Guajamers A—I, Rearranged Polycyclic Phloroglucinol Meroterpenoids from Psidium guajava Leaves and Their Antibacterial Activity
Ji-Wu Huang
State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines, Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100050 China
Search for more papers by this authorChuang-Jun Li
State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines, Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100050 China
Search for more papers by this authorJing-Zhi Yang
State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines, Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100050 China
Search for more papers by this authorChuan Li
State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines, Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100050 China
Search for more papers by this authorYu Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines, Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100050 China
Search for more papers by this authorKe Liu
State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines, Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100050 China
Search for more papers by this authorYue Yu
State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines, Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100050 China
Search for more papers by this authorJian-Dong Jiang
State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines, Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100050 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dong-Ming Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines, Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100050 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorJi-Wu Huang
State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines, Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100050 China
Search for more papers by this authorChuang-Jun Li
State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines, Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100050 China
Search for more papers by this authorJing-Zhi Yang
State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines, Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100050 China
Search for more papers by this authorChuan Li
State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines, Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100050 China
Search for more papers by this authorYu Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines, Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100050 China
Search for more papers by this authorKe Liu
State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines, Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100050 China
Search for more papers by this authorYue Yu
State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines, Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100050 China
Search for more papers by this authorJian-Dong Jiang
State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines, Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100050 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dong-Ming Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines, Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100050 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorMain observation and conclusion
Eight new polycyclic phloroglucinol meroterpenoids guajamers A—H (1—8), a methylated benzoylphloroglucinol meroterpenoid guajamer I (9) representing a new skeleton, and two known analogues (10 and 11) were isolated from the leaves of Psidium guajava. The structures of new molecules were elucidated by detailed analysis of spectroscopic data, and those of 1, 2, 8, and 9 were unambiguously confirmed by single-crystal X-ray diffraction study. Structurally, compounds 1—8 were sesquiterpene and monoterpene- based meroterpenoids with rearranged skeletons, while compound 9 was the first case of 3-alkyl-5-formyl-benzoylphloroglucinol- coupled sesquiterpene containing an unusual C-1-spiro-fused 6/6/9/4 polycyclic skeleton. In addition, all the isolated compounds were evaluated for their antibacterial activity against three bacterial strains, and most of them (compounds 2—7, 10, and 11) showed antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis with MIC values of 8—32 μmol/L. These findings suggested that meroterpenoids isolated from Psidium guajava can be considered as potential antibacterial leading compounds for pharmaceutical industry.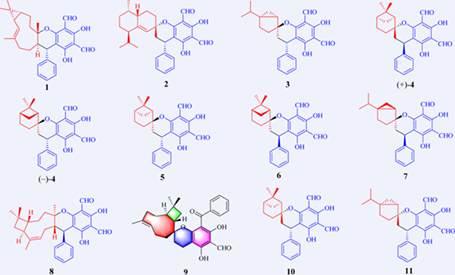
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202000640-sup-0001-Supinfo.pdfPDF document, 10 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Gutiérrez, R.; Mitchell, S.; Solis, R. Psidium guajava: a review of its traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 117, 1–27.
- 2 Li, Y. Y.; Li, D. L.; An, Q.; Ma, H.; Mu, Y.; Qiao, W. J.; Zhang, Z. G.; Zhang, J. S.; Huang, X. S.; Li, L. Y. New acylated phenolic glycosides with ROS-scavenging activity from Psidium guajava leaves. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 11089–11098.
- 3 Wang, L.; Luo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Z. Fermentation and complex enzyme hydrolysis for improving the total soluble phenolic contents, flavonoid aglycones contents and bio-activities of guava leaves tea. Food Chem. 2018, 264, 189–198.
- 4 Díaz-de-Cerio, E.; Verardo, V.; Gómez-Caravaca, A. M.; Fernández- Gutiérrez, A.; Segura-Carretero, A. Health effects of Psidium guajava L. leaves: an overview of the last decade. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 897.
- 5 Matsuzaki, K.; Ishii, R.; Kobiyama, K.; Kitanaka, S. New benzophenone and quercetin galloyl glycosides from Psidium guajava L. J. Nat. Med. 2010, 64, 252–256.
- 6 Prabu, G.; Gnanamani, A.; Sadulla, S. Guaijaverin - a plant flavonoid as potential antiplaque agent against Streptococcus mutans. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 101, 487–495.
- 7 Park, B.; Matsuta, T.; Kanazawa, T.; Chang, K.; Park, C.; Onjo, M. Phenolic compounds from the leaves of Psidium guajava. I. Hydrolysable tannins and benzophenone glycosides. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2011, 47, 632–635.
- 8 Shu, J.; Liu, J.; Chou, G.; Wang, Z. Two new triterpenoids from Psidium guajava. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2012, 23, 827–830.
- 9 Jian, Y. Q.; Huang, X. J.; Zhang, D. M.; Jiang, R. W.; Chen, M. F.; Zhao, B. X.; Wang, Y.; Ye, W. C. Guapsidial A and guadials B and C: three new meroterpenoids with unusual skeletons from the leaves of Psidium guajava. Chem.-Eur. J. 2015, 21, 9022–9027.
- 10 Yang, X. L.; Hsieh, K. L.; Liu, J. K. Guajadial: an unusual meroterpenoid from guava leaves Psidium guajava. Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 5135–5138.
- 11 Begum, S.; Siddiqui, B.; Hassan, S. Triterpenoids from Psidium guajava leaves. Nat. Prod. Lett. 2002, 16, 173–177.
- 12 Shao, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, D. M.; Cao, H. H.; Jiang, R. W.; Fan, C. L.; Zhang, X. Q.; Chen, H. R.; Yao, X. S.; Ye, W. C. Psiguadials A and B, two novel meroterpenoids with unusual skeletons from the leaves of Psidium guajava. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 5040–5043.
- 13 Dhiman, A.; Nanda, A.; Ahmad, S.; Narasimhan, B. In vitro antimicrobial activity of methanolic leaf extract of Psidium guajava L. J. Pharm. Bioall. Sci. 2011, 3, 226–229.
- 14 de Araújo, A. A.; Soares, L. A. L.; Assunção Ferreira, M. R.; de Souza Neto, M. A.; da Silva, G. R.; de Araújo, R. F.; Guerra, G. C. B.; de Melo, M. C. N. Quantification of polyphenols and evaluation of antimicrobial, analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of aqueous and acetone–water extracts of Libidibia ferrea, Parapiptadenia rigida and Psidium guajava. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 156, 88–96.
- 15 Ning, S.; Liu, Z. L.; Wang, Z. C.; Liao, M. J.; Xie, Z. X. Biomimetic synthesis of psiguajdianone guided discovery of the meroterpenoids from Psidium guajava. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 8700–8704.
- 16 Li, C. J.; Ma, J.; Sun, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, D. M. Guajavadimer A, a dimeric caryophyllene-derived meroterpenoid with a new carbon skeleton from the leaves of Psidium guajava. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 168–171.
- 17 Hou, J. Q.; Fan, C. L.; Pei, X.; Zhang, P. L.; Deng, F.; Jiang, W. Q.; Wang, G. C.; Zhang, X. Q.; Ye, W. C.; Wang, H. Psiguadiols A–J, rearranged meroterpenoids as potent PTP1B inhibitors from Psidium guajava. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 3267–3278.
- 18 Qin, X. J.; Yan, H.; Ni, W.; Yu, M. Y.; Khan, A.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H. X.; He, L.; Hao, X. J.; Di, Y. T.; Liu, H. Y. Cytotoxic meroterpenoids with rare skeletons from Psidium guajava cultivated in temperate zone. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32748.
- 19 Gao, Y.; Li, G. T.; Li, Y.; Hai, P.; Wang, F.; Liu, J. K. Guajadials C−F, four unusual meroterpenoids from Psidium guajava. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2013, 3, 14–19.
- 20 Shao, M.; Wang, Y.; Jian, Y. Q.; Huang, X. J.; Zhang, D. M.; Tang, Q. F.; Jiang, R. W.; Sun, X. G.; Lv, Z. P.; Zhang, X. Q.; Ye, W. C. Guadial A and psiguadials C and D, three unusual meroterpenoids from Psidium guajava. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 5262–5265.
- 21 Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341.
- 22 Bruhn, T.; Schaumlöffel, A.; Hemberger, Y.; Pescitelli, G. SpecDis, Version 1.70, Berlin, Germany, 2017, https://specdis-software.jimdo. com/.
- 23 Wang, Q.; Lv, Y. M.; Pang, J.; Li, X.; Lu, X.; Wang, X. K.; Hu, X. X.; Nie, T. Y.; Yang, X. Y.; Xiong, Y. Q.; Jiang, J. D.; Li, C. R.; You, X. F. In vitro and in vivo activity of D-serine in combination with β-lactam antibiotics against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 496–504.




