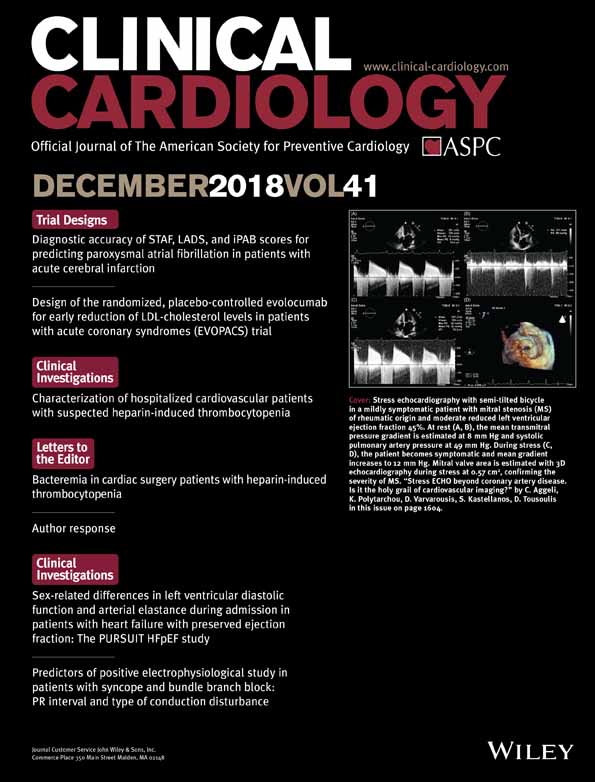
Diagnostic accuracy of STAF, LADS, and iPAB scores for predicting paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in patients with acute cerebral infarction
Abstract
Background and objective
The scoring scales scoring system for targeting atrial fibrillation (STAF), left atrial diameter, age, diagnosis of stroke, and smoking status (LADS), and identified by past history of arrhythmia or antiarrhythmic agent use, atrial dilation, and elevation of Brain natriuretic peptide (iPAB) have been proposed for predicting atrial fibrillation in patients with acute cerebral infarction, but their relative accuracies are not clear. This prospective study compared STAF, LADS, and iPAB scores for predicting paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (PAF) in patients with acute cerebral infarction.
Methods
Patients with acute cerebral infarction (n = 744; 495 men, 249 women; aged 65 ± 12 years) were consecutively enrolled throughout the year 2016 at the Department of Neurology of Huizhou Municipal Central Hospital. Patients were followed for 3 months. The sensitivity, specificity, area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), and best cutoff points of STAF, LADS, and iPAB scores for predicting PAF were computed.
Results
Among the 744 patients, 37 patients had PAF. The AUCs of the STAF, LADS, and iPAB scores for predicting PAF were 0.87, 0.79, and 0.84, respectively, and with a cutoff at four points, the sensitivities were 73%, 70.3%, and 83.8%, and specificities were 92.1%, 82.2%, and 77%.
Conclusions
The STAF, LADS, and iPAB scores could satisfactorily predict PAF in patients with acute cerebral infarction. STAF was superior to the others in diagnostic performance.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare no potential conflict of interests