Enabling an intrinsically safe and high-energy-density 4.5 V-class Li-ion battery with nonflammable electrolyte
Ziqi Zeng
Hubei Key Laboratory of Electrochemical Power Sources, College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorXingwei Liu
Hubei Key Laboratory of Electrochemical Power Sources, College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorXiaoyu Jiang
Hubei Key Laboratory of Electrochemical Power Sources, College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorZhenjie Liu
State Key Laboratory of Electroanalytical Chemistry, Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun, Jilin, China
Search for more papers by this authorZhangquan Peng
State Key Laboratory of Electroanalytical Chemistry, Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun, Jilin, China
Search for more papers by this authorXiangming Feng
College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorWeihua Chen
College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorDingguo Xia
Key Lab of Theory and Technology for Advanced Batteries Materials, College of Engineering, Peking University, Beijing, China
Search for more papers by this authorXinping Ai
Hubei Key Laboratory of Electrochemical Power Sources, College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorHanxi Yang
Hubei Key Laboratory of Electrochemical Power Sources, College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yuliang Cao
Hubei Key Laboratory of Electrochemical Power Sources, College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Correspondence
Yuliang Cao, Hubei Key Laboratory of Electrochemical Power Sources, College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430072, China.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorZiqi Zeng
Hubei Key Laboratory of Electrochemical Power Sources, College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorXingwei Liu
Hubei Key Laboratory of Electrochemical Power Sources, College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorXiaoyu Jiang
Hubei Key Laboratory of Electrochemical Power Sources, College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorZhenjie Liu
State Key Laboratory of Electroanalytical Chemistry, Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun, Jilin, China
Search for more papers by this authorZhangquan Peng
State Key Laboratory of Electroanalytical Chemistry, Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun, Jilin, China
Search for more papers by this authorXiangming Feng
College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorWeihua Chen
College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorDingguo Xia
Key Lab of Theory and Technology for Advanced Batteries Materials, College of Engineering, Peking University, Beijing, China
Search for more papers by this authorXinping Ai
Hubei Key Laboratory of Electrochemical Power Sources, College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorHanxi Yang
Hubei Key Laboratory of Electrochemical Power Sources, College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yuliang Cao
Hubei Key Laboratory of Electrochemical Power Sources, College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Correspondence
Yuliang Cao, Hubei Key Laboratory of Electrochemical Power Sources, College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430072, China.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorFunding information: National Key R&D Program of China, Grant/Award Number: 2016YFB0100200; National Nature Science Foundation of China, Grant/Award Number: 21972108
Abstract
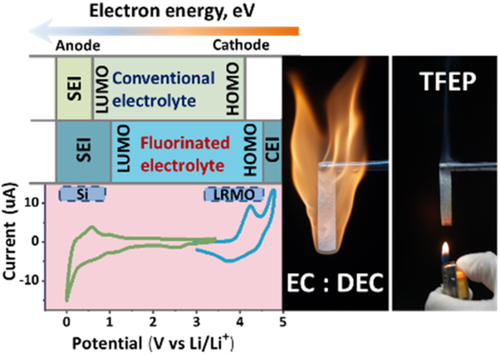
Developing nonflammable electrolyte with a wide electrochemical window has become an urgent demand for high-energy-density and high-safe lithium-ion batteries (LIBs). Herein, a fluorinated nonflammable phosphate electrolyte is developed to construct a safe 4.5 V-class LIB (Si-SiC-C/0.35Li2MnO3·0.65LiNi0.5Mn0.5O2). The proposed fluorinated phosphate electrolyte, 0.8 M LiPF6/tris(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl) phosphate (TFEP) + 5 vol% fluoroethylene carbonate (FEC) + 5 vol% vinylene carbonate (VC), is not only completely nonflammable but also exhibits excellent oxidative/reductive stability on 0.35Li2MnO3·0.65LiNi0.5Mn0.5O2 cathode and Si-SiC-C anode. The in situ differential electrochemical mass spectrometry and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy proved that TFEP-based electrolyte does not decompose into gases but forms a high-quality electrode-electrolyte interface on cathode surface at high working potential. The 4.5 V-class LIBs using 0.8 M LiPF6 TFEP-based nonflammable electrolyte shed some light on potential application for high-safe and low-cost larger-scale energy storage.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| inf212089-sup-0001-supinfo.docxWord 2007 document , 1.5 MB | Data S1 Supporting information |
| inf212089-sup-0001-VideoS1.movQuickTime video, 4.3 MB | Video S1 Combustion experiment of 1.0 M LiPF6/EC:DEC electrolyte. |
| inf212089-sup-0002-VideoS2.movQuickTime video, 4.7 MB | Video S2 Combustion experiment of 1.0 M LiPF6/TFEP+FEC + VC electrolyte |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
REFERENCES
- 1Choi JW, Aurbach D. Promise and reality of post-lithium-ion batteries with high energy densities. Nat Rev Mater. 2016; 1:16013.
