Design, Synthesis, and Bioactivity of Eighteen Novel 2H-1,4-Benzoxazin-3(4H)-one Containing a Propanolamine Moiety
Jia-Rui Rao
Guizhou Tea Research Institute, Guizhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Guiyang, 550006 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yu-Feng Zhou
Guizhou Tea Research Institute, Guizhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Guiyang, 550006 China
Search for more papers by this authorXin Zhang
Institute of Biotechnology, Guizhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Guiyang, 550006 China
Search for more papers by this authorXing-Li Zhao
Institute of Biotechnology, Guizhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Guiyang, 550006 China
Search for more papers by this authorJia-Rui Rao
Guizhou Tea Research Institute, Guizhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Guiyang, 550006 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yu-Feng Zhou
Guizhou Tea Research Institute, Guizhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Guiyang, 550006 China
Search for more papers by this authorXin Zhang
Institute of Biotechnology, Guizhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Guiyang, 550006 China
Search for more papers by this authorXing-Li Zhao
Institute of Biotechnology, Guizhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Guiyang, 550006 China
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
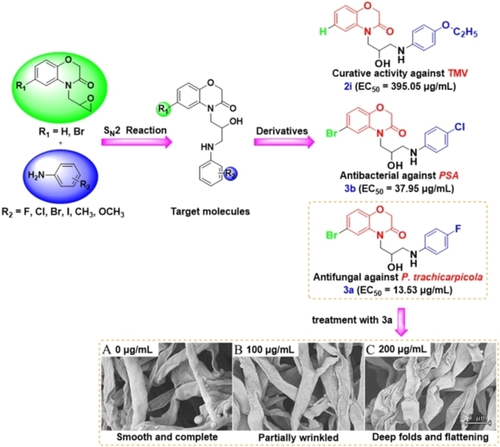
To develop a novel skeleton for broad-spectrum pesticides with high-efficiency against tea tree diseases, a series of aniline 2H-1,4-benzoxazin-3(4H)-one derivatives containing a propanolamine structure was synthesized and confirmed by 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, 19F-NMR, HRMS, and single-crystal diffraction analysis. Bioactivities were evaluated against tobacco mosaic virus (TMV, the model virus), three kinds of bacteria, and five typical plant fungi. Bioassay results showed that compound 2i (EC50=395.05 μg/mL) had the best curative activity against TMV, 3d (EC50=45.70 μg/mL) had the best inhibitory activity against Pseudomonas syringae pv. Actinidiae, and 3a (EC50=13.53 μg/mL) had the best inhibitory activity against Pestalotiopsis trachicarpicola. Scanning electron microscope morphological observation of P. trachicarpicola treated with 0, 100, and 200 μg/mL 3a revealed dried, flattened and folded outer walls of the hyphae at higher concentrations, leading to inhibition of fungal growth. The broad-spectrum bioactivities (against viruses, bacteria and fungi) of this series of target compounds indicate that these 2H-1,4-benzoxazin-3(4H)-one derivatives containing a propanolamine moiety are potential skeletons for developing pesticides with wide-ranging activities against various tea tree diseases.
Graphical Abstract
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cbdv202200567-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf6.4 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1J. R. Rao, Z. W. Lei, Y. F. Zhou, ‘Bioactivity of 10 natural products against tea grey blight’, Guizhou Agriculture Sciences 2021, 49, 49–55.
- 2Y. H. Cheng, X. Z. Huang, J. F. Zhang, Z.H . Meng, S. J. Lu, S. Li, S. Q. Liu, Y. F. Zhou, ‘Phylogenetic analysis and biological characteristics of tea leaf spot disease in guizhou’, Mol. Plant Breed. 2022, 19, 1–21.
- 3L. Zhang, X. Wang, X. H. Li, C. Y. Gong, L. X. Zhang, ‘Identification of the pathogen Acidovorax avenae subsp. avenae causing shoot blight of Camellia sinensis’, Plant Protection 2021, 47, 143–147.
- 4X. Y. Hao, W. F. Zhang, F. M. Zhao, Y. Liu, W. J. Qian, Y. C. Wang, L. Wang, J. M. Zeng, Y. J. Yang, X. C. Wang, ‘Discovery of plant viruses from tea plant (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) by metagenomic sequencing’, Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2175–2190.
- 5X. Q. Yu, X. Y. Zhu, Y. Zhou, Q. L. Li, Z. Hu, T. Li, J. Tao, M. L. Dou, M. Zhang, Y. Shao, R. F. Sun, ‘Discovery of n-aryl-pyridine-4-ones as novel potential agrochemical fungicides and bactericides’, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13904–13913.
- 6Y. Y. Wang, F. Z. Xu, D. X. Luo, S. X. Guo, F. He, A. Dai, B. A. Song, J. Wu, ‘Synthesis of anthranilic diamide derivatives containing moieties of trifluoromethyl pyridine and hydrazone as potential anti-viral agents for plants’, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13344–13352.
