Co-Ni Electromagnetic Coupling in Hollow Mo2C/NC Sphere for Enhancing Electromagnetic Wave Absorbing Performance†
Xiufang Yang
Key Laboratory of Chemical Additives for China National Light Industry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710021 China
Search for more papers by this authorWenming Gao
Key Laboratory of Chemical Additives for China National Light Industry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710021 China
Search for more papers by this authorJiamin Chen
Key Laboratory of Chemical Additives for China National Light Industry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710021 China
Search for more papers by this authorXing Lu
Key Laboratory of Chemical Additives for China National Light Industry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710021 China
Search for more papers by this authorDong Yang
Key Laboratory of Chemical Additives for China National Light Industry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710021 China
Search for more papers by this authorYifan Kang
Key Laboratory of Chemical Additives for China National Light Industry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710021 China
Search for more papers by this authorQi Liu
Northwest Institute of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Xianyang, Shaanxi, 712099 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yuchang Qing
State Key Laboratory of Solidification Processing, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710072 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Wenhuan Huang
Key Laboratory of Chemical Additives for China National Light Industry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710021 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorXiufang Yang
Key Laboratory of Chemical Additives for China National Light Industry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710021 China
Search for more papers by this authorWenming Gao
Key Laboratory of Chemical Additives for China National Light Industry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710021 China
Search for more papers by this authorJiamin Chen
Key Laboratory of Chemical Additives for China National Light Industry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710021 China
Search for more papers by this authorXing Lu
Key Laboratory of Chemical Additives for China National Light Industry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710021 China
Search for more papers by this authorDong Yang
Key Laboratory of Chemical Additives for China National Light Industry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710021 China
Search for more papers by this authorYifan Kang
Key Laboratory of Chemical Additives for China National Light Industry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710021 China
Search for more papers by this authorQi Liu
Northwest Institute of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Xianyang, Shaanxi, 712099 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yuchang Qing
State Key Laboratory of Solidification Processing, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710072 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Wenhuan Huang
Key Laboratory of Chemical Additives for China National Light Industry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710021 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this author†Dedicated to the Special Issue of Emerging Investigators in 2022.
Comprehensive Summary
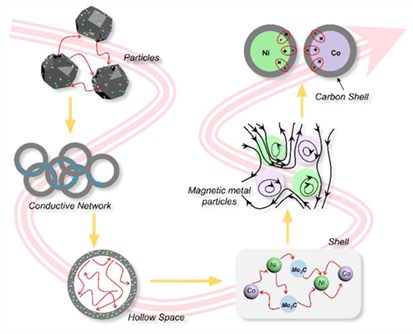
For enhancing the electromagnetic wave (EW) attenuation and adsorption, rational constructing and homogeneously distributing bimetallic electromagnetic coupling units in hollow structure is an effective way, but hard to achieve. Herein, a CoNi-doped hybrid zeolite imidazole framework was synthesized as precursor, which was further converted into a hollow CoNi-bimetallic doped molybdenum carbide sphere (H-CoNi@MoC/NC) through a two-step etching and calcination strategy. At the loading amount of 15 wt%, a strong absorption of minimum reflection loss (RLmin) of –60.05 dB at 7.2 GHz with the thickness of 3.1 mm and a wide effective adsorption bandwidth (EAB) of 3.52 GHz at the thickness of 2.5 mm were achieved, which was far beyond the reported MoC-based metallic hybrids. The crucial synergistic Co-Ni electromagnetic coupling effect in the composite was characterized, not only enhancing the dipolar/interfacial polarization, but also promoting the impedance matching, displaying the optimized EW absorbing performance.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202200475-sup-0001-Supinfo.pdfPDF document, 1.7 MB |
Appendix S1 Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Xiang, Z.; Huang, C.; Song, Y.; Deng, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, X.; Batalu, D.; Tutunaru, O.; Lu, W. Rational construction of hierarchical accordion-like Ni@porous carbon nanocomposites derived from metal-organic frameworks with enhanced microwave absorption. Carbon 2020, 167, 364–377.
- 2 Shu, J.; Cao, W.; Cao, M. Diverse Metal–Organic Framework Architectures for Electromagnetic Absorbers and Shielding. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2100470.
- 3 Wu, Z.; Pei, K.; Xing, L.; Yu, X.; You, W.; Che, R. Enhanced Microwave Absorption Performance from Magnetic Coupling of Magnetic Nanoparticles Suspended within Hierarchically Tubular Composite. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1901448.
