Performance evaluation of Elecsys HIV Duo on cobas e 801 using clinical samples in China
Bowen Zhang and Qiang Ma made equal contribution to the study. They should share the first authorship.
Trademark: All trademarks mentioned enjoy legal protection.
Abstract
The prevalence and incidence of human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) infection are rapidly increasing, and novel HIV genotypes are emerging. This study evaluated the sensitivity and specificity of Elecsys HIV Duo assay in population with the epidemic of multiple genotypes of HIV-1 infection. Specificity of the Elecsys HIV Duo assay was determined using 3039 serum samples from patients receiving routine HIV-1 screening tests in China. Sensitivity was assessed with seroconversion panels. Additional 67 positive from newly diagnosed HIV-1 infected samples were also included to test assay performance on various HIV-1 genotypes. The assay performance was compared with that of the Elecsys HIV Combi PT assay. The genotypes of all HIV-1 positive samples were determined with phylogenetic analyses on the 1.1 kb Pro-RT region of pol gene for drug resistance tests. The Elecsys HIV Duo assay had a slightly higher specificity (99.93% vs 99.84%) and equivalent sensitivity to Elecsys HIV Combi PT assay. Seventy-two HIV-1 positive samples, including 12 antigens positive samples, were distinguished by Elecsys HIV Duo. Among them, 43 samples were circulating recombinant form (CRF)01_AE, followed by 13 of CRF07_BC, 10 of subtype B, 4 of URF_0107, 1 of URF_01B and 1 of CRF02_AG. The Elecsys HIV Duo assay showed good performance for the Chinese population with an epidemic of multiple HIV genotypes.
Highlights
-
The overall performance of cobas e 801 and Elecsys® HIV Duo were found to be slightly better than that of the currently available platform and assay.
-
Seventy-two HIV-1 positive samples, including 12 antigens positive samples, were distinguished by Elecsys® HIV Duo.
-
The Elecsys® HIV Duo assay (cobas e 801 analyzer) showed excellent performance for detecting HIV-1 strains of different subtypes and new recombinants.
-
The Elecsys® HIV Duo assay is suitable for routine clinical diagnostic use, including preoperative assessment, in areas affected by the associated HIV-1 strains.
1 BACKGROUND
According to the World Health Organization, over 36 million people are currently infected with human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) worldwide. Approximately 2 million new HIV cases are diagnosed every year,1 but a significant number of people are unaware that they have the infection.2 An effective strategy for HIV testing is crucial for disease control and public health management.3
As well as epidemiological studies, recent studies have also investigated the complexity of HIV genotypes, their distribution, and dynamics, in particular among high-risk populations.4 In a national HIV molecular epidemiology study in 1404 Chinese samples, a total of ten HIV-1 subtypes and circulating recombinant forms (CRFs) were detected, among which CRF07_BC, CRF01_AE, CRF08_BC, and subtype B were the most common HIV-1 subtypes, accounting for 92.8% of all infections.5 Multiple HIV genotypes have also been reported among high-risk populations from a wide range of regions across China, with new recombinants continually identified and reported.6, 7
The Elecsys HIV Combi PT assay (Roche Diagnostics) for use on the cobas e 601 analyzer is currently available for clinical use in China. The next generation cobas e 801 analyzer was launched in China in June 2018. This new instrument allows for continuous loading of reagents and consumables, and has a high uptime while requiring less hands-on time; turn-around times are very rapid, at 18 minutes for routine testing and 9 minutes for emergency testing. This study is the first to evaluate the performance of the Elecsys HIV Duo assay (Roche Diagnostics) on the new cobas e 801 analyzer, using clinical samples from a Chinese population.
2 OBJECTIVES
This study evaluated the performance of the Elecsys HIV Duo assay on the cobas e 801 analyzer in clinical samples for routine HIV-1 screening from Chinese patients.
3 STUDY DESIGN
3.1 Study conduct
This study was conducted in the First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, China. After an initial familiarization phase, 3039 serum samples from patients receiving routine HIV-1 screening tests in China and 67 HIV-1 positive samples from newly diagnosed patients in 2019 were included. Two commercially available HIV-1 seroconversion panels representing 14 samples were also used.
The study protocol was approved by the ethics committee at the research site. Principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and local regulations were fully applied. Exemption for obtaining informed consent from subjects was granted as the samples used in this clinical trial were all residual blood samples and there was no direct contact with patients.