- 7C. C. Yu, D. Y. Hao, Q. Chu, T. Wang, S. N. Liu, T. Lan, F. H. Wang, C. P. Pan, ‘A one adsorbent QuEChERS method coupled with LC/MS/MS for simultane- ous determination of 10 organophosphorus pesticide residues in tea’, Food Chem. 2020, 321, 126657–126687.
- 8Y. S. Huang, T. Shi, X. Luo, H. L. Xiong, F. Fang, ‘Determination of multi-pesticide residues in green tea with a modified QuEChERS protocol coupled to HPLC/MS/MS’, Food Chem. 2019, 275, 255–264.
- 9L. L. Huang, S. Ahmed, Y. F. Gu, J. H. Huang, B. Y. An, C. R. Wu, Y. J. Zhou, G. Y. Cheng, ‘The effects of natural products and environmental conditions on antimicrobial resistance’, Molecules 2021, 26, 4277–4295.
- 10M. Śmist, H. Kwiecień, M. Krawczyk, ‘Synthesis and antifungal activity of 2H-1,4-benzoxazin-3(4H)-one derivatives’, J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2016, 51, 393–401.
- 11L. Zamani, S. Khabnadideh, K. Zomorodian, A. Sakhteman, A. Gholami, Z. Rezaei, A. Mehdipoor, M. E. Dehkordi, R. Mortazavi, S. Ghafari, ‘Docking, synthesis, antifungal and cytotoxic activities of some novel substituted 4H-benzoxazin-3-one’, Polycyclic Aromat. Compd. 2019, 41, 347–352.
- 12J. C. Wouter, D. Bruijn, H. Gruppen, J. P. Vincken, ‘Structure and biosynthesis of benzoxazinoids: plant defence metabolites with potential as antimicrobial scaffolds’, Phytochemistry 2018, 155, 233–243.
- 13R. Bollu, S. Banu, R. Bantu, A. G. Reddy, L. Nagarapu, K. Sirisha, C. G. Kumar, S. K. Gunda, K. Shaik, ‘Potential antimicrobial agents from triazole-functionalized 2H-benzo[b][1,4]oxazin-3(4H)-ones’, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 5158–5162.
- 14W. J. C. Bruijn, J. A. Hageman, C. Araya-Cloutier, H. Gruppen, J. P. Vincken, ‘QSAR of 1,4-benzoxazin-3-one antimicrobials and their drug design perspectives’, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 6105–6114.
- 15M. E. D. L. Calle, G. Cabrera, D. Cantero, A. Valle, J. Bolivar, ‘A genetically engineered escherichia coli strain overexpressing the nitroreductase NfsB is capable of producing the herbicide D-DIBOA with 100 % molar yield’, Microb. Cell Fact. 2019, 86, 4571–4588.
- 16M. R. Freitas, S. V. Matias, R. L. G. Macedo, M. P. D. Freitas, N. Venturin, ‘Aug-MIA-QSAR modeling of the phytotoxicities of benzoxazinone herbicides and related compounds on problematic weeds’, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 8499–8503.
- 17A. Nagaraju, S. K. Nukala, T. N. S. Thirukovela, R. Manchal, ‘In vitro anticancer and in silico studies of some 1,4-benzoxazine-1,2,4-oxadiazole hybrids’, ChemistrySelect 2021, 6, 3318–3321.
- 18V. R. Nagavelli, S. K. Nukala, S. Narsimha, K. S. Battula, S. J. Tangeda, Y. N. Reddy, ‘Synthesis, characterization and biological evaluation of 7-substituted4-((1-aryl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl) methyl)-2H-benzo[b][1,4]oxazin3(4H)-ones as anticancer agents’, Med. Chem. Res. 2016, 25, 1781–1793.
- 19A. R. Gangloff, J. Brown, R. D. Jong, D. R. Dougan, C. E. Grimshaw, M Hixon, A. Jennings, R. Kamran, A. Kiryanov, S. O. Connell, ‘Discovery of novel benzo[b][1,4]oxazin-3(4H)-ones as poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase inhibitors’, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 4501–4505.
- 20C. Rajitha, P. K. Dubey, V. Sunku, F. J. Piedrafita, V. R. Veeramaneni, ‘Synthesis and pharmacological evaluations of novel 2H-benzo[b][1,4]oxazin-3(4H)-one derivatives as a new class of anti-cancer agents’, Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 4887–4896.
- 21O. Hiromasa, Y. Koichi, K. Akio, I. Kazuhiro, A. Norio, S. Shohei, M. Satoshi, W. Toshihiro, K. Tetsuo, T. Yukihiro, ‘Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel biphenyl-4-carboxamide derivatives as orally available TRPV1 antagonists’, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 3716–3726.
- 22M. Gleńsk, B. Gajda, R. Franiczek, B. Krzyżanowska, M. Włodarczyk, ‘In vitro evaluation of the antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of DIMBOA [2,4-dihydroxy-7- methoxy-2H-1,4-benzoxazin-3(4H)-one]’, Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 30, 1305–1308.