- 4 Sun, R.; Zhang, H.-B.; Liu, J.; Xie, X.; Yang, R.; Li, Y.; Hong, S.; Yu, Z.-Z. Highly Conductive Transition Metal Carbide/Carbonitride(MXene)@ polystyrene Nanocomposites Fabricated by Electrostatic Assembly for Highly Efficient Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1702807.
- 5 Iqbal, A.; Sambyal, P.; Koo, C. M. 2D MXenes for Electromagnetic Shielding: A Review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000883.
- 6 Zhao, Z.; Lan, D.; Zhang, L.; Wu, H. A Flexible, Mechanically Strong, and Anti-Corrosion Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Composite Film with Periodic Electroconductive Patterns. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 32, 2111045.
- 7 Liu, P.; Gao, S.; Zhang, G.; Huang, Y.; You, W.; Che, R. Hollow Engineering to Co@N-Doped Carbon Nanocages via Synergistic Protecting-Etching Strategy for Ultrahigh Microwave Absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2102812.
- 8 Liu, Y.; Sun, X.; Song, Z.; Liu, X.; Yu, R. Parallel-Orientation-Induced Strong Resonances Enable Ni Submicron-Wire Array: an Ultrathin and Ultralight Electromagnetic Wave Absorbing Material. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2021, 7, 2000970.
- 9 Ying, M.; Zhao, R.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, W.; Yu, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Rong, H.; Wu, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X. Wrinkled Titanium Carbide (MXene) with Surface Charge Polarizations through Chemical Etching for Superior Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, 202201323.
- 10 Yuan, K.; Che, R.; Cao, Q.; Sun, Z.; Yue, Q.; Deng, Y. Designed fabrication and characterization of three-dimensionally ordered arrays of core-shell magnetic mesoporous carbon microspheres. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 5312–5319.
- 11 Wang, M.; Sun, Z.; Yue, Q.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Deng, Y.; Yu, C.; Zhao, D. An interface-directed coassembly approach to synthesize uniform large-pore mesoporous silica spheres. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 1884–1892.
- 12 Yang, M.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, S.; Liang, L.; Ning, Y.; Li, J.; Yin, W.; Che, R.; Li, Y. Dramatically enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption of hierarchical CNT/Co/C fiber derived from cotton and metal-organic-framework. Carbon 2020, 161, 517–527.
- 13 Zhang, X. J.; Wang, G. S.; Cao, W. Q.; Wei, Y. Z.; Liang, J. F.; Guo, L.; Cao, M. S. Enhanced microwave absorption property of reduced graphene oxide (RGO)-MnFe2O4 nanocomposites and polyvinylidene fluoride. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 7471–8.
- 14 Wu, F.; Zeng, Q.; Xia, Y.; Sun, M.; Xie, A. The effects of annealing temperature on the permittivity and electromagnetic attenuation performance of reduced graphene oxide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 112, 192902.
- 15 Yang, Y.; Xia, L.; Zhang, T.; Shi, B.; Huang, L.; Zhong, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Wen, G. Fe3O4@LAS/RGO composites with a multiple transmission-absorption mechanism and enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 352, 510–518.
- 16 Lu, S.; Xia, L.; Xu, J.; Ding, C.; Li, T.; Yang, H.; Zhong, B.; Zhang, T.; Huang, L.; Xiong, L.; Huang, X.; Wen, G. Permittivity-Regulating Strategy Enabling Superior Electromagnetic Wave Absorption of Lithium Aluminum Silicate/rGO Nanocomposites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 18626–18636.
- 17 Liang, C.; Qiu, H.; Han, Y.; Gu, H.; Song, P.; Wang, L.; Kong, J.; Cao, D.; Gu, J. Superior electromagnetic interference shielding 3D graphene nanoplatelets/reduced graphene oxide foam/epoxy nanocomposites with high thermal conductivity. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 2725–2733.
- 18 Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, H.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y. Metal organic framework-derived three-dimensional graphene- supported nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube spheres for electromagnetic wave absorption with ultralow filler mass loading. Carbon 2019, 155, 233–242.
- 19 Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Ye, J.; Shi, L.; Feng, X. Magnetic CoFe alloy@C nanocomposites derived from ZnCo-MOF for electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 383, 123096.
