Total Bioactive Contents, Metabolic Profiling, Docking Studies, Antioxidant and Enzyme Inhibition Activities of Convolvulus Arvensis L. and Multivariate Analysis to Unravel a Potential Herb as Natural Resource for Pharmaceutical Industry
Corresponding Author
Muhammad Imran Tousif
Department of Chemistry, Division of Science and Technology, University of Education, 54000 Lahore, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorMamona Nazir
Department of Chemistry, Government Sadiq Women College University, Bahawalpur, 63100-Bahawalpur Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorMuhammad Saleem
Division of Organic Chemistry, Institute of Chemistry, Baghdad-ul-Jadeed Campus, The Islamia University of Bahawalpur, 63100- Bahawalpur, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorSaba Tauseef
Dr. Panjwani Center for Molecular Medicine and Drug Research., International Center for Chemical and Biological Sciences, University of Karachi, 75270 Karachi, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorReaz Uddin
Dr. Panjwani Center for Molecular Medicine and Drug Research., International Center for Chemical and Biological Sciences, University of Karachi, 75270 Karachi, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Gokhan Zengin
Department of Biology, Science Faculty, Selcuk University, 42130 Konya, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorMohamad Fawzi Mahomoodally
Department of Health Sciences, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Mauritius, Réduit, 80837 Mauritius
Center for Transdisciplinary Research, Department of Pharmacology, Saveetha Dental College, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Science, Chennai, 600077 India
Center of Excellence for Pharmaceutical Sciences, North-West University, Private Bag X6001, Potchefstroom, 2520 South Africa
Search for more papers by this authorZaheer Abbas
Department of Botany, Division of Science and Technology, University of Education, 54000 Lahore, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Muhammad Imran Tousif
Department of Chemistry, Division of Science and Technology, University of Education, 54000 Lahore, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorMamona Nazir
Department of Chemistry, Government Sadiq Women College University, Bahawalpur, 63100-Bahawalpur Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorMuhammad Saleem
Division of Organic Chemistry, Institute of Chemistry, Baghdad-ul-Jadeed Campus, The Islamia University of Bahawalpur, 63100- Bahawalpur, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorSaba Tauseef
Dr. Panjwani Center for Molecular Medicine and Drug Research., International Center for Chemical and Biological Sciences, University of Karachi, 75270 Karachi, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorReaz Uddin
Dr. Panjwani Center for Molecular Medicine and Drug Research., International Center for Chemical and Biological Sciences, University of Karachi, 75270 Karachi, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Gokhan Zengin
Department of Biology, Science Faculty, Selcuk University, 42130 Konya, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorMohamad Fawzi Mahomoodally
Department of Health Sciences, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Mauritius, Réduit, 80837 Mauritius
Center for Transdisciplinary Research, Department of Pharmacology, Saveetha Dental College, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Science, Chennai, 600077 India
Center of Excellence for Pharmaceutical Sciences, North-West University, Private Bag X6001, Potchefstroom, 2520 South Africa
Search for more papers by this authorZaheer Abbas
Department of Botany, Division of Science and Technology, University of Education, 54000 Lahore, Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
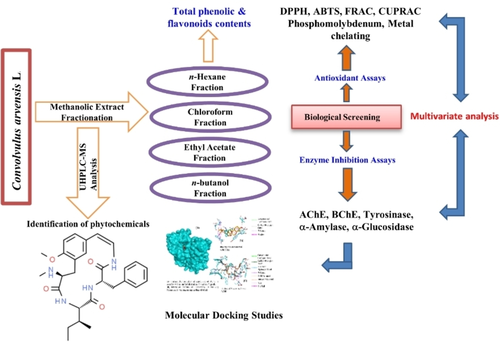
Convolvulus arvensis L. is an evergreen herb growing in various regions of Pakistan. Despite of several medicinal properties associated to this herb, it was not investigated scientifically for its bioactive compounds and detailed pharmaceutical properties. Therefore, its methanolic extract was divided into hexane (CA−H), chloroform (CA−C), ethyl acetate (CA−E) and butanol (CA−B) soluble fractions. CA−H and CA−C were found rich in phenolics (30.73±0.63 and 20.15±0.59 mg GAE/g of the extract, respectively), and the same fractions exhibited significant antioxidant activities (DPPH: 5.23±0.11 & 12.34±0.17 mg TE/g extract, respectively; ABTS: 36.82±0.04 & 56.74±0.61 mg TE/g extract, respectively). Also in CUPRAC activity assay, CA−H and CA−C exhibited highest activities as 87.30±0.46 and 56.74±0.61 mg TE/g extract, respectively, while CA−C was most active in FRAP activity assay with value of 40.21±2.19 mg TE/g extract. Total antioxidant capacity (1.23±0.033 mmol TE/g extract) was also found higher for CA−C, while CA−H activity was also comparable, however, CA−H showed higher metal chelating activity (22.74±0.001 mg EDTAE/g extract) than that of CA−C (17.55±0.22 mg EDTAE/g extract). These activities clearly revealed a direct relation between antioxidant potential and phenolic contents of CA−H and CA−C. In AChE and BChE inhibitory assay, CA−H and CA−E showed better inhibition (AChE: 8.24±0.77 & 4.46±0.007 mg GALAE/g extract; BChE: 5.40±0.02 & 1.92±0.24 mg GALAE/g extract) as compared to other fractions, whereas, against tyrosinase, CA−B was most active (37.35±0.53 mg KAE/g extract). CA−H and CA−C also showed higher inhibitory potential (0.98±0.08 & 0.58±0.01 mmol ACAE/g extract) against α-Amylase; while against α-Glucosidase, CA−E was the most active fraction. UHPLC/MS analysis of the methanolic extract of C. arvensis disclosed the presence of 62 compounds as sterols, triterpenes, flavonoids, fatty acids, alkaloids and coumarins. In Multivariate Analysis, the total phenolic contents were correlated strongly with all antioxidant assays except FRAP and DPPH. Regarding enzyme inhibitory properties, only AChE, BChE and α-amylase were correlated with the total phenolic contents in the extracts. Docking analyses confirmed these findings, as identified compounds had high binding free energy and inhibition constants with the enzymes studied. It was finally concluded that C. arvensis is a potential industrial crop, which can be a component of nutraceuticals and functional foods, if evaluated for its toxicity.
Graphical Abstract
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
- 1S. Mathur, C. Hoskins, ‘Drug development: Lessons from nature’, Biomed. Rep. 2017, 6, 612–614.
- 2C. Veeresham, ‘Natural products derived from plants as a source of drugs’, J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2012, 3, 200.
- 3M.-A. Shibata, I. A. Khan, M. Iinuma, T. Shirai, Vol. 2012, Hindawi, 2012.
- 4T. Beddes, M. Caron, J. Barnhill, K. Kopp, ‘Suppression and Control of Field Bindweed-(Perennial Morning Glory) in Residential Areas’, 2017.
- 5H. Iqbal, Z. Sher, Z. U. Khan, ‘Medicinal plants from salt range pind dadan khan, district jhelum, punjab, pakistan’, J. Med. Plant Res. 2011, 5, 2157–2168.
- 6D. F. Austin, ‘Bindweed (Convolvulus arvensis, Convolvulaceae) in North America, from medicine to menace’, J. Torrey Bot. Soc. 2000, 127, 172–177.
- 7M. Ali, M. I. Qadir, M. Saleem, K. H. Janbaz, H. Gul, L. Hussain, B. Ahmad, ‘Hepatoprotective potential of Convolvulus arvensis against paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity’, Bangladesh J. Pharmacol. 2013, 8, 300–304.
- 8M. L. Leporatti, S. Ivancheva, ‘Preliminary comparative analysis of medicinal plants used in the traditional medicine of Bulgaria and Italy’, J. Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 87, 123–142.
- 9N. Ahmed, A. Mahmood, A. Mahmood, S. Tahir, A. Bano, R. N. Malik, S. Hassan, M. Ishtiaq, ‘Relative importance of indigenous medicinal plants from Layyah district, Punjab Province, Pakistan’, J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 509–523.
- 10M. U. Khan, M. Q. Hayat, ‘Phytochemical analyses for antibacterial activity and therapeutic compounds of Convolvulus arvensis L., collected from the salt range of Pakistan’, Adv. Life Sci. 2015, 2, 83–90.
- 11S. Edrah, E. Osela, A. Kumar, ‘Preliminary phytochemical and antibacterial studies of Convolvulus arvensis and Thymus capitatus plants extracts’, RJPP. 2013, 5, 220–223.
- 12U. Saleem, S. Zaib, S. Khalid, F. Anwar, M. F. Akhtar, B. Ahmad, ‘Chemical characterization, docking studies, anti-arthritic activity and acute oral toxicity of Convolvulus arvensis L. leaves’, Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2020, 10, 442.
- 13S. Khan, M. Nazir, H. Saleem, N. Raiz, M. Saleem, S. M. M. Anjum, G. Zengin, M. Mukhtar, M. I. Tousif, F. M. Mahomoodally, ‘Valorization of the antioxidant, enzyme inhibition and phytochemical propensities of Berberis calliobotrys Bien. ex Koehne: a multifunctional approach to probe for bioactive natural products’, Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 141, 111693.
- 14M. Saleem, N. Shazmeen, M. Nazir, N. Riaz, G. Zengin, H. M. Ataullah, F. Nisar, M. Mukhtar, M. I. Tousif, ‘Investigation on the Phytochemical Composition, Antioxidant and Enzyme Inhibition Potential of Polygonum Plebeium R. Br: A Comprehensive Approach to Disclose New Nutraceutical and Functional Food Ingredients’, Chem. Biodivers. 2021, 18, e2100706.
- 15D. M. Grochowski, S. Uysal, G. Zengin, M. Tomczyk, ‘In vitro antioxidant and enzyme inhibitory properties of Rubus caesius L’, Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2019, 29, 237–245.
- 16M. Zubair, M. Nazir, M. Saleem, N. Raiz, S. Touseef, G. Zengin„ S. Khan, M. E. Mazhar, M. I. Tousif„ ‘Chemodiversity, biological activities and molecular docking studies of Leptadenia pyrotechnica (Forssk.) Decne: A comprehensive approach to validate its medicinal use’, Chem. Biodivers 2022, 19, e202100884..
- 17S. Kim, J. Chen, T. Cheng, A. Gindulyte, J. He, S. He, Q. Li, B. A. Shoemaker, P. A. Thiessen, B. Yu, ‘PubChem 2019 update: improved access to chemical data’, Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D1102–D1109.
- 18N. Mills, ChemDraw Ultra 10.0 CambridgeSoft, 100 CambridgePark Drive, Cambridge, MA 02140. www.cambridgesoft.com. Commercial Price: $1910 for download, $2150 for CD-ROM; Academic Price: $710 for download, $800 for CD-ROM. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 13649-13650 .
- 19J. L. Sussman, D. Lin, J. Jiang, N. O. Manning, J. Prilusky, O. Ritter, E. E. Abola, ‘Protein Data Bank (PDB): database of three-dimensional structural information of biological macromolecules’, Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 1998, 54, 1078–1084.
- 20S. M. D. Rizvi, S. Shakil, M. J. E. J. Haneef, ‘A simple click by click protocol to perform docking: AutoDock 4.2 made easy for non-bioinformaticians’, 2013, 12, 831.
- 21S. Khan, M. Nazir, N. Raiz, M. Saleem, G. Zengin, G. Fazal, H. Saleem, M. Mukhtar, M. I. Tousif, R. B. Tareen, ‘Phytochemical profiling, in vitro biological properties and in silico studies on Caragana ambigua stocks (Fabaceae): A comprehensive approach’, Ind. Crops and Prod. 2019, 131, 117–124.
- 22N. Phuyal, P. K. Jha, P. P. Raturi, S. Rajbhandary, ‘Total phenolic, flavonoid contents, and antioxidant activities of fruit, seed, and bark extracts of Zanthoxylum armatum DC’, Sci. World J. 2020, 2020.
10.1155/2020/8780704 Google Scholar
- 23B. Salehi, B. Krochmal-Marczak, D. Skiba, J. K. Patra, S. K. Das, G. Das, J. B. Popović-Djordjević, A. Ž Kostić, N. V. Anil Kumar, A. Tripathi, ‘Convolvulus plant–A comprehensive review from phytochemical composition to pharmacy’, Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 315–328.
- 24A. Kumari, A. K. Parida, J. Rangani, A. Panda, ‘Antioxidant activities, metabolic profiling, proximate analysis, mineral nutrient composition of Salvadora persica fruit unravel a potential functional food and a natural source of pharmaