Coordination Insertion Mechanism of Ring-Opening Polymerization of Lactide Catalyzed by Stannous Octoate†
Weihan Rao
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Engineering of Polymers, Department of Macromolecular Science, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorCaiyun Cai
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Engineering of Polymers, Department of Macromolecular Science, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorJingyu Tang
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Engineering of Polymers, Department of Macromolecular Science, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorYiman Wei
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Engineering of Polymers, Department of Macromolecular Science, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorCaiyun Gao
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Engineering of Polymers, Department of Macromolecular Science, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorLin Yu
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Engineering of Polymers, Department of Macromolecular Science, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
Zhuhai Fudan Innovation Institute, Zhuhai, Guangdong, 519000 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Jiandong Ding
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Engineering of Polymers, Department of Macromolecular Science, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
Zhuhai Fudan Innovation Institute, Zhuhai, Guangdong, 519000 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorWeihan Rao
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Engineering of Polymers, Department of Macromolecular Science, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorCaiyun Cai
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Engineering of Polymers, Department of Macromolecular Science, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorJingyu Tang
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Engineering of Polymers, Department of Macromolecular Science, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorYiman Wei
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Engineering of Polymers, Department of Macromolecular Science, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorCaiyun Gao
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Engineering of Polymers, Department of Macromolecular Science, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorLin Yu
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Engineering of Polymers, Department of Macromolecular Science, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
Zhuhai Fudan Innovation Institute, Zhuhai, Guangdong, 519000 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Jiandong Ding
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Engineering of Polymers, Department of Macromolecular Science, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
Zhuhai Fudan Innovation Institute, Zhuhai, Guangdong, 519000 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this author† In Memory of Professor Lina Zhang.
Main observation and conclusion
Ring-opening polymerization (ROP) of cyclic esters in the presence of stannous octoate (Sn(Oct)2) is the main way to obtain biodegradable aliphatic polyesters, an important family of biodegradable polymers which have been widely used and still rapidly developed in the fields of biomedical polymers and environment-friendly materials. The underlying mechanism is thought via a coordination-insertion way, but the pathway is still open owing to the absence of direct experimental evidence. Herein, we inquire this issue through density functional theory (DFT) calculations. According to our DFT calculations and the following Curtin-Hammett evaluation, the carbonyl oxygen has a significant advantage over the ester oxygen, and thus the ring is opened mainly through pathway A instead of pathway B. The stannous octoate is identified as a catalyst rather than an initiator. We eventually summarize the main stages during the whole polymerization of lactide.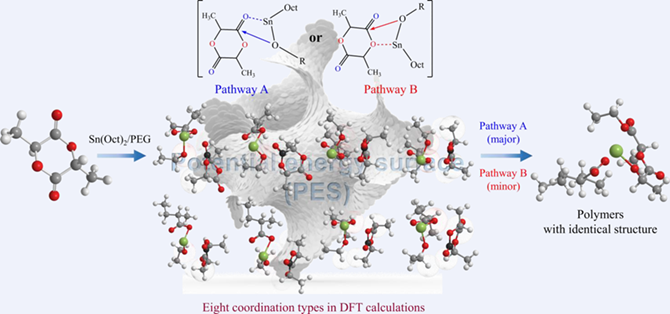
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc_202000519_sm_suppl.pdfPDF document, 7 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Langer, R.; Vacanti, J. P. Tissue engineering. Science 1993, 260, 920–926.
- 2 Yu, L.; Ding, J. D. Injectable hydrogels as unique biomedical materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1473–1481.
- 3 Duan, J. J.; Zhang, L. N. Robust and smart hydrogels based on natural polymers. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2017, 35, 1165–1180.
- 4 Fang, Y.; Zhang, R. R.; Duan, B.; Liu, M. L.; Lu, A.; Zhang, L. N. Recyclable universal solvents for chitin to chitosan with various degrees of acetylation and construction of robust hydrogels. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2725–2733.
- 5 Meng, F. D.; Sun, J.; Li, Z. B. Stimuli-responsive polypeptide-based supramolecular hydrogels mediated by Ca2+ ion cross-linking. Chin. J. Chem. 2019, 37, 1137–1141.