- 20 Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Li, M.; Yang, L.; Liu, J.; Ha, Y.; Wu, R. Heterostructured CoFe@C@MnO2 nanocubes for efficient microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 123039.
- 21 Shu, R.; Li, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, G. Nitrogen-doped Co-C/MWCNTs nanocomposites derived from bimetallic metal-organic frameworks for electromagnetic wave absorption in the X-band. Chem. Eng. J. (Amsterdam, Neth.) 2019, 362, 513–524.
- 22 Wen, G.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Yan, D.; Hou, Z. Electromagnetic wave absorption performance and electrochemical properties of multifunctional materials: Air@Co@Co3Sn2@SnO2 hollow sphere/reduced graphene oxide composites. Chem. Eng. J. (Amsterdam, Neth.) 2021, 420, 130479.
- 23 Wu, H.; Qin, M.; Zhang, L. NiCo2O4 constructed by different dimensions of building blocks with superior electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Compos. B. Eng. 2020, 182, 107620 .
- 24 Xi, L.; Wang, Z.; Zuo, Y.; Shi, X. The enhanced microwave absorption property of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles coated with a Co3Fe7-Co nanoshell by thermal reduction. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 045707.
- 25 Zhang, X.; Yan, F.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, H.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y. Hollow N-Doped Carbon Polyhedron Containing CoNi Alloy Nanoparticles Embedded within Few-Layer N-Doped Graphene as High-Performance Electromagnetic Wave Absorbing Material. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 24920–24929.
- 26 Liu, P.; Gao, S.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Luo, J. Core-Shell CoNi@Graphitic Carbon Decorated on B,N-Codoped Hollow Carbon Polyhedrons toward Lightweight and High-Efficiency Microwave Attenuation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 25624–25635.
- 27 Li, Z.; Han, X.; Ma, Y.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; Xu, P.; Li, C.; Du, Y. MOFs-Derived Hollow Co/C Microspheres with Enhanced Microwave Absorption Performance. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 8904–8913.
- 28 Qin, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, X.; Wu, H. Defect Induced Polarization Loss in Multi-Shelled Spinel Hollow Spheres for Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Application. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 2021, 8, 2004640.
- 29 Jin, C.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Qian, X.; Xu, H.; Che, R. 1D Electromagnetic-Gradient Hierarchical Carbon Microtube via Coaxial Electrospinning Design for Enhanced Microwave Absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 15939–15949.
- 30 Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Che, R. Hierarchical Engineering of Double-Shelled Nanotubes toward Hetero-Interfaces Induced Polarization and Microscale Magnetic Interaction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2202588.
- 31 Abdalla, I.; Elhassan, A.; Yu, J.; Li, Z.; Ding, B. Hybrid comprised of porous carbon nanofibers and rGO for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 2020, 157, 703–713.
- 32 Zhang, X.; Cheng, J.; Xiang, Z.; Cai, L.; Lu, W. A hierarchical Co@mesoporous C/macroporous C sheet composite derived from bimetallic MOF and oroxylum indicum for enhanced microwave absorption. Carbon 2022, 187, 477–487.
- 33 Miao, P.; Zhang, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, J.; Gao, T.; Wang, Y.; Kong, J.; Chen, K. J. A Two-Dimensional Semiconductive Metal-Organic Framework for Highly Efficient Microwave Absorption. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 40, 467–474.
- 34 Cheng, Y.; Zhao, H.; Lv, H.; Shi, T.; Ji, G.; Hou, Y. Lightweight and Flexible Cotton Aerogel Composites for Electromagnetic Absorption and Shielding Applications. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2019, 6, 1900796.
- 35 Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Lin, C.; Shi, L.; Li, X.; Wu, G. Metal organic frameworks-derived Fe-Co nanoporous carbon/graphene composite as a high-performance electromagnetic wave absorber. J. Alloy Compd. 2019, 785, 765–773.
- 36 Zhao, B.; Wang, S.; Zhao, C.; Li, R.; Hamidinejad, S. M.; Kazemi, Y.; Park, C. B. Synergism between carbon materials and Ni chains in flexible poly(vinylidene fluoride) composite films with high heat dissipation to improve electromagnetic shielding properties. Carbon 2018, 127, 469–478.
- 37 Zhao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Xi, K.; Cao, Q.; Wang, D.; Yang, Y.; Du, Y. Excellent microwave absorption property of Graphene-coated Fe nanocomposites. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3421.
