Bioinspired Coordination for Fabricating Self-healing and Injectable Hydrogels with Antibacterial and Immunoregulatory Activities†
Youlu Diao
Institute for Advanced Materials, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Jiangsu University, 301 Xuefu Rd, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, 212013 China
The authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorJia Gao
Institute for Advanced Materials, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Jiangsu University, 301 Xuefu Rd, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, 212013 China
The authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorXinrui Li
Institute for Advanced Materials, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Jiangsu University, 301 Xuefu Rd, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, 212013 China
† Dedicated to the Special Issue of Biomimetic Materials.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Miao Wang
Institute for Advanced Materials, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Jiangsu University, 301 Xuefu Rd, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, 212013 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Guoqing Pan
Institute for Advanced Materials, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Jiangsu University, 301 Xuefu Rd, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, 212013 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorYoulu Diao
Institute for Advanced Materials, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Jiangsu University, 301 Xuefu Rd, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, 212013 China
The authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorJia Gao
Institute for Advanced Materials, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Jiangsu University, 301 Xuefu Rd, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, 212013 China
The authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorXinrui Li
Institute for Advanced Materials, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Jiangsu University, 301 Xuefu Rd, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, 212013 China
† Dedicated to the Special Issue of Biomimetic Materials.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Miao Wang
Institute for Advanced Materials, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Jiangsu University, 301 Xuefu Rd, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, 212013 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Guoqing Pan
Institute for Advanced Materials, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Jiangsu University, 301 Xuefu Rd, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, 212013 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorComprehensive Summary
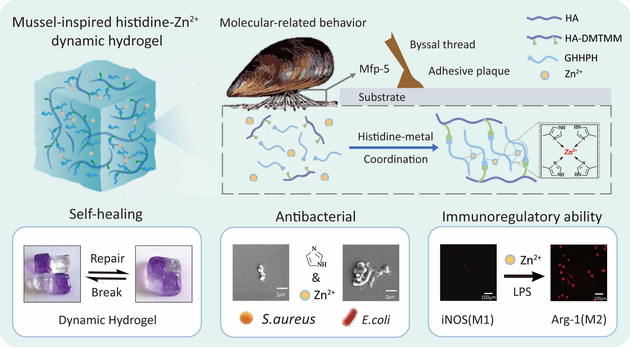
Inspired by the molecular mechanism of mussel adhesion, here, we developed a class of injectable and self-healing hydrogels based on natural polysaccharide hyaluronic acid (HA). The dynamic property of hydrogels is derived from histidine-metal coordination, which widely exists in the mussel adhesive plaque. To mimic components of mussel byssal threads, we first grafted histidine-containing peptides onto the HA chains. Followed by the addition of Zn2+ ions, the modified HA could then transform into a pH-sensitive hydrogel network (HA-His-Zn) with tunable sol-gel transitions. The dynamic metal-ligand coordination could significantly enhance the mechanical properties of HA hydrogels and also endow them with self-healing and injectable abilities. In addition, the HA-His-Zn hydrogels could also exhibit antibacterial and immunoregulatory activities due to the bioactive Zn2+ ions. These results, together with the dynamic properties and good biocompatibility, indicated that the HA-His-Zn hydrogels could be applied as a class of easy-to-handle scaffold materials for regeneration medicine, particularly for tissue traumas with chronic inflammations and infections.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202401108-sup-0001-supinfo.pdfPDF document, 542.3 KB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Chen, J. S.; Zeng, H. B. Mussel-Inspired Reversible Molecular Adhesion for Fabricating Self-Healing Materials. Langmuir 2022, 38, 12999–13008.
- 2 Pan, G. Q.; Li, B. A dynamic biointerface controls mussel adhesion. Science 2023, 382, 763–764.
- 3 Tunn, I.; Harrington, M. J.; Blank, K. G. Bioinspired Histidine–Zn2+ Coordination for Tuning the Mechanical Properties of Self-Healing Coiled Coil Cross-Linked Hydrogels. Biomimetics 2019, 4, 25.
- 4 Kim, S.; Regitsky, A. U.; Song, J.; Ilavsky, J.; McKinley, G. H.; Holten-Andersen, N. In situ mechanical reinforcement of polymer hydrogels via metal-coordinated crosslink mineralization. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 667.
- 5 Ayarza, J.; Wang, J.; Kim, H.; Huang, P. R.; Cassaidy, B.; Yan, G.; Liu, C.; Jaeger, H. M.; Rowan, S. J.; Esser-Kahn, A. P. Bioinspired mechanical mineralization of organogels. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8319.