- 6 Gao, J. M.; Ding, X. Q.; Yu, X. Y.; Chen, X. B.; Zhang, X. Y.; Cui, S. Q.; Shi, J. Y.; Chen, J.; Yu, L.; Chen, S. Y.; Ding, J. D. Cell-Free Bilayered porous scaffolds for osteochondral regeneration fabricated by continuous 3D-printing using nascent physical hydrogel as ink. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2021, 10, 2001404.
- 7 Vert, M.; Li, S. M.; Spenlehauer, G.; Guerin, P. J. Bioresorbability and biocompatibility of aliphatic polyesters. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Med. 1992, 3, 432–446.
- 8
Ikada, Y.; Tsuji, H. Biodegradable polyesters for medical and ecological applications. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2000, 21, 117–132.
10.1002/(SICI)1521-3927(20000201)21:3<117::AID-MARC117>3.0.CO;2-X CAS Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 9 Auras, R.; Harte, B.; Selke, S. An overview of polylatides as packaging materials. Macromol. Biosci. 2004, 4, 835–864.
- 10 Nair, L. S.; Laurencin, C. T. Biodegradable polymers as biomaterials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 762–798.
- 11 Pan, Z.; Ding, J. D. Poly(lactide-co-glycolide) porous scaffolds for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Interface Focus 2012, 2, 366–377.
- 12 Qu, Z. H.; Ding, J. D. Sugar-fiber imprinting to generate microgrooves on polymeric film surfaces for contact guidance of cells. Chin. J. Chem. 2012, 30, 2292–2296.
- 13 Li, K.; Huang, J. C.; Gao, H. C.; Zhong, Y.; Cao, X. D.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L. N.; Cai, J. Reinforced mechanical properties and tunable biodegradability in nanoporous cellulose gels poly(l-lactide-co-caprolactone) nanocomposites. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 1506–1515.
- 14 Rumian, Ł.; Wolf-Brandsetter, R.; Rößler, S.; Reczyńska, K.; Tiainen, H.; Haugen, H.; Scharnweber, D.; Pamuła, E. Sodium alendronate loaded poly(L-lactideco-glycolide) microparticles immobilized on ceramic scaffolds for local treatment of bone defects. Regen. Biomater. 2020, 7, 293–302.
- 15 Gong, X. H.; Liang, Z. Q.; Yang, Y. X.; Liu, H. F.; Ji, J.; Fan, Y. B. A resazurin-based, nondestructive assay for monitoring cell proliferation during a scaffold-based 3D culture process. Regen. Biomater. 2020, 7, 271–281.
- 16 Liu, Z.; Ye, W. L.; Zheng, J. C.; Wang, Q. D.; Ma, G. W.; Liu, H. Y.; Wang, X. M. Hierarchically electrospraying a PLGA@chitosan sphere-in- sphere composite microsphere for multi-drug-controlled release. Regen. Biomater. 2020, 7, 381–390.
- 17 He, Y. Z.; Jin, Y. H; Ying, X. X.; Wu, Q.; Yao, S. L.; Li, Y. Y.; Liu, H. Y.; Ma, G. W.; Wang, X. M. Development of an antimicrobial peptide-loaded mineralized collagen bone scaffold for infective bone defect repair. Regen. Biomater. 2020, 7, 515–525.
- 18 Pan, Z.; Duan, P. G.; Liu, X. N.; Wang, H. R.; Cao, L.; He, Y.; Dong, J.; Ding, J. D. Effect of porosities of bilayered porous scaffolds on spontaneous osteochondral repair in cartilage tissue engineering. Regen. Biomater. 2015, 2, 9–19.
- 19 Wu, L. B.; Ding, J. D. In vitro degradation of three-dimensional porous poly(d,l-lactide-coglycolide) scaffolds for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 5821–5830.
- 20 Dechy-Cabaret, O.; Martin-Vaca, B.; Bourissou, D. Controlled ring- opening polymerization of lactide and glycolide. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 6147–6176.