- 38 Qian, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Li, X.; Wang, M.; Che, R. Multi-Path Electron Transfer in 1D Double-Shelled Sn@Mo2C/C Tubes with Enhanced Dielectric Loss for Boosting Microwave Absorption Performance. Small 2021, 17, 2100283.
- 39 Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, G.; Lai, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, C.; Han, J.; Du, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Yang, J. Tunable magnetic and microwave absorption properties of Sm1.5Y0.5Fe17–xSix and their composites. Acta Mater. 2018, 145, 331–336.
- 40 Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Chang, H.; Xiao, P.; Chen, H.; Huang, Z.; Chen, Y. Broadband and tunable high-performance microwave absorption of an ultralight and highly compressible graphene foam. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2049–53.
- 41 Zhang, X.; Tian, X.; Liu, C.; Qiao, J.; Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Zeng, Z. MnCo-MOF-74 derived porous MnO/Co/C heterogeneous nanocomposites for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 2022, 194, 257–266.
- 42 Zhou, J.; Zhang, G.; Luo, J.; Hu, Y.; Hao, G.; Guo, H.; Guo, F.; Wang, S.; Jiang, W. A MOFs-derived 3D superstructure nanocomposite as excellent microwave absorber. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 130725.
- 43 Liu, Y.; Zou, H.; Ma, H.; Ko, J.; Sun, W.; Andrew Lin, K.; Zhan, S.; Wang, H. Highly efficient activation of peroxymonosulfate by MOF-derived CoP/CoOx heterostructured nanoparticles for the degradation of tetracycline. Chem. Eng. J. (Amsterdam, Neth.) 2022, 430, 132816.
- 44 Wu, F.; Wan, L.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, B. Ternary assembled MOF-derived composite: Anisotropic epitaxial growth and microwave absorption. Compos. B. Eng. 2022, 236, 109839.
- 45 Qiu, Y.; Wen, B.; Yang, H.; Lin, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Jin, L. MOFs derived Co@C@MnO nanorods with enhanced interfacial polarization for boosting the electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 602, 242–250.
- 46 Wei, W.; Liu, X.; Lu, W.; Zhang, H.; He, J.; Wang, H.; Hou, Y. Light-weight Gadolinium Hydroxide@polypyrrole Rare-Earth Nanocomposites with Tunable and Broadband Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 12752–12760.
- 47 Wang, H.; Xiang, L.; Wei, W.; An, J.; He, J.; Gong, C.; Hou, Y. Efficient and Lightweight Electromagnetic Wave Absorber Derived from Metal Organic Framework-Encapsulated Cobalt Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 42102–42110.
- 48 Wang, H.; Meng, F.; Huang, F.; Jing, C.; Li, Y.; Wei, W.; Zhou, Z. Interface Modulating CNTs@PANi Hybrids by Controlled Unzipping of the Walls of CNTs To Achieve Tunable High-Performance Microwave Absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 12142–12153.
- 49 Guo, R.; Su, D.; Chen, F.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Gong, R.; Luo, H. Hollow Beaded Fe3C/N-Doped Carbon Fibers toward Broadband Microwave Absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 3084–3094.
- 50 Zhang, X.; Zhu, J.; Yin, P.; Guo, A.; Huang, A.; Guo, L.; Wang, G. Tunable High-Performance Microwave Absorption of Co1–xS Hollow Spheres Constructed by Nanosheets within Ultralow Filler Loading. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1800761.
- 51 Wen, H.-M.; Jin, H.; Pan, J.; Hong, Q.; Lv, H.; Xie, B.; Xiao, J. Q.; Hu, J. Hollow FeNi/NiFe2O4-Codoped Carbon Composite Nanorods for Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 3406–3414.
- 52 Xiong, J.; Xiang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Yu, L.; Cui, E.; Deng, B.; Liu, Z.; Liu, R.; Lu, W. Layered NiCo alloy nanoparticles/nanoporous carbon composites derived from bimetallic MOFs with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Carbon 2019, 154, 391–401.
- 53 Fan, R.-H.; Peng, R.-W.; Huang, X.-R.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Q.; Wang, M.; Zhang, X. Transparent Metals for Ultrabroadband Electromagnetic Waves. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1980–1986.
- 54 Feng, J.; Zong, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Long, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Zheng, X. Optimization of porous FeNi3/N-GN composites with superior microwave absorption performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 345, 441–451.