3.2 Investigational products
The Elecsys HIV Duo assay is intended for use in the in vitro qualitative determination of HIV-1 p24 antigen and antibodies to HIV-1 (including group O) and HIV-2 in human serum and plasma. Sub-results (HIV Ag and anti-HIV) are intended as an aid in the selection of the confirmation algorithm for reactive samples. This assay is run on cobas e 801 analyzer. Assay performance was compared with the older generation, Elecsys HIV Combi PT assay (cobas e 601 analyzer), which is currently available in China.
3.3 Assay performance
Specificity of the Elecsys HIV Duo assay (cobas e 801 analyzer) and Elecsys HIV Combi PT assay (cobas e 601 analyzer) were evaluated in 3039 unselected pseudonymizedresidual clinical samples from routine screening of Chinese patients. Sensitivity of the two assays was tested in two seroconversion panels (SeraCareAccuVert Panel HIV-1/0600-0251 and SeraCareAccuVert Panel HIV-1/0600-0237) and 67 newly diagnosed positive samples. Cutoff indices were calculated for the Elecsys HIV Combi PT assay and Elecsys HIV Duo assay (HIV Ag, anti-HIV, and HIV Duo). Resolution of weak positive or discrepant results was performed using the confirmatory algorithm shown in Figure S1.
3.4 Phylogenetic analyses
HIV-1 RNA was extracted from 140 μL serum according to the manufacturer's instructions of QIAamp Viral RNA Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). The one-step RNA PCR Kit (Takara, Japan) was used to synthesize complementary DNA and amplify the entire protease and partial reverse transcriptase as described previously.8 The PCR products were sequenced by bi-directional sequencing with five specific primers according to the published literature.9
The sequences were assembled by Contig Express 6.0 and aligned with HIV-1 reference sequences from the HIV sequences database (https://www.hiv.lanl.gov). Phylogenetic trees were constructed with the neighbor-joining method using Mega 7.0.14 based on the Kimura 2-parameter model and 1000 bootstrap replications (http://www.megasoftware.net/index.html). The genotype of each sequence was based on the neighbor-joining tree with a bootstrap value above 90%. Preliminary analysis of HIV recombination by HIV database online program RIP and jpHMM (https://www.hiv.lanl.gov) and then Simplot software 3.5.1 were used to confirm recombination and determine the breakpoint with a window size of 200 bp and a step size of 20 bp.
4 RESULTS
4.1 Specificity of Elecsys HIV Duo assay
Specificity was 99.93% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 99.76%-99.99%) for the Elecsys HIV Duo assay and 99.84% (95% CI: 99.62%-99.95%) for the Elecsys HIV Combi PT assay (Table 1). Two false-positive results were observed with the Elecsys HIV Duo assay and five with the Elecsys HIV Combi PT assay.
| Parameter | Elecsys HIV Duo assay | Elecsys HIV Combi PT assay |
|---|---|---|
| Number of samples, N | 3039 | 3039 |
| NR confirmed indeterminate, n/N | 0/3032 | 0/3029 |
| NR confirmed positive, n/N | 0/3032 | 0/3029 |
| Negative, n | 3034 | 3034 |
| True negative, n | 3032 | 3029 |
| R | 7 | 10 |
| False positive, n | 2 | 5 |
| R confirmed positive, n/N | 5/7 | 5/10 |
| R confirmed indeterminate, n/N | 0/7 | 0/10 |
| R confirmed negative, n/N | 2/7 | 5/10 |
| Specificity (95% CI)a, % | 99.93 (99.76-99.99) | 99.84 (99.62-99.95) |
- Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; NR, nonreactive; R, reactive.
- a Two-sided test.
4.2 Sensitivity of Elecsys HIV Duo assay
Sensitivity results for the Elecsys HIV Duo assay and Elecsys HIV Combi PT assay, assessed in two seroconversion panels, are provided in Table 2. In both seroconversion panels, the two assays were able to detect positive results at the same time point. Sixty-seven HIV-1 positive samples were all reactivity for both the Elecsys HIV Duo assay and Elecsys HIV Combi PT assay. Together with the five positive samples from HIV screening, 12 antigens positive samples can be distinguished by the Elecsys HIV Duo assay (Table 3).