- 21 Cui, S. Q.; Yu, L.; Ding, J. D. Injectable thermogels based on block copolymers of appropriate amphiphilicity. Acta Polym. Sin. 2018, 997–1015 (in Chinese).
- 22 Shen, Y.; Li, Z. B. Ring-opening polymerization of cyclic esters by utilizing organophosphazene bases toward biodegradable polyesters. Acta Polym. Sin. 2020, 51, 777–790 (in Chinese).
- 23 Sodergard, A.; Stolt, M. Properties of lactic acid based polymers and their correlation with composition. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2002, 27, 1123–1163.
- 24 Zhu, A. P.; Chen, R. Q.; Chan-Park, M. B. Patterning of a random copolymer of poly[lactide-co-glycotide-co-(e-caprolactone)] by UV embossing for tissue engineering. Macromol. Biosci. 2006, 6, 51–57.
- 25 Caruso, M. M.; Davis, D. A.; Shen, Q. L.; Odom, S. A.; Sottos, N. R.; White, S. R.; Moore, J. S. Mechanically-induced chemical changes in polymeric materials. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 5755–5798.
- 26 Chen, M.; Chen, C. L. Controlling the ring-opening polymerization process using external stimuli. Chin. J. Chem. 2020, 38, 282–286.
- 27 Mecerreyes, D.; Robert, J.; Philippe, D. Novel macromolecular architectures based on aliphatic polyesters relevance of the “coordination-insertion” ring-opening polymerization. Macromolecular Architectures 1999, 1–59.
- 28 Williams, C. K. Synthesis of functionalized biodegradable polyesters. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 1573–1580.
- 29 Penczek, S.; Duda, A.; Kowalski, A.; Libiszowski, J.; Majerska, K.; Biela, T. On the mechanism of polymerization of cyclic esters induced by Tin(II) octoate. Macromol. Symp. 2000, 157, 61–70.
- 30 Knop, K.; Hoogenboom, R.; Fischer, D.; Schubert, U. S. Poly(ethylene glycol) in drug delivery pros and cons as well as potential alternatives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6288–6308.
- 31 Ye, K.; Wang, X.; Cao, L. P.; Li, S. Y.; Li, Z. H.; Yu, L.; Ding, J. D. Matrix stiffness and nanoscale spatial organization of cell-adhesive ligands direct stem cell fate. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 4720–4729.
- 32 Wang, X.; Li, S. Y.; Yan, C.; Liu, P.; Ding, J. D. Fabrication of RGD micro/nanopattern and corresponding study of stem cell differentiation. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 1457–1467.
- 33 Peng, Y. M.; Liu, Q. J.; He, T. L.; Ye, K.; Yao, X.; Ding, J. D. Degradation rate affords a dynamic cue to regulate stem cells beyond varied matrix stiffness. Biomaterials 2018, 178, 467–480.
- 34 Hu, Y. W.; Yao, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, R. L.; Cui, S. Q.; Ding, J. D. Left-right symmetry or asymmetry of cells on stripe-like micropatterned material surfaces. Chin. J. Chem. 2018, 36, 605–611.
- 35 Yao, X.; Liu, R. L.; Liang, X. Y.; Ding, J. D. Critical areas of proliferation of single cells on micropatterned surfaces and corresponding cell type dependence. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 15366–15380.
- 36 Yao, X.; Ding, J. D. Effects of microstripe geometry on guided cell migration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 27971–27983.
- 37 Liu, Q.; Zheng, S.; Ye, K.; He, J. H.; Shen, Y.; Cui, S. Q.; Huang, J. L.; Gu, Y. X.; Ding, J. D. Cell migration regulated by RGD nanospacing and enhanced under moderate cell adhesion on biomaterials. Biomaterials 2020, 263, 120327.
- 38 Xu, H.; Ma, B. X.; Jiang, J. Z.; Xiao, S. T.; Peng, R. R.; Zhuang, W. H.; Li, G. C.; Wang, Y. B. Integrated prodrug micelles with two-photon bioimaging and pH-triggered drug delivery for cancer theranostics. Regen. Biomater. 2020, 7, 171–180.
