A Pincer Cobalt Complex as Catalyst with Dual Hydrogenation Activities for Hydrodeoxygenation of Ketones with H2†
Bingxue Liu
Center of Basic Molecular Science (CBMS), Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Qiang Liu
Center of Basic Molecular Science (CBMS), Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorBingxue Liu
Center of Basic Molecular Science (CBMS), Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Qiang Liu
Center of Basic Molecular Science (CBMS), Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorDedicated to the Memory of Professor Xiyan Lu.
Comprehensive Summary
Reductive deoxygenation of ketones using H2 is a highly desirable but also challenging transformation in both chemical synthesis, industrial-scale petroleum and biomass feedstock reforming processes. Herein, we report a cooperative cobalt/Lewis acid (LA)-catalyzed hydrodeoxygenation of ketones using H2 as the reductant. In particular, the newly developed pincer cobalt catalyst possesses dual hydrogenation activities for both ketones and alkenes under the same reaction conditions. This reaction features a broad substrate scope, excellent functional-group compatibility, and potential applicability.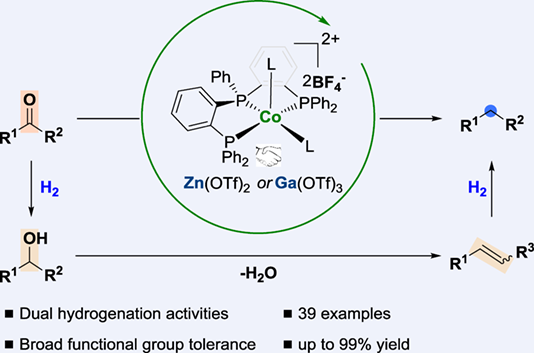
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202300418-sup-0001-supinfo.pdfPDF document, 5.4 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1(a) Alonso, D. M.; Wettstein, S. G.; Dumesic, J. A. Bimetallic catalysts for upgrading of biomass to fuels and chemicals. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 8075–8098; (b) Ruppert, A. M.; Weinberg, K.; Palkovits, R. Hydrogenolysis Goes Bio: From Carbohydrates and Sugar Alcohols to Platform Chemicals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 2564–2601.
- 2(a) Clemmensen, E. Über eine allgemeine Methode zur Reduktion der Carbonylgruppe in Aldehyden und Ketonen zur Methylengruppe. (III. Mitteilung.). Ber. dtsch. chem. Ges. 1914, 47, 681–687; (b) Todd, D. The Wolff-Kishner Reduction. Org. React. 1948, 4, 378–422.
- 3(a) Mehta, M.; Holthausen, M. H.; Mallov, I.; Pérez, M.; Qu, Z.-W.; Grimme, S.; Stephan, D. W. Catalytic Ketone Hydrodeoxygenation Mediated by Highly Electrophilic Phosphonium Cations. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 8250–8254; (b) Volkov, A.; Gustafson, K. P. J.; Tai, C.-W.; Verho, O.; Bäckvall, J.-E.; Adolfsson, H. Mild Deoxygenation of Aromatic Ketones and Aldehydes over Pd/C Using Polymethylhydrosiloxane as the Reducing Agent. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 5122–5126; (c) Andrews, R. J.; Chitnis, S. S.; Stephan, D. W. Carbonyl and olefin hydrosilylation mediated by an air-stable phosphorus(iii) dication under mild conditions. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 5599–5602; (d) Cook, A.; MacLean, H.; St. Onge, P.; Newman, S. G. Nickel-Catalyzed Reductive Deoxygenation of Diverse C–O Bond- Bearing Functional Groups. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 13337–13347.
- 4 Zhang, B.; Guo, X.; Tao, L.; Li, R.; Lin, Z.; Zhao, W. Rhodium-Catalyzed Regioselective and Chemoselective Deoxygenative Reduction of 1,3-Diketones. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 4640–4647.
- 5 Gui, R.; Li, C.-J. Ruthenium(ii)-catalyzed deoxygenation of ketones. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 10572–10575.
- 6(a) Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, P.; Li, H.; Wang, Y. Synthesis of Palladium Nanoparticles Supported on Mesoporous N-Doped Carbon and Their Catalytic Ability for Biofuel Upgrade. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 16987–16990; (b) Luska, K. L.; Migowski, P.; El Sayed, S.; Leitner, W. Synergistic Interaction within Bifunctional Ruthenium Nanoparticle/SILP Catalysts for the Selective Hydrodeoxygenation of Phenols. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 15750–15755; (c) Mahdi, T.; Stephan, D. W. Facile Protocol for Catalytic Frustrated Lewis Pair Hydrogenation and Reductive Deoxygenation of Ketones and Aldehydes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 8511–8514; (d) Tian, C.; Zhu, X.; Abney, C. W.; Tian, Z.; Jiang, D.-e.; Han, K. S.; Mahurin, S. M.; Washton, N. M.; Dai, S. Use of steric encumbrance to develop conjugated nanoporous polymers for metal-free catalytic hydrogenation. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 11919–11922; (e) Schwob, T.; Kunnas, P.; de Jonge, N.; Papp, C.; Steinrück, H.-P.; Kempe, R. General and selective deoxygenation by hydrogen using a reusable earth-abundant metal catalyst. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav3680; (f) Antil, N.; Kumar, A.; Akhtar, N.; Newar, R.; Begum, W.; Manna, K. Metal–Organic Framework- Confined Single-Site Base-Metal Catalyst for Chemoselective Hydrodeoxygenation of Carbonyls and Alcohols. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 9029–9039; (g) Ou, W.; Xiang, X.; Zou, R.; Xu, Q.; Loh, K. P.; Su, C. Room-Temperature Palladium-Catalyzed Deuterogenolysis of Carbon Oxygen Bonds towards Deuterated Pharmaceuticals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 6357–6361; (h) Xu, C.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, B.; Zhai, J.; Zhang, K.; Wu, W.; Mei, X.; He, M.; Han, B. Highly effective and chemoselective hydrodeoxygenation of aromatic alcohols. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 1629–1635.