| Name | Days since 1st bleed | Elecsys HIV combi PT assay, COI | Elecsys HIV Duo assay, COI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIV Ag | Anti-HIV Ab | Duo | |||
| Panel HIV-1/0600-0251 | |||||
| PRB969-01 | 0 | 0.247 | 0.207 | 0.101 | 0.23 |
| PRB969-02 | 29 | 0.227 | 0.227 | 0.102 | 0.249 |
| PRB969-03 | 48 | 0.244 | 0.211 | 0.100 | 0.233 |
| PRB969-04 | 53 | 0.257 | 0.212 | 0.099 | 0.234 |
| PRB969-05 | 55 | 0.233 | 0.221 | 0.102 | 0.243 |
| PRB969-06 | 61 | 0.389 | 0.440 | 0.103 | 0.452 |
| PRB969-07 | 63 | 0.522 | 0.703 | 0.109 | 0.711 |
| PRB969-08 | 70 | 3.390 | 1.510 | 4.690 | 4.930 |
| PRB969-09 | 72 | 9.320 | 1.140 | 18.500 | 18.500 |
| PRB969-10 | 77 | 32.260 | 0.449 | 20.500 | 20.500 |
| Panel HIV-1/0600-0237 | |||||
| PRB953-01 | 0 | 0.301 | 0.299 | 0.149 | 0.334 |
| PRB953-02 | 3 | 0.562 | 0.926 | 0.115 | 0.933 |
| PRB953-03 | 7 | 6.040 | 13.300 | 0.416 | 13.300 |
| PRB953-04 | 10 | 87.190 | 32.000 | 30.600 | 44.300 |
- Note: Bold values indicate a positive test result.
- Abbreviations: Ab, antibody; Ag, antigen; COI, cutoff index; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus.
| Genotype | Elecsys HIV combi PT assay | Elecsys HIV Duo assay | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIV Ag | Anti-HIV Ab | Duo | ||
| CRF01_AE, n (%) | 43 (59.7%) | 7 (9.7%) | 43 (59.7%) | 43 (59.7%) |
| CRF07_BC, n (%) | 13 (18.0%) | 2 (2.8%) | 13 (18.0%) | 13 (18.0%) |
| B, n(%) | 10 (13.9%) | 3 (4.2%) | 10 (13.9%) | 10 (13.9%) |
| URF_0107, n (%) | 4 (5.6%) | 0 (0%) | 4 (5.6%) | 4 (5.6%) |
| URF_01B, n (%) | 1 (1.4%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (1.4%) | 1 (1.4%) |
| CRF02_AG, n (%) | 1 (1.4%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (1.4%) | 1 (1.4%) |
| Number of samples, N (%) | 72 (100.0%) | 12(16.7%) | 72 (100.0%) | 72 (100.0%) |
- Abbreviations: CRF, circulating recombinant form; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus.
4.3 Multiple HIV-1 genotypes among the studied samples
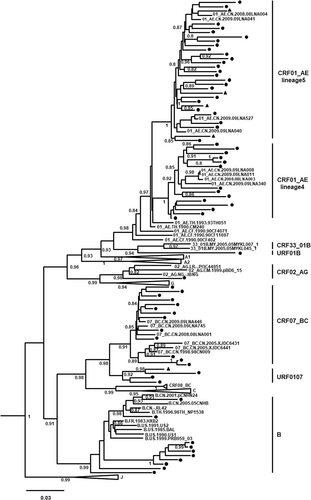
According to the phylogenetic tree of the PR/RT region of pol gene, among the 72 HIV positive samples, 43 samples (59.7%) were identified as CRF01_AE genotype and followed by 13 of CRF07_BC (18.0%), 10 of subtype B (13.9%), 4 of URF_0107 (5.6%), 1 of CRF02_AG (1.4%), and 1 of URF_01B (1.4%) (Figure 1). Moreover, two of CRF01_AE lineages that have been reported in China before could be determined, including 29 samples belonged to the CRF01_AE lineage 5 and 14 samples belong to the CRF01_AE lineage 4, both of two lineages were the predominant epidemic strain in the research area.