- 39 He, C. L.; Kim, S. W.; Lee, D. S. In situ gelling stimuli-sensitive block copolymer hydrogels for drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2008, 127, 189–207.
- 40 Lee, D. S.; Shim, M. S.; Kim, S. W.; Lee, H.; Park, I.; Chang, T. Y. Novel thermoreversible gelation of biodegradable PLGA-block-PEO-block- PLGA triblock copolymers in aqueous solution. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2001, 22, 587–592.
- 41 Jeong, B.; Lee, K. M.; Gutowska, A.; An, Y. H. H. Thermogelling biodegradable copolymer aqueous solutions for injectable protein delivery and tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 865−868.
- 42 Yu, L.; Zhang, H.; Ding, J. D. A subtle end-group effect on macroscopic physical gelation of triblock copolymer aqueous solutions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 2232–2235.
- 43 Zhang, Z.; Lai, Y. X.; Yu, L. Ding, J. D. Effects of immobilizing sites of RGD peptides in amphiphilic block copolymers on efficacy of cell adhesion. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 7873–7882.
- 44 Zhang, Z.; Ni, J.; Chen, L.; Yu, L.; Xu, J. W.; Ding, J. D. Biodegradable and thermoreversible PCLA–PEG–PCLA hydrogel as a barrier for prevention of post-operative adhesion. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 4725–4736.
- 45 Chang, G. T.; Ci, T. Y.; Yu, L.; Ding, J. D. Enhancement of the fraction of the active form of an antitumor drug topotecan via an injectable hydrogel. J. Control. Release 2011, 156, 21–27.
- 46 Chen, L.; Ci, T. Y.; Yu, L.; Ding, J. D. Effects of molecular weight and its distribution of PEG block on micellization and thermogellability of PLGA–PEG–PLGA copolymer aqueous solutions. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 3662–3671.
- 47 He, C. L.; Ma, H. C.; Cheng, Y. L.; Li, D. S.; Gong, Y. B.; Liu, J. G.; Tian, H. Y.; Chen, X. S. PLK1shRNA and doxorubicin co-loaded thermosensitive PLGA–PEG–PLGA hydrogels for localized and combined treatment of human osteosarcoma. J. Control. Release 2015, 213, e8.
- 48 Yuan, B. M.; He, C. L.; Dong, X. M.; Wang, J. C.; Gao, Z. L.; Wang, Q.; Tian, H. Y.; Chen, X. S. 5-Fluorouracil loaded thermosensitive PLGA–PEG– PLGA hydrogels for the prevention of postoperative tendon adhesion. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 25295–25303.
- 49 Cui, S. Q.; Yu, L.; Ding, J. D. Semi-bald micelles and corresponding percolated micelle networks of thermogels. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 6405–6420.
- 50 Cui, S. Q.; Yu, L.; Ding, J. D. Thermogelling of amphiphilic block copolymers in water: ABA type versus AB or BAB type. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 3697–3715.
- 51 Chen, X. B.; Zhang, J. L.; Wu, K. T.; Wu, X. H.; Tang, J. Y.; Cui, S. Q.; Cao, D. L. G.; Liu, R. L.; Peng, C.; Yu, L.; Ding, J. D. Visualizing the in vivo evolution of an injectable and thermosensitive hydrogel using tri-modal bioimaging. Small Methods 2020, 4, 2000310.
- 52 Yang, X. W.; Chen, X. B.; Wang, Y. B.; Xu, G. H.; Yu, L.; Ding, J. D. Controlled release of liraglutide using thermogelling polymers in treatment of diabetes. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 396, 125320.
- 53 Cui, S. Q.; Yu, L.; Ding, J. D. Strategy of “Block Blends” to Generate Polymeric Thermogels versus That of One-Component Block Copolymer. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 11051–11064.
- 54 Sun, J. L.; Wei, Q.; Shen, N.; Tang, Z. H.; Chen, X. S. Predicting the Loading Capability of mPEG-PDLLA to Hydrophobic Drugs Using Solubility Parameters. Chin. J. Chem. 2020, 38, 690–696.
