Ionic Liquids-Assisted Highly Luminescent Copper Nanoclusters with Triangle Supramolecular Nanostructures
Corresponding Author
Bingyan Han
State Key Laboratory of Fine Chemicals, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, Liaoning, 116023 China
School of Chemical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Panjin, Liaoning, 124221 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorQin Yan
State Key Laboratory of Fine Chemicals, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, Liaoning, 116023 China
School of Chemical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Panjin, Liaoning, 124221 China
These authors contribute equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorZe Xin
State Key Laboratory of Fine Chemicals, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, Liaoning, 116023 China
School of Chemical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Panjin, Liaoning, 124221 China
These authors contribute equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorQifang Yan
State Key Laboratory of Fine Chemicals, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, Liaoning, 116023 China
School of Chemical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Panjin, Liaoning, 124221 China
Search for more papers by this authorJingmei Jiang
State Key Laboratory of Fine Chemicals, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, Liaoning, 116023 China
School of Chemical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Panjin, Liaoning, 124221 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Bingyan Han
State Key Laboratory of Fine Chemicals, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, Liaoning, 116023 China
School of Chemical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Panjin, Liaoning, 124221 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorQin Yan
State Key Laboratory of Fine Chemicals, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, Liaoning, 116023 China
School of Chemical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Panjin, Liaoning, 124221 China
These authors contribute equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorZe Xin
State Key Laboratory of Fine Chemicals, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, Liaoning, 116023 China
School of Chemical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Panjin, Liaoning, 124221 China
These authors contribute equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorQifang Yan
State Key Laboratory of Fine Chemicals, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, Liaoning, 116023 China
School of Chemical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Panjin, Liaoning, 124221 China
Search for more papers by this authorJingmei Jiang
State Key Laboratory of Fine Chemicals, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, Liaoning, 116023 China
School of Chemical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Panjin, Liaoning, 124221 China
Search for more papers by this authorMain observation and conclusion
A novel and facile approach towards highly luminescent CuNCs@MMI (2-mercapto-1-methylimidazole) has been developed within 30 s with the assistance of ionic liquids (ILs)—[Bmim]BF4. FT-IR spectra, Zeta potential, TEM and SEM images showed that the as-prepared CuNCs@MMI within [Bmim]BF4 could assemble into well-ordered triangle supramolecular nanostructures via electrostatic interaction. In addition, pH-responsion of CuNCs@MMI in photoluminescence intensity indicated the great potential for pH sensing applications.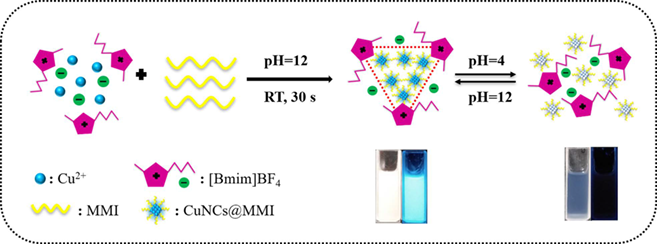
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202100012-sup-0001-Supinfo.pdfPDF document, 719.3 KB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1(a) Ghosh, R.; Sahoo, A. K.; Ghosh, S. S.; Paul, A.; Chattopadhyay, A. Blue-emitting copper nanoclusters synthesized in the presence of lysozyme as candidates for cell labeling. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 3822–3828; (b) Zhong, W.; Wen, M.; Xu, J.; Wang, H.; Tan, L.; Shang, L. Simultaneous regulation of optical properties and cellular behaviors of gold nanoclusters by pre-engineering the biotemplates. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 11414–11417.
- 2 Miao, Z.; Hou, W.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, S. BSA capped bi-functional fluorescent Cu nanoclusters as pH sensor and selective detection of dopamine. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 1446–1456.
- 3 Heo, G. S.; Zhao, Y.; Sultan, D.; Zhang, X.; Detering, L.; Luehmann, H. P.; Zhang, X.; Li, R.; Choksi, A.; Sharp, S.; Levingston, S.; Primeau, T.; Reichert, D. E.; Sun, G.; Razani, B.; Li, S.; Weilbaecher, K. N.; Dehdashti, F.; Wooley, K. L.; Liu, Y. Assessment of copper nanoclusters for accurate in vivo tumor imaging and potential for translation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 19669–19678.
- 4 Liu, J.; Wu, Z.; Tian, Y.; Li, Y.; Ai, L.; Li, T.; Zou, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Yang, B. Engineering the Self-Assembly Induced Emission of Cu Nanoclusters by Au(I) Doping. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 24899–24907.
- 5 Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Li, T.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Peng, S.; Wang, Z. Ligand-assisted reduction and reprecipitation synthesis of highly luminescent metal nanoclusters. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 834–839.
- 6(a) Xu, J.; Han, B. Y. Synthesis of protein-directed orange/red-emitting copper nanoclusters via hydroxylamine hydrochloride reduction approach and their applications on Hg2+ sensing. Nano 2016, 11, 1650108; (b) Mohamed, H. I.; Bingshi, L.; Guobao, X. Novel synthesis of thiolated gold nanoclusters induced by lanthanides for ultrasensitive and luminescent detection of the potential anthrax spores biomarker. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 32888–32897; (c) Chang, H.; Karan, N. S.; Shin, K.; Bootharaju, M. S.; Nah, S.; Chae, S. I.; Baek, W.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Son, Y. J.; Kang, T. Y.; Ko, G.; Kwon, S. H.; Hyeon, T. Highly fluorescent gold cluster assembly. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 143, 326–334.