4.4 New recombinants were determined
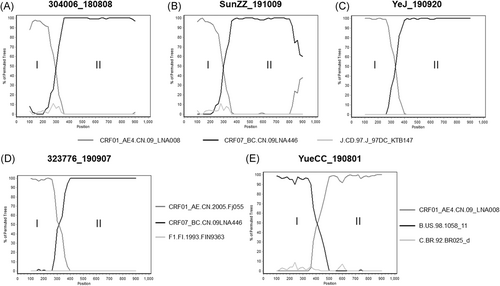
Recombination analyses demonstrated that three out of the four URF0107 strains, 304006_180808, SunZZ_191009, and YeJ_190920, shared the same origin, similar breakpoints and recombination structure in the pol region of the HIV-1 genome. These three strains were originated from the recombination between HIV-1 strains of CRF01_AE lineage 4 and CRF07_ BC lineage predominant among men-who-have-sex-with-men (MSM) population. The breakpoints of the three strains located in HXB2: 2243, 2568, and 2579, respectively (Figure 2A-C). Other URF0107 strains, 323776_190907, had different CRF01_AE origin and originated from the recombination between HIV-1 strains of CRF01_AE lineage 6 and CRF07_BC lineage predominant among MSM population. The breakpoint at the pol region located at HXB2:2614 (Figure 2D). While the only URF_01B strain, YueCC_190801, was composed of CRF01_AE linage 4 and subtype B, breakpoint at pol region located at HXB2:2683 (Figure 2E).
5 DISCUSSION
In a comparison of two platforms for diagnosis of HIV using Chinese clinical samples, the overall performance of the Elecsys HIV Duo assay (cobas e 801 analyzer) was slightly better than the Elecsys HIV Combi PTassay (cobas e601 analyzer), which is currently available for use in China. Although the Elecsys HIV Duo assay had slightly higher specificity, the difference was not significant, and sensitivity of the two assays was equivalent. High sensitivity is important in the identification of potentially infected patients and enables clinicians to initiate antiretroviral treatments early as possible.
We demonstrated that the Elecsys HIV Duo and Elecsys HIV Combi PT assays had equally excellent seroconversion sensitivity. The advantage of the new generation Elecsys HIV Duo assay is that it detects HIV antibodies and HIV p24 antigens separately. The HIV-1 p24 antigen typically appears at around 2 weeks postinfection, which is earlier than anti-HIV immunoglobulin M and immunoglobulin G antibodies that are detected approximately 3 and 6 weeks postinfection, respectively.3 The Elecsys HIV Duo assay is therefore not only able to detect HIV-1 infection during the early stages of the infection,10 but also can distinguish who are recently infected cases, which might be helpful for medical treatment, and start early public health intervention aiming at reducing the transmission risk.
The HIV genome is highly variable and can be divided into complex types, groups, subtypes, sub-subtypes, and recombinant types. The different subtypes and recombinant HIV-1 are distributed widely around the world. In China, there are more than ten different HIV genotypes, among which the most frequent strains include CRF01_AE, CRF07_BC, B, B', CRF08_BC, and the recently identified recombinant strains CRF55_01B and CRF59_01B.11 The emergence of novel recombinant strains is rapidly increasing, especially among the MSM population.4 Wide cocirculation of, and dual infection with, CRF01_AE and subtype B has led to the emergence of novel CRFs of HIV across regions of Asia.12-15 In Liaoning province, where this study was conducted, multiple HIV genotypes have been reported before. In this study, multiple HIV-1 genotypes were identified as expected, however, as high as 6.9% unidentified recombinants were detected is beyond our expectation. It is fortunate that the samples of such complicated HIV genotypes can be detected effectively with the Elecsys HIV Duo assay. According to this trend, more complicated HIV genotypes might appear in the near future, which presents a challenge for the laboratory diagnosis of HIV infection. Therefore, further studies to evaluate the performance of new assays on different HIV genotypes may be beneficial.
6 CONCLUSION
The Elecsys HIV Duo assay (cobas e 801 analyzer) demonstrated better specificity and the same sensitivity as the Elecsys HIV Combi PT assays that currently available for use in China. The new function detecting HIV-1 p24 antigen and antibodies separately can be helpful with the diagnosis of early-infected cases who are at extremely high risk of transmitting HIV-1 to other people. The awareness of their early HIV infection status may help with early treatment and public health prevention. The excellent performance on detecting HIV strains of various genotypes and the improvement of antigens and antibodies discrimination make the Elecsys HIV Duo assay suitable for routine clinical diagnostic use, including preoperative assessment, in areas affected by the associated HIV-1 strains.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Medical editing support, under the guidance of the authors, was provided by Chloe Fletcher, MSc (Gardiner-Caldwell Communications, Macclesfield, UK) and funded by Roche Diagnostics International Ltd. COBAS, COBAS E, and ELECSYS are trademarks of Roche. This work was supported by Roche Diagnostics. The sponsor contributed to the design of the study and reviewed the manuscript. Open access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL.
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
Cunying Pu is a Roche employee.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
All authors participated in the design and sample analysis of the study and were involved in the interpretation of the study results. The manuscript was reviewed and approved by all authors for publication.