- 55 Yu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Ding, J. D. Biodegradability and biocompatibility of thermoreversible hydrogels formed from mixing a sol and a precipitate of block copolymers in water. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 2169–2178.
- 56 Penczek, S.; Cypryk, M.; Duda, A.; Kubisa, P.; Slomkowski, S. Living ring-opening polymerizations of heterocyclic monomers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 247–282.
- 57 Duda, A.; Penczek, S.; Kowalski, A.; Libiszowski, J. Polymerizations of ε-caprolactone and L, L-dilactide initiated with stannous octoate and stannous butoxide-a comparison. Macromol. Symp. 2000, 153, 41–53.
- 58 Fan, L.; Xiong, Y. B.; Tu, K. H.; Shen, Z. Q. Ring–opening polymerization of D,L-lactide by lanthanide tris(2,4,6-trimethylphenolate): characteristics and kinetics. Chin. J. Chem. 2005, 23, 613–616.
- 59 Kowalski, A.; Libiszowski, J.; Majerska, K.; Duda, A.; Penczek, S. Kinetics and mechanism of 3-caprolactone and L,L-lactide polymerization coinitiated with zinc octoate or aluminum acetylacetonate: The next proofs for the general alkoxide mechanism. Polymer 2007, 48, 3952–3960.
- 60 Duan, R. L.; Qu, Z.; Pang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z. Q.; Zhang, H.; Bian, X. C.; Chen, X. S. Ring-Opening Polymerization of Lactide Catalyzed by Bimetallic Salen-Type Titanium Complexes. Chin. J. Chem. 2017, 35, 640–644.
- 61 Dubois, Ph.; Jacobs, C.; Jerome, R.; Teyssie, Ph. Macromolecular engineering of polylactones and polylactides. 4. Mechanism and kinetics of lactide homopolymerization by aluminum isopropoxide. Macromolecules 1991, 24, 2266–2270.
- 62
Kowalski, A.; Duda, A.; Penczek, S. Kinetics and mechanism of cyclic esters polymerization initiated with tin (II) octoate, 1. Polymerization of ε-caprolactone. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 1998, 19, 567–572.
10.1002/(SICI)1521-3927(19981101)19:11<567::AID-MARC567>3.0.CO;2-T CAS Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 63 Kowalski, A.; Duda, A.; Penczek, S. Mechanism of cyclic ester polymerization initiated with Tin octoate. 2. Macromolecules fitted with Tin alkoxide species observed directly in MALDI-TOF spectra. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 689–695.
- 64 Libiszowski, J.; Kowalski, A.; Duda, A.; Penczek, S. Kinetics and mechanism of cyclic esters polymerization initiated with covalent metal carboxylates, 5. End-group studies in the model ε-caprolactone and L,L-dilactide/Tin(II) and zinc octoate/butyl alcohol system. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2002, 203, 1694–1701.
- 65 Bero, M.; Kasperczyk, J.; Jedlinski, Z. J. Coordination polymerization of lactides, 1. Structure determination of obtained polymers. Makromol. Chem. 1990, 191, 2287–2296.
- 66 Kricheldorf, H. R.; Kreiser-Saunders, I.; Boettcher, C. Polylactones 31. Sn(II)octoate-initiated polymerization of L-lactide: a mechanistic study. Polymer 1995, 36, 1253–1259.
- 67 Bero, M.; Kasperczyk, J. Coordination polymerization of lactides, 5. Influence of lactide structure on the transesterification processes in the copolymerization with ε-caprolactone. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1996, 197, 3251–3258.
- 68 Veld, P. J. A. I.; Velner, E. M.; Witte, P. V. D.; Hamhuis, J.; Dijkstra, P. J.; Feijen, J. Melt block copolymerization of ε-caprolactone and L-Lactide. J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Chem. 1997, 35, 219–226.
- 69
Schwach, G.; Coudane, J.; Engel, R.; Vert, M. More about the polymerization of lactides in the presence of stannous octoate. J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Chem. 1997, 35, 3431–3440.