- 7 Prakash, K. T.; Singh, N.; Venkatesh, V. Synthesis of novel luminescent copper nanoclusters with substituent driven self-assembly and aggregation induced emission (AIE). Chem. Commun. 2018, 55, 322–325.
- 8(a) Wang, W.; Leng, F.; Zhan, L.; Chang, Y.; Yang, X. X.; Lan, J.; Huang, C. Z. One-step prepared fluorescent copper nanoclusters for reversible pH-sensing. Analyst 2014, 139, 2990–2993; (b) Yang, J.; Wang, T.; Zhao, L.; Rajasekhar, V. K.; Joshi, S.; Andreou, C.; Pal, S.; Hsu, H.; Zhang, H.; Cohen, I. J.; Huang, R.; Hendrickson, R. C.; Miele, M. M.; Pei, W.; Brendel, M. B.; Healey, J. H.; Chiosis, G.; Kircher, M. F. Gold/ alpha-lactalbumin nanoprobes for the imaging and treatment of breast cancer. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 686–703.
- 9(a) Li, R. Y.; Wang, H. Y.; Zhou, X. Y.; Liao, X. Q.; Sun, X. L.; Li, Z. J. D-Penicillamine and bovine serum albumin co-stabilized copper nanoclusters with remarkably enhanced fluorescence intensity and photostability for ultrasensitive detection of Ag+. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 732–739; (b) Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, J.; Jing, H.; Gao, Z.; Huang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, C. Design of "turn-on" fluorescence sensor for L-cysteine based on the instability of metal-organic frameworks. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 268, 88–92; (c) Maity, S.; Bain, D.; Patra, A. Engineering atomically precise copper nanoclusters with aggregation induced emission. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 2506–2515; (d) Hambarde, G.; Bothra, S.; Upadhyay, Y.; Bera, R. K.; Sahoo, S. K. m-Dinitrobenzene directed aggregation-induced emission enhancement of cysteine modified fluorescent copper nanoclusters. Microchem. J. 2019, 147, 899–904.
- 10 Chen, T.; Xu, Y.; Wang, L.; Jiang, W.; Jiang, W.; Xie, Z. Ionic-liquid-assisted microwave preparation of tunable photoluminescent Copper- Indium-Zinc-Sulfide quantum dots. Chemistry 2018, 24, 16407–16417.
- 11 Fan, C.; Liang, Y.; Dong, H.; Yang, J.; Tang, G.; Zhang, W.; Kong, D.; Li, J.; Cao, Y. Guanidinium ionic liquid-controlled synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate framework for improving its adsorption property. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 163–173.
- 12 Blach, D.; Martinez, F. Gold nanoparticles optical properties induced by water and an ionic liquid (BmimBF4) inside cationic reverse micelles. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 13104–13113.
- 13(a) Li, Z.; Jia, Z.; Luan, Y.; Mu, T. Ionic liquids for synthesis of inorganic nanomaterials. Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science 2008, 12, 1–8; (b) Pang, J.; Luan, Y.; Li, F.; Cai, X.; Li, Z. Ionic liquid-assisted synthesis of silica particles and their application in drug release. Mater. Lett. 2010, 64, 2509–2512.
- 14(a) Yin, S.; Luo, Z.; Xia, J.; Li, H. Size-controlled synthesis and morphology evolution of Nd2O3 nano-powders using ionic liquid surfactant templates. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2010, 71, 1785–1788; (b) Huang, B.; Huang, C.; Chen, J.; Sun, X. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 712, 164–171; (c) Choi, H.; Kim, Y. J.; Varma, R. S.; Dionysiou, D. D. Thermally stable nanocrystalline TiO2 photocatalysts synthesized via Sol−Gel methods modified with ionic liquid and surfactant molecules. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 5377–5384; (d) Shen, J.; Wang, Z.; Xia, C.; Sun, D.; Yuan, S.; Xin, X. Amphiphilicity regulation of Ag(I) nanoclusters: self-assembly and its application as luminescent probe. Chem.-Eur. J. 2019, 25, 4713–4721.
- 15 Zhou, Y.; Schattka, J. H.; Markus, A. Room-temperature ionic liquids as template to monolithic mesoporous silica with wormlike pores via a Sol−Gel nanocasting technique. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 477–481.
- 16(a) Endres, F.; Zein El Abedin, S. Air and water stable ionic liquids in physical chemistry. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 2101–2116; (b) Park, H. S.; Choi, Y. S.; Kim, Y. J.; Hong, W. H.; Song, H. 1D and 3D ionic liquid-aluminum hydroxide hybrids prepared via an ionothermal process. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 2411–2418; (c) Picalek, J.; Minofar, B.; Kolafa, J.; Jungwirth, P. Aqueous solutions of ionic liquids: study of the solution/vapor interface using molecular dynamics simulations. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2008, 10, 5765–5775.