- 6 Bai, J. X.; Ge, G. R.; Wang, Q.; Li, W. M.; Zheng, K.; Xu, Y. Z.; Yang, H. L.; Pan, G. Q.; Geng, D. C. Engineering Stem Cell Recruitment and Osteoinduction via Bioadhesive Molecular Mimics to Improve Osteoporotic Bone-Implant Integration. Research 2022, 2022, 9823784.
- 7 Carrington, E.; Waite, J. H.; Sarà, G.; Sebens, K. P. Mussels as a Model System for Integrative Ecomechanics. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2015, 7, 443–469.
- 8
Chen, X.; Gao, Y. Q.; Wang, Y. L.; Pan, G. Q. Mussel-inspired peptide mimicking: An emerging strategy for surface bioengineering of medical implants. Smart Mater. Med. 2021, 2, 26–37.
10.1016/j.smaim.2020.10.005 Google Scholar
- 9 Zhang, C.; Wu, B. H.; Zhou, Y. S.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. M.; Wang, Z. K. Mussel-inspired hydrogels: from design principles to promising applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 3605–3637.
- 10 Xu, Q.; Xu, M.; Lin, C. Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, R.; Dong, X. X.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, S. C.; Tian, Y.; Xia, Z. H. Metal Coordination-Mediated Functional Grading and Self-Healing in Mussel Byssus Cuticle. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1902043.
- 11 Guo, Q.; Chen, J. S.; Wang, J. L.; Zeng, H. B.; Yu, J. Recent progress in synthesis and application of mussel-inspired adhesives. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 1307–1324.
- 12
Jiang, Z. M.; Qin, S. A.; Wang, W. Y.; Du, T. X.; Zang, Y. R.; He, Y. Z.; Dong, X. F.; Liu, H. Y.; Ma, G. W. Investigating the anti-inflammatory and bone repair-promoting effects of an injectable porous hydrogel containing magnesium ions in a rat periodontitis mode. Smart Mater. Med. 2024, 5, 207–220.
10.1016/j.smaim.2023.12.002 Google Scholar
- 13 Liang, Y. P.; Li, M.; Yang, Y. T.; Qiao, L. P.; Xu, H. R.; Guo, B. L. pH/Glucose Dual Responsive Metformin Release Hydrogel Dressings with Adhesion and Self-Healing via Dual-Dynamic Bonding for Athletic Diabetic Foot Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 3194–3207.
- 14 Ding, X. Y.; Fan, L.; Wang, L.; Zhou, M.; Wang, Y. X.; Zhao, Y. J. Designing self-healing hydrogels for biomedical applications. Mater. Horiz. 2023, 10, 3929–3947.
- 15 Wei, S. X.; Lu, W.; Le, X. X.; Ma, C. X.; Lin, H.; Wu, B. Y.; Zhang, J. W.; Theato, P.; Chen, T. Bioinspired Synergistic Fluorescence-Color- Switchable Polymeric Hydrogel Actuators. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 16243–16251.
- 16 Muir, V. G.; Burdick, J. A. Chemically Modified Biopolymers for the Formation of Biomedical Hydrogels. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 10908–10949.
- 17 Li, Q.; Barrett, D. G.; Messersmith, P. B.; Holten-Andersen, N. Controlling Hydrogel Mechanics via Bio-Inspired Polymer-Nanoparticle Bond Dynamics. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 1317–1324.
- 18 Sun, W. X.; Xue, B.; Fan, Q. Y.; Tao, R. H.; Wang, C. X.; Wang, X.; Li, Y. R.; Qin, M.; Wang, W.; Chen, B.; Cao, Y. Molecular engineering of metal coordination interactions for strong, tough, and fast-recovery hydrogels. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz9531.
- 19 Zheng, W.; Chen, L. J.; Yang, G.; Sun, B.; Wang, X.; Jiang, B.; Yin, G. Q.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Liu, M.; Chen, G.; Yang, H. B. Construction of Smart Supramolecular Polymeric Hydrogels Cross-linked by Discrete Organoplatinum(II) Metallacycles via Post-Assembly Polymerization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 4927–4937.
- 20 He, W. B.; Bai, J. X.; Chen, X.; Suo, D.; Wang, S. H.; Guo, Q. P.; Yin, W. L.; Geng, D. C.; Wang, M.; Pan, G. Q.; Zhao, X.; Li, B. Reversible dougong structured receptor-ligand recognition for building dynamic extracellular matrix mimics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2022, 119, e2117221119.