10.1002/(SICI)1099-0518(19971130)35:16<3431::AID-POLA10>3.0.CO;2-G CAS Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 70 Majerska, K.; Duda, A.; Penczek, S. Kinetics and mechanism of cyclic esters polymerisation initiated with tin(II) octoate, 4. Influence of proton trapping agents on the kinetics of ε-caprolactone and L,L-dilactide polymerisation. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2000, 21, 1327–1332.
- 71 Kricheldorf, H. R.; Kreiser-Saunders, I.; Stricker, A. Polylactones 48. Sn(Oct)2-initiated polymerizations of lactide: A mechanistic study. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 702–709.
- 72 Platel, R. H.; Hodgson, L. M.; Williams, C. K. Biocompatible initiators for lactide polymerization. Polym. Rev. 2008, 48, 11–63.
- 73 Wang, H.; Xu, K.; Yao, X. Y.; Ye, D. H.; Pei, L.; Hu, H. R.; Qiao, M. H.; Li, Z. H.; Zhang, X. X.; Zong, B. N. Undercoordinated site-abundant and tensile-strained nickel for low-temperature COx methanation. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 1207–1211.
- 74 Li, X. X.; Yang, J. L. Computational design of one-dimensional ferromagnetic semiconductors in transition metal embedded stannaspherene nanowires. Chin. J. Chem. 2019, 37, 1021–1024.
- 75 Yang, L.; Yin, C. Z.; Ali, M. A.; Dong, C. Y.; Xie, X. M.; Wu, X. P.; Mao, J.; Wang, Y. X.; Yu, Y.; Xie, L. H.; Bian, L. Y.; Bao, J. M.; Ran, X. Q.; Huang, W. Theoretical studies on novel gridspiroarenes structures, noncovalent interactions and reorganization energies. Chin. J. Chem. 2019, 37, 915–921.
- 76 Du, Y. J.; Wang, C. M.; Yang, G.; Yang, W. M. Comparison of ethylation at external surface and internal cavity of H-MCM-22 zeolite from theoretical calculations. Chin. J. Chem. 2020, 38, 50–56.
- 77 Gilding, D. K.; Reed, A. M. Biodegradable polymers for use in surgery polyglycolic/poly(actic acid) homo- and copolymers 1. Polymer 1979, 20, 1459–1464.
- 78 Du, Y. J.; Lemstra, P. J.; Nijenhuis, A. J.; van Aert, H. A. M.; Bastiaansen, C. ABA type copolymers of lactide with poly(ethy1ene glycol). Kinetic, mechanistic, and model studies. Macromolecules 1995, 28, 2124–2132.
- 79 Ghosh, S.; Nguyen, T. N.; Thi, T. T. Mejia, E. Re-evaluation of the ring-opening polymerization of ε-caprolactone catalyzed by dialkylmagnesium reagents. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 112, 45–50.
- 80 Jensen, F. Introduction to computational chemistry, 3rd Ed., John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., Chichester, 2017, chapter 6, pp. 235–237.
- 81
Ikada, Y.; Tsuij, H. Biodegradable polyesters for medical and ecological applications. Macormol. Rapid Commun. 2000, 21, 117–132.
10.1002/(SICI)1521-3927(20000201)21:3<117::AID-MARC117>3.0.CO;2-X CAS Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 82 Li, X.; Zhang, W. Q.; Lin, W. J.; Qiu, H.; Qi, Y. L.; Ma, X.; Qi, H. P.; He, Y.; Zhang, H. J.; Qian, J.; Zhang, G.; Gao, R. L.; Zhang, D. Y.; Ding, J. D. Long-term efficacy of biodegradable metal−polymer composite stents after the first and the second implantations into porcine coronary arteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 15703–15715.
- 83 Liu, R. L.; Ding, J. D. Chromosomal repositioning and gene regulation of cells on a micropillar array. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 35799–35812.
- 84 Tsuji, H. Poly(lactide) stereocomplexes: Formation, structure, properties, degradation, and applications. Macromol. Biosci. 2005, 5, 569–597.