- 23S. Xia, J. Q. Liu, X. H. Wang, Y. Tian, Y. Wang, J. H. Wang, L. Fang, H. Zuo, ‘The synthesis of 4,7-disubstituted-2H-benzo[b][1,4]-oxazin-3(4H)-ones using Smiles rearrangement and their in vitro evaluation as platelet aggregation inhibitors’, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 1479–1483.
- 24J. R. C. Reddy, B. V. S. K. Rao, M. S. L. Karuna, K. P. Kumar, U. S. N. Murthy, R. B. N. Prasad, ‘Chemo-enzymatic synthesis and antimicrobial evaluation of alkyloxy propanol amine-based cationic ether lipids’, J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2013, 90, 437–448.
- 25Y. L. Zhao, X. Huang, L. W. Liu, P. Y. Wang, Q. S. Long, ‘Identification of racemic and chiral carbazole derivatives containing an isopropanolamine linker as prospective surrogates against plant pathogenic bacteria: in vitro and in vivo assays and quantitative proteomics’, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 7512–7525.
- 26M. Xiang, T. R. Zhou, P. Y. Wang, L. W. Liu, L. Wei, S. Yang, ‘Design, synthesis, antibacterial evaluation, and induced apoptotic behaviors of epimeric and chiral 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid ester derivatives with an isopropanolamine bridge against phytopathogens’, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13212–13220.
- 27C. Bonini, L. Chiummiento, N. D. Blasio, M. Funicello, P. Lupattelli, F. Tramutola, F. Berti, A. Ostric, S. Miertus, V. Frecer, ‘Synthesis and biological evaluation of new simple indolic non peptidic HIV Protease inhibitors: The effect of different substitution patterns’, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 4792–4802.
- 28J. C. Chen, T. Y. Wang, S. T. Xu, A. J. Lin, H. Q. Yao, W. J. Xie, Z. Y. Zhu, J. Y. Xu, ‘Novel hybrids of natural β-elemene bearing isopropanolamine moieties: Synthesis, enhanced anticancer profile, and improved aqueous solubility’, Fitoterapia 2017, 5, 117–125.
- 29R. Bai, X. Huang, X. Yang, W. Hong, Y. Tang, H. Yao, J. Jiang, J. Liu, M. Shen, X. Wu, ‘Novel hybrids of natural isochroman-4-one bearing N-substituted isopropanolamine as potential antihypertensive candidates’, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 2495–2502.
- 30J. R. Rao, L. W. Liu, D. Zeng, M. W. Wang, M. Xiang, S. Yang, ‘Antibiotic activities of propanolamine containing 1,4-benzoxazin-3-ones against phytopathogenic bacteria’, RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 682–688.
- 31X. Zhang, S. J. Lu, Y. H. Cheng, K. Y. Wang, F. J. Zhang, Y. F. Zhou, ‘Pathogen identification of tea gray blight’, Guizhou Agricultural Sciences 2020, 48, 62–68.
- 32L. Zhang, X. Zhao, J. Zhang, L. Shuai, Z. Meng, Y. Zhou, ‘Isolation and identification of colletotrichum camelliae pathogen’, Guizhou Agricultural Sciences 2018, 46, 36–39.
- 33H. L. Zheng, J. Q. Kuang, H. Zhang, X. Niu, Z. B. Wu, ‘Design, synthesis, and bioassay of novel 1-(3-CHloropyridin2-yl)-5-amino-4-pyrazole derivatives containing a 1,3,4-thiadiazole thioether or sulfone moiety’, J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2022, 59, 943–951.
- 34X. Tang, S. J. Su, M. Chen, J. He, R. J. Xia, T. Guo, Y. Chen, C. Zhang, J. Wang, W. Xue, ‘Novel chalcone derivatives containing a 1,2,4- triazine moiety: design, synthesis, antibacterial and antiviral activities’, RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 6011–6020.
- 35P. Y. Qi, T. H. Zhang, Y. M. Feng, M. W. Wang, W. B. Shao, D. Zeng, L. H. Jin, P. Y. Wang, X. Zhou, S. Yang, ‘Exploring an Innovative Strategy for Suppressing Bacterial Plant Disease: Excavated Novel Isopropanolamine-Tailored Pterostilbene Derivatives as Potential Antibiofilm Agents’, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 4899–4911.
- 36X. Niu, H. Zhang, C. Z. Zhang, L. Dou, Z. B. Wu, ‘Design, Synthesis and in vitro Antifungal Mechanism of Novel Phenylalanine Derivatives’, Chem. Biodiversity 2022, 19, 1–11.
- 37M. W. Wang, H. H. Zhu, P. Y. Wang, D. Zeng, Y. Y. Wu, L. W. Liu, Z. B. Wu, Z. Li, S. Yang, ‘Synthesis of thiazolium-labeled 1,3,4-oxadiazole thioethers as prospective antimicrobials: in vitro and in vivo bioactivity and mechanism of action’, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 12696–12708.