- 7(a) Sutton, A. D.; Waldie, F. D.; Wu, R.; Schlaf, M.; ‘Pete’ Silks, L. A.; Gordon, J. C. The hydrodeoxygenation of bioderived furans into alkanes. Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 428–432; (b) Moos, G.; Emondts, M.; Bordet, A.; Leitner, W. Selective Hydrogenation and Hydrodeoxygenation of Aromatic Ketones to Cyclohexane Derivatives Using a Rh@SILP Catalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 11977–11983.
- 8(a) Jia, X.; Wang, Z.; Xia, C.; Ding, K. Recent Advances in Rh-Catalyzed Asymmetric Hydroformylation of Olefins. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 33, 1369–1381; (b) Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W. Development of the Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Enol Esters. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 36, 447–459; (c) Ai, W.; Zhong, R.; Liu, X.; Liu, Q. Hydride Transfer Reactions Catalyzed by Cobalt Complexes. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 2876–2953; (d) Shao, Z.; Zhong, R.; Ferraccioli, R.; Li, Y.; Liu, Q. General and Phosphine-Free Cobalt-Catalyzed Hydrogenation of Esters to Alcohols. Chin. J. Chem. 2019, 37, 1125–1130; (e) Liu, X.; Rong, X.; Liu, S.; Lan, Y.; Liu, Q. Cobalt-Catalyzed Desymmetric Isomerization of Exocyclic Olefins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 20633–20639; (f) Shao, Z.; Yuan, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, Q. Using Methanol as a Formaldehyde Surrogate for Sustainable Synthesis of N-Heterocycles via Manganese-Catalyzed Dehydrogenative Cyclization. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 40, 1137–1143; (g) Pang, X.; Shu, X.-Z. Reductive Deoxygenative Functionalization of Alcohols by First-Row Transition Metal Catalysis. Chin. J. Chem. 2023, 41, 1637–1652.
- 9(a) Wang, H.; Xin, Z.; Xiang, R.; Liu, S.; Gao, X.; Li, C. Functional Polypyridine Co Complex as an Efficient Catalyst for Photo-Induced Water Oxidation. Chin. J. Chem. 2016, 34, 757–762; (b) Zhong, R.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liu, S.; Liu, Q. A Practical and Stereoselective In Situ NHC-Cobalt Catalytic System for Hydrogenation of Ketones and Aldehydes. Chem 2019, 5, 1552–1566; (c) Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Yang, H.; Li, H.; Lan, Y.; Liu, Q. Structure, reactivity and catalytic properties of manganese-hydride amidate complexes. Nat. Chem. 2022, 14, 1233–1241; (d) Wei, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q. A Tailored Versatile and Efficient NHC-Based NNC-Pincer Manganese Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Polar Unsaturated Compounds. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202301042.
- 10(a) Kalutharage, N.; Yi, C. S. Scope and Mechanistic Analysis for Chemoselective Hydrogenolysis of Carbonyl Compounds Catalyzed by a Cationic Ruthenium Hydride Complex with a Tunable Phenol Ligand. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 11105–11114; (b) Scott, D. J.; Simmons, T. R.; Lawrence, E. J.; Wildgoose, G. G.; Fuchter, M. J.; Ashley, A. E. Facile Protocol for Water-Tolerant “Frustrated Lewis Pair”-Catalyzed Hydrogenation. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 5540–5544; (c) Sun, R.; Guo, H.-Y.; Ma, S.-S.; Wang, Y.-F.; Yu, Z.-K.; Xu, B.-H. Ru(dppbsa)-catalyzed hydrodeoxygenation and reductive etherification of ketones and aldehydes. Org. Chem. Front. 2022, 9, 1943–1954.
- 11 Liu, B.; Li, Y.; Liu, Q. Cobalt/Lewis acid cooperative catalysis for reductive etherification of ketones and aldehydes with alcohols. Chem Catal. 2022, 2, 883–897.
- 12
Xiong, T.; Yuan, H.; Yang, F.; Jiang, J. Brønsted acid-catalyzed 1,6-hydrophosphination of propargylic para-quinone methides and aza-para-quinone methides for the rapid construction of phosphorus-substituted quaternary carbon centers. Green Synth. Catal. 2022, 3, 46–52.
10.1016/j.gresc.2021.10.005 Google Scholar
- 13 Keehn, P. Cyclophanes, Elsevier Science, 2012, pp. 1–390.
- 14 Islam, M. M.; Akther, T.; Rahman, S.; Georghiou, P. E.; Matsumoto, T.; Tanaka, J.; Redshaw, C.; Yamato, T. Synthesis, Conformational Properties and DFT Computational Studies of Polymethyl-Substituted [3.3]Metacyclophanes. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 7255–7262.