- 85 Simon, D.; Borreguero, A. M.; de Lucas, A.; Rodriguez, J. F. Recycling of polyurethanes from laboratory to industry, a journey towards the sustainability. Waste Manage. 2018, 76, 147–171.
- 86 Farah, S.; Anderson, D. G.; Langer, R. Physical and mechanical properties of PLA, and their functions in widespread applications-A comprehensive review. Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev. 2016, 107, 367–392.
- 87 Cui, S. Q.; Chen, L.; Yu, L.; Ding, J. D. Synergism among polydispersed amphiphilic block copolymers leading to spontaneous physical hydrogelation upon heating. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 7726–7739.
- 88 Wu, K. T.; Yu, L.; Ding, J. D. Synthesis of PCL−PEG−PCL triblock copolymer via organocatalytic Ring-Opening polymerization and its application as an injectable hydrogel — an interdisciplinary learning trial. J. Chem. Educ. 2020, 97, 4158–4165.
- 89 Penczek, S.; Biela, T.; Duda, A. Living polymerization with reversible chain transfer and reversible deactivation: The case of cyclic esters. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2000, 21, 941–950.
- 90 Cerrai, P.; Tricoli, M. Macromol. Block copolymers from L-lactide and poly(ethy1ene glycol) through a non-catalyzed route. Rapid Commun. 1993, 14, 529–538.
- 91 Muller, P. Pure and Applied Chemistry] Glossary of terms used in physical organic chemistry (IUPAC Recommendations 1994). Pure Appl. Chem. 1994, 66, 1077–1184.
- 92 Kowalski, A.; Duda, A.; Penczek, S. Kinetics and mechanism of cyclic esters polymerization initiated with Tin(II) octoate, 3. Polymerization of L,L-dilactide. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 7359–7370.
- 93 Ryner, M.; Stridsberg, K.; Albertsson, A. C. Mechanism of ring-opening polymerization of 1,5-dioxepan–2-one and l-lactid with stannous 2-ethylhexanoate. A theoretical study. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 3877–3881.
- 94 Miranda, M. O.; DePorre, Y.; Vazquez-Lima, H.; Johnson, A. M.; Marell, J. D.; Cramer, J. C.; Tolman, B. W. Understanding the mechanism of polymerization of epsilon-caprolactone catalyzed by aluminum salen complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 13692–13701.
- 95 Sattayanon, C.; Kungwan N.; Punyodom, W, Meepowpan, P.; Jungsuttiwong, S. Theoretical investigation on the mechanism and kinetics of the ring-opening polymerization of ε-caprolactone initiated by tin(II) alkoxides. J. Mol. Model. 2013, 19, 5377–5385.
- 96 Sattayanon, C.; Sontising, W.; Jitonnom, J.; Meepowpan, P.; Punyodom, W.; Kungwan, N. Theoretical study on the mechanism and kinetics of ring-opening polymerization of cyclic esters initiated by tin(II) n-butoxide. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2014, 1044, 29–35.
- 97 Sattayanon, C.; Sontising, W.; Limwanich, W.; Meepowpan, P.; Punyodom, W.; Kungwan, N. Effects of alkoxide alteration on the ring-opening polymerization of ε-caprolactone initiated by n-Bu3SnOR: A DFT study. Struct. Chem. 2015, 26, 695–703.
- 98 Marlier, E. E.; Macaranas, J. A.; Marell, D. J.; Dunbar, R. C.; Johnson, A. M.; DePorre, Y.; Miranda, O. M.; Neisen, D. B.; Cramer, J. C.; Hillmyer, A. M.; Tolman, B. W. Mechanistic studies of epsilon-caprolactone polymerization by (salen)AlOR complexes and a predictive model for cyclic ester polymerizations. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 1215–1224.
- 99 Li, P. J.; Xi, Y. X.; Li, L. F.; Li, H.; Sun, W. H.; Lei, M. A DFT study on ring-opening polymerization of epsilon-caprolactone initiated by Mg and Al complexes. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2018, 477, 34–39.