- 55 Wang, H.-Y.; Sun, X.-B.; Yang, S.-H.; Zhao, P.-Y.; Zhang, X.-J.; Wang, G.-S.; Huang, Y. 3D Ultralight Hollow NiCo Compound@MXene Composites for Tunable and High-Efficient Microwave Absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 206.
- 56 Cao, W.; Ma, C.; Tan, S.; Ma, M.; Wan, P.; Chen, F. Ultrathin and Flexible CNTs/MXene/Cellulose Nanofibrils Composite Paper for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. Nano-Micro Lett. 2019, 11, 72.
- 57 Liu, P.; Yang, M.; Zhou, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, Y. Hierarchical shell-core structures of concave spherical NiO nanospines@carbon for high performance supercapacitor electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 294, 383–390.
- 58 Li, M.; Yu, S.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Z.; Lv, F.; Nan, B.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wang, W.; Wu, S.; Liu, H.; Tang, Y.; Lu, Z. MoC ultrafine nanoparticles confined in porous graphitic carbon as extremely stable anode materials for lithium- and sodium-ion batteries. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2017, 4, 289–295.
- 59 Ning, M.; Jiang, P.; Ding, W.; Zhu, X.; Tan, G.; Man, Q.; Li, J.; Li, R. Phase Manipulating toward Molybdenum Disulfide for Optimizing Electromagnetic Wave Absorbing in Gigahertz. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2011229.
- 60 Zhao, Z.; Xu, S.; Du, Z.; Jiang, C.; Huang, X. Metal-Organic Framework-Based PB@MoS2 Core-Shell Microcubes with High Efficiency and Broad Bandwidth for Microwave Absorption Performance. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 7183–7192.
- 61 He, P.; Ma, R.; Li, C.; Ran, L.; Yuan, W.; Han, Y.; Deng, L.; Yan, J. Molybdenum blue preassembly strategy to design bimetallic Fe0.54Mo0.73/Mo2C@C for tuneable and low-frequency electromagnetic wave absorption. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2022, 9, 1931–1942.
- 62 Ouyang, J.; He, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhao, Q. Trimetallic FeCoNi@C Nanocomposite Hollow Spheres Derived from Metal-Organic Frameworks with Superior Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Ability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 39304–39314.
- 63 Ahsan, A. M.; He, T.; Eid, K.; Abdullah, A. M.; Sanad, M. F.; Aldalbahi, A.; Alvarado-Tenorio, B.; Du, A.; Puente Santiago, A. R.; Noveron, J. C. Controlling the Interfacial Charge Polarization of MOF-Derived 0D-2D vdW Architectures as a Unique Strategy for Bifunctional Oxygen Electrocatalysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 3919–3929.
- 64 Wang, L.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Che, R. Enhanced polarization from hollow cube-like ZnSnO3 wrapped by multiwalled carbon nanotubes: as a lightweight and high-performance microwave absorber. ACS Appl. Mater. I Interfaces 2018, 10, 22602–22610.
- 65 Wang, L.; Wen, B.; Bai, X.; Liu, C.; Yang, H. Facile and green approach to the synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate framework nanosheet-derived 2D Co/C composites for a lightweight and highly efficient microwave absorber. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 540, 30–38.
- 66 Wang, L.; Bai, X.; Wen, B.; Du, Z.; Lin, Y. Honeycomb-like Co/C composites derived from hierarchically nanoporous ZIF-67 as a lightweight and highly efficient microwave absorber. Compos. B. Eng. 2019, 166, 464–471.
- 67 Zhang, H.; Cheng, J.; Wang, H.; Huang, Z.; Zheng, Q.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, D.; Che, R.; Cao, M. Initiating VB-Group Laminated NbS2 Electromagnetic Wave Absorber toward Superior Absorption Bandwidth as Large as 6.48 GHz through Phase Engineering Modulation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2108194.
- 68 Shi, Y.; Yu, L.; Li, K.; Li, S.; Dong, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Meng, F. Well-matched impedance of polypyrrole-loaded cotton non-woven fabric/polydimethylsiloxane composite for extraordinary microwave absorption. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 197, 108246.
- 69 Hua, J.; Ma, W.; Liu, X.; Zhuang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Huang, H.; Lin, S. Efficient microwave traps with markedly enhanced interfacial polarization and impedance matching enabled by dual-shelled, dual-cavity magnetic@dielectric hollow nanospheres. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 16489–16497.




