G. K. Such, J. Cui, A. Postma, F. Caruso, Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 3141; c) J. Saiz-Poseu, J. Sedó, B. García, C. Benaiges, T. Parella, R. Alibés, J. Hernando, F. Busqué, D. Ruiz-Molina, Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2066.
- 11 F. Daubiné, D. Cortial, G. Ladam, H. Atmani, Y. Haïkel, J.-C. Voegel, P. Clézardin, N. Benkirane-Jessel, Biomaterials 2009, 30, 6367.
- 12 T. G. Kim, H. Lee, Y. Jang, T. G. Park, Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 1532.
- 13 T. Boudou, P. Kharkar, J. Jing, R. Guillot, I. Pignot-Paintrand, R. Auzely-Velty, C. Picart, J. Control. Release 2012, 159, 403.
- 14
L. Hosta-Rigau,
P. Schattling,
B. M. Teo,
M. Lynge,
B. Stadler,
J. Mater. Chem. B
2014, DOI: 10.1039/C4TB00825A
10.1039/C4TB00825A Google Scholar
- 15 B. M. Teo, L. Hosta-Rigau, M. E. Lynge, B. Städler, Nanoscale 2014, 6, 6426.
- 16 a) N. Graf, A. Tanno, A. Dochter, N. Rothfuchs, J. Voros, T. Zambelli, Soft Matter 2012, 8, 3641; b) M. E. Lynge, R. Ogaki, A. O. R. Laursen, J. Lovmand, D. S. Sutherland, B. Staädler, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 2142.
- 17 a) B. E. B. Jensen, L. Hosta-Rigau, P. R. Spycher, E. Reimhult, B. Städler, A. N. Zelikin, Nanoscale 2013, 5, 6758; b) M. E. Lynge, M. Baekgaard Laursen, L. Hosta-Rigau, B. E. B. Jensen, R. Ogaki, A. A. A. Smith, A. N. Zelikin, B. Städler, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 2967; c) M. E. Lynge, B. M. Teo, M. B. Laursen, Y. Zhang, B. Städler, Biomater. Sci. 2013, 1, 1181.
- 18 L. Hosta-Rigau, M. J. York-Duran, Y. Zhang, K. N. Goldie, B. Städler, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 12771.
- 19 P. C. DeMuth, J. J. Moon, H. Suh, P. T. Hammond, D. J. Irvine, ACS Nano 2012, 6, 8041.
- 20 R. van der Westen, L. Hosta-Rigau, D. S. Sutherland, K. N. Goldie, F. Albericio, A. Postma, B. Städler, Biointerphases 2012, 7, 8.
- 21 X. Zhang, K. K. Sharma, M. Boeglin, J. Ogier, D. Mainard, J. C. Voegel, Y. Mely, N. Benkirane-Jessel, Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 2432.
- 22 a) I. A. Khalil, K. Kogure, H. Akita, H. Harashima, Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 32; b) S. Mukherjee, R. N. Ghosh, F. R. Maxfield, Physiol. Rev. 1997, 77, 759.
- 23 C. Lamaze, S. L. Schmid, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1995, 7, 573.
- 24 J. E. Schnitzer, P. Oh, E. Pinney, J. Allard, J. Cell Biol. 1994, 127, 1217.
- 25 C. M. Canessa, L. Schild, G. Buell, B. Thorens, I. Gautschi, J.-D. Horisberger, B. C. Rossier, Nature 1994, 367, 463.
- 26 a) T. Fujiwara, H. Akita, K. Furukawa, T. Ushida, H. Mizuguchi, H. Harashima, Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 29, 1511; b) S. S. Harris, T. D. Giorgio, Gene Ther. 2005, 12, 512; c) L. Hosta-Rigau, B. Städler, Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 2707.
- 27 a) C. Fillafer, G. Ratzinger, J. Neumann, Z. Guttenberg, S. Dissauer, I. K. Lichtscheidl, M. Wirth, F. Gabor, M. F. Schneider, Lab Chip 2009, 9, 2782; b) O. C. Farokhzad, A. Khademhosseini, S. Jon, A. Hermmann, J. Cheng, C. Chin, A. Kiselyuk, B. Teply, G. Eng, R. Langer, Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 5453; c) S. Kona, J.-F. Dong, Y. Liu, J. Tan, K. T. Nguyen, Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 423, 516.
- 28 D. Kim, Y.-S. Lin, C. L. Haynes, Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8377.
- 29 L. Hosta-Rigau, Y. Zhang, B. M. Teo, A. Postma, B. Städler, Nanoscale 2013, 5, 89.
- 30 a) J. Han, B. J. Zern, V. V. Shuvaev, P. F. Davies, S. Muro, V. Muzykantov, ACS Nano 2012, 6, 8824; b) S. P. Samuel, N. Jain, F. O'Dowd, T. Paul, D. Kashanin, V. A. Gerard, Y. K. Gun'ko, A. Prina-Mello, Y. Volkov, Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 2943.
- 31 B. Fejerskov, N. B. S. Jensen, B. M. Teo, B. Städler, A. N. Zelikin, Small 2013, 10, 1314.
- 32 R. Chandrawati, B. Städler, A. Postma, L. A. Connal, S. F. Chong, A. N. Zelikin, F. Caruso, Biomaterials 2009, 30, 5988.
- 33 S. M. Sagnella, C. E. Conn, I. Krodkiewska, X. Mulet, C. J. Drummond, Soft Matter 2011, 7, 5319.
- 34 B. F. Daubert, H. H. Fricke, H. E. Longenecker, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1943, 65, 2142.