- 100 Curtin, D. Y.; Stereochemical control of organic reactions differences in behavior of diasteromers. Rec. Chem. Prog. 1954, 15, 111–128.
- 101 Hammett, L. P. Physical Organic Chemistry, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1970, Chapter 5.
- 102 Winstein, S.; Holness, N. J. Neighboring carbon and hydrogen. XIX. f-butylcyclohexyl derivatives. Quantitative conformational analysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1955, 77, 5562–5578.
- 103 Seeman, J. I. Effect of conformational change on reactivity in organic chemistry. Evaluations, applications, and extensions of Curtin- Hammett/Winstein-Holness kinetics. Chem. Rev. 1983, 83, 83–134.
- 104 Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D. G. The M06 suite of density functionals for main group thermochemistry, thermochemical kinetics, noncovalent interactions, excited states, and transition elements: two new functionals and systematic testing of four M06-class functionals and 12 other functionals, Theor. Chem. Account 2008, 120, 215–241.
- 105 Grimme, S.; Antony, J.; Ehrlich, S.; Krieg, H. A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 154104.
- 106 Goerigk, L.; Grimme, S. A thorough benchmark of density functional methods for general main group thermochemistry, kinetics, and noncovalent interactions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 6670–6688.
- 107 Dunning, T. H.; Hay, P. J. Modern Theoretical Chemistry, Plenum, New York, 1976, Vol. 3, pp. 1–28.
- 108 Bergner, A.; Dolg, M.; Küchle, W.; Stoll, H.; Preuß, H. Ab initio energy- adjusted pseudopotentials for elements of groups 13–17. Mol. Phys. 1993, 80, 1431–1441.
- 109 Weigend, F.; Ahlrichs, R. Balanced basis sets of split valence, triple zeta valence and quadruple zeta valence quality for H to Rn: Design and assessment of accuracy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2005, 7, 3297–3305.
- 110Frisch, M. J.; Trucks, G. W.; Schlegel, H. B.; Scuseria, G. E.; Robb, M. A.; Cheeseman, J. R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G. A.; Nakatsuji, H.; Caricato, M.; Li, X.; Hratchian, H. P.; Izmaylov, A. F.; Bloino, J.; Zheng, G.; Sonnenberg, J. L.; Hada, M; Ehara, M.; Toyota, K.; Fukuda, R.; Hasegawa, J.; Ishida, M.; Nakajima, T.; Honda, Y.; Kitao, O.; Nakai, H.; Vreven, T.; Montgometry, J. A. Jr.; Peralta, J. E.; Ogliaro, F.; Bearpark, M.; Heyd, J. J.; Brothers, E.; Kudin, K. N.; Staroverov, V. N.; Kobayashi, R.; Normand, J.; Raghavachari, K.; Rendell, A.; Burant, J. C.; Iyengar, S. S.; Tomasi, J.; Cossi, M.; Rega, N.; Millam, J. M.; Klene, M.; Knox, J. E.; Cross, J. B.; Bakken, V.; Adamo, C.; Jaramillo, J.; Gomperts, R.; Stratmann, R. E.; Yazyev, O.; Austin, A. J.; Cammi, R.; Pomelli, C.; Ochterski, J. W.; Martin, R. L.; Morokuma, K.; Zakrzewski, V. G.; Voth, G. A.; Salvador, P.; Dannenberg, J. J.; Dapprich, S.; Daniels, A. D.; Farkas, Ö.; Foresman, J. B.; Ortiz, J. V.; Cioslowski, J.; Fox, D. J. Gaussian 09, Revision D.01, Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford CT, 2016.
- 111 Hay, P. J.; Wadt, W. R. Ab initio Effective core potentials for molecular calculations. Potentials for the transition-metal atoms Sc to Hg. J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 82, 270–283.
- 112 Wadt, W. R.; Hay, P. J. Ab initio effective core potentials for molecular calculations. Potentials for main group elements Na to Bi. J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 82, 284–298.
- 113 Hay, P. J.; Wadt, W. R. Ab initio effective core potentials for molecular calculations. Potentials for K to Au including the outermost core orbitals. J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 82, 299–310.