- 2Nayak PK, Erickson EM, Schipper F, et al. Review on challenges and recent advances in the electrochemical performance of high capacity li- and Mn-rich cathode materials for li-ion batteries. Adv Energy Mater. 2018; 8(8):1702397.
- 3Manthiram A, Knight JC, Myung S-T, Oh S-M, Sun Y-K. Nickel-rich and lithium-rich layered oxide cathodes: progress and perspectives. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016; 6(1):1501010.
- 4Chen S, Wen K, Fan J, Bando Y, Golberg D. Progress and future prospects of high-voltage and high-safety electrolytes in advanced lithium batteries: from liquid to solid electrolytes. J Mater Chem A. 2018; 6(25): 11631-11663.
- 5Kalhoff J, Eshetu GG, Bresser D, Passerini S. Safer electrolytes for Lithium-ion batteries: state of the art and perspectives. ChemSusChem. 2015; 8(13): 2154-2175.
- 6Zheng J, Lochala JA, Kwok A, Deng ZD, Xiao J. Research progress towards understanding the unique interfaces between concentrated electrolytes and electrodes for energy storage applications. Adv Sci. 2017; 4(8):1700032.
10.1002/advs.201700032 Google Scholar
- 7Fan X, Chen L, Ji X, et al. Highly fluorinated interphases enable high-voltage Li-metal batteries. Chem. 2018; 4(1): 174-185.
- 8Yoshida K, Nakamura M, Kazue Y, et al. Oxidative-stability enhancement and charge transport mechanism in glyme–lithium salt equimolar complexes. J Am Chem Soc. 2011; 133(33): 13121-13129.
- 9Suo L, Borodin O, Sun W, et al. Advanced high-voltage aqueous lithium-ion battery enabled by "water-in-bisalt" electrolyte. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2016; 55(25): 7136-7141.
- 10Suo L, Borodin O, Gao T, et al. “Water-in-salt” electrolyte enables high-voltage aqueous lithium-ion chemistries. Science. 2015; 350(6263): 938-943.
- 11Yamada Y, Furukawa K, Sodeyama K, et al. Unusual stability of acetonitrile-based superconcentrated electrolytes for fast-charging lithium-ion batteries. J Am Chem Soc. 2014; 136(13): 5039-5046.
- 12Zeng Z, Murugesan V, Han KS, et al. Non-flammable electrolytes with high salt-to-solvent ratios for li-ion and li-metal batteries. Nat Energy. 2018; 3(8): 674-681.
- 13Wang J, Yamada Y, Sodeyama K, et al. Fire-extinguishing organic electrolytes for safe batteries. Nat Energy. 2018; 3(1): 22-29.
- 14Yang C, Chen J, Qing T, et al. 4.0 V Aqueous Li-Ion Batteries. Joule. 2017; 1(1): 122-132.
- 15Suo L, Xue W, Gobet M, et al. Fluorine-donating electrolytes enable highly reversible 5-V-class li metal batteries. Proc Nati Acad Sci. 2018; 115(6): 1156-1161.
- 16Fan X, Chen L, Borodin O, et al. Non-flammable electrolyte enables li-metal batteries with aggressive cathode chemistries. Nat Nanotech. 2018; 13(8): 715-722.
- 17Zhu X, Jiang X, Ai X, Yang H, Cao Y. Bis(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl) ethylphosphonate as novel high-efficient flame retardant additive for safer lithium-ion battery. Electrochim Acta. 2015; 165: 67-71.
- 18Zeng Z, Jiang X, Wu B, et al. Bis(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl) methylphosphonate: a novel flame-retardant additive for safe lithium-ion battery. Electrochim Acta. 2014; 129: 300-304.