- 21
Wang, C.; Zeng, H. S.; Liu, K. X.; Lin, Y. N.; Yang, H.; Xie, X. Y.; Wei, D. X.; Ye, J. W. Biosensor-based therapy powered by synthetic biology. Smart Mater. Med. 2023, 4, 212–224.
10.1016/j.smaim.2022.10.003 Google Scholar
- 22 Gao, R.; Bouillet, S.; Stock, A. M. Structural Basis of Response Regulator Function. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 73, 175–197.
- 23 Ding, X. Y.; Yu, Y. R.; Shang, L. R.; Zhao, Y. J. Histidine-Triggered GO Hybrid Hydrogels for Microfluidic 3D Printing. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 19533–19542.
- 24 Biswas, A.; Chandel, A. K. S.; Anuradha; Vadadoriya, N.; Mamtani, V.; Jewrajka, S. K. Structurally Heterogeneous Amphiphilic Conetworks of Poly(vinyl imidazole) Derivatives with Potent Antimicrobial Properties and Cytocompatibility. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 46333–46346.
- 25 Yi, X.; He, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, G.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, J.; Chen, D.; Wang, R.; Tian, W.; Yu, P.; Zhou, L.; Ning, C. Tunable Mechanical, Antibacterial, and Cytocompatible Hydrogels Based on a Functionalized Dual Network of Metal Coordination Bonds and Covalent Crosslinking. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 6190–6198.
- 26 Rollas, S.; Gulerman, N.; Erdeniz, H. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of some new hydrazones of 4-fluorobenzoic acid hydrazide and 3-acetyl-2,5-disubstituted-1,3,4-oxadiazolines. Farmaco 2002, 57, 171–174.
- 27 Khabnadideh, S.; Rezaei, Z.; Khalafi-Nezhad, A.; Bahrinajafi, R.; Mohamadi, R.; Farrokhroz, A. A. Synthesis of N-alkylated derivatives of imidazole as antibacterial agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2003, 13, 2863–2865.
- 28 Wang, T. T.; Li, C. P.; Xie, X. S.; Lu, B. G.; He, Z. X.; Liang, S. Q.; Zhou, J. Anode Materials for Aqueous Zinc Ion Batteries: Mechanisms, Properties, and Perspectives. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 16321–16347.
- 29 Francolini, I.; D'Ilario, L.; Guaglianone, E.; Donelli, G.; Martinelli, A.; Piozzi, A. Polyurethane anionomers containing metal ions with antimicrobial properties: thermal, mechanical and biological characterization. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 3482–3490.
- 30 Hu, H.; Zhang, W.; Qiao, Y.; Jiang, X.; Liu, X.; Ding, C. Antibacterial activity and increased bone marrow stem cell functions of Zn-incorporated TiO2 coatings on titanium. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 904–915.
- 31 Liu, J. T.; Du, P.; Liu, T. R.; Córdova Wong, B. J.; Wang, W. P.; Ju, H. X.; Lei, J. P. A black phosphorus/manganese dioxide nanoplatform: Oxygen self-supply monitoring, photodynamic therapy enhancement and feedback. Biomaterials 2019, 192, 179–188.
- 32 Guo, Q. P.; Yin, W. L.; Wang, H.; Gao, J.; Gu, Y.; Wang, W. S.; Liu, C. Y.; Pan, G. Q.; Li, B. Dynamic Proteinaceous Hydrogel Enables In-Situ Recruitment of Endogenous TGF-β1 and Stem Cells for Cartilage Regeneration. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2403055.
- 33 Chen, X.; Li, X. R.; He, W. B.; Wang, M.; Gao, A.; Tong, L. P.; Guo, S.; Wang, H. Y.; Pan, G. Q. Rational multivalency construction enables bactericidal effect amplification and dynamic biomaterial design. Innovation (Camb) 2023, 4, 100483.
- 34 Luo, M.; Zhao, F. K.; Cheng, H.; Su, M.; Wang, Y. M. Macrophage polarization: an important role in inflammatory diseases. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1352946.
- 35 An, J. X.; Han, Z. Y.; Qin, Y. T.; Li, C. X.; He, J. L.; Zhang, X. Z. Bacteria-Based Backpacks to Enhance Adoptive Macrophage Transfer against Solid Tumors. Adv. Mater. 2023, 36, e2305384.
- 36 Wang, T.; Bai, J.; Lu, M.; Huang, C.; Geng, D.; Chen, G.; Wang, L.; Qi, J.; Cui, W.; Deng, L. Engineering immunomodulatory and osteoinductive implant surfaces via mussel adhesion-mediated ion coordination and molecular clicking. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 160.




