Microfluidic Synthesis of Pharmacologically Responsive Supramolecular Biohybrid Microgels
Abstract
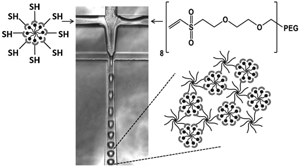
Biohybrid hydrogels that change their mechanical properties in response to pharmacological cues hold high promises as externally controlled drug depots for biomedical applications. In this study, we devise a generically applicable method for the synthesis of micrometer-scale, injection-ready biohybrid materials. We use droplet-based microfluidics to generate monodisperse pre-microgel fluid droplets, wherein which we react fluorescein-modified 8-arm poly(ethylene glycol) with a thiol-functionalized humanized anti-fluorescein single chain antibody fragment and vinylsulfone-functionalized 8-arm poly(ethylene glycol), resulting in the formation of stable, narrowly dispersed supramolecular microgels (30 and 150 μm diameter). We demonstrate that the addition of free fluorescein to these microgels results in a weakening of their hydrogel structure, eventually leading to its disintegration. This method of formation of pharmacologically responsive biohybrid hydrogels in an injection-ready formulation is a pioneering example of a general approach for the synthesis of biohybrid hydrogel-based drug depots for biomedical applications.