- 19Jia H, Wang J, Lin F, Monroe CW, Yang J, NuLi Y. TPPi as a flame retardant for rechargeable lithium batteries with sulfur composite cathodes. Chem Commun (Cambridge, U K). 2014; 50(53): 7011-7013.
- 20Pires J, Castets A, Timperman L, et al. Tris(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl) phosphite as an electrolyte additive for high-voltage lithium-ion batteries using lithium-rich layered oxide cathode. J Power Sources. 2015; 296: 413-425.
- 21Jeon H, Roh Y, Jin D, Ryou M-H, Jeong Y-C, Lee YM. Crosslinkable polyhedral silsesquioxane-based ceramic-coated separators for Li-ion batteries. J Ind Eng Chem. 2019; 71: 277-283.
- 22Kim S, Han T, Jeong J, Lee H, Ryou M-H, Lee YM. A flame-retardant composite polymer electrolyte for lithium-ion polymer batteries. Electrochim Acta. 2017; 241: 553-559.
- 23Yeon D, Lee Y, Ryou M-H, Lee YM. New flame-retardant composite separators based on metal hydroxides for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta. 2015; 157: 282-289.
- 24Zeng Z, Wu B, Xiao L, et al. Safer lithium ion batteries based on nonflammable electrolyte. J Power Sources. 2015; 279: 6-12.
- 25Jiang X, Liu X, Zeng Z, et al. A bifunctional fluorophosphate electrolyte for safer sodium-ion batteries. iScience. 2018; 10: 114-122.
- 26Haregewoin AM, Wotango AS, Hwang BJ. Electrolyte additives for lithium ion battery electrodes: progress and perspectives. Energy & Environ Sci. 2016; 9: 1955-1988.
- 27Jin Y, Kneusels N-JH, Marbella LE, et al. Understanding fluoroethylene carbonate and vinylene carbonate based electrolytes for Si anodes in lithium ion batteries with NMR spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc. 2018; 140(31): 9854-9867.
- 28Lee WJ, Prasanna K, Jo YN, Kim KJ, Kim HS, Lee CW. Depth profile studies on nickel rich cathode material surfaces after cycling with an electrolyte containing vinylene carbonate at elevated temperature. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2014; 16(32): 17062-17071.
- 29Yabuuchi N, Yoshii K, Myung S-T, Nakai I, Komaba S. Detailed studies of a high-capacity electrode material for rechargeable batteries, Li2MnO3−LiCo1/3Ni1/3Mn1/3O2. J Am Chem Soc. 2011; 133(12): 4404-4419.
- 30Hong J, Lim H-D, Lee M, et al. Critical role of oxygen evolved from layered Li–excess metal oxides in lithium rechargeable batteries. Chem Mater. 2012; 24(14): 2692-2697.
- 31El Ouatani L, Dedryvère R, Siret C, et al. The effect of vinylene carbonate additive on surface film formation on both electrodes in li-ion batteries. J Electrochem Soc. 2009; 156(2): A103-A113.
- 32Wang H, Rus E, Sakuraba T, Kikuchi J, Kiya Y, Abruña HD. CO2 and O2 evolution at high voltage cathode materials of li-ion batteries: a differential electrochemical mass spectrometry study. Anal Chem. 2014; 86(13): 6197-6201.
- 33Castel E, Berg EJ, El Kazzi M, Novák P, Villevieille C. Differential electrochemical mass spectrometry study of the Interface of xLi2MnO3·(1–x) LiMO2 (M = Ni, Co, and Mn) material as a positive electrode in li-ion batteries. Chem Mater. 2014; 26(17): 5051-5057.
- 34Markevich E, Salitra G, Aurbach D. Fluoroethylene carbonate as an important component for the formation of an effective solid electrolyte interphase on anodes and cathodes for advanced Li-ion batteries. ACS Energy Lett. 2017; 2(6): 1337-1345.
- 35Chen L, Wang K, Xie X, Xie J. Enhancing electrochemical performance of silicon film anode by vinylene carbonate electrolyte additive. Electrochem Solid-State Lett. 2006; 9(11): A512-A515.
- 36Christopher MT, John FB, Ian H, Ian JM, Matthew JW. Fluorinated phosphorus compounds part 2. The synthesis of some bis(fluoroalkyl) alkyl phosphonates. J Fluorine Chem. 2000; 104: 215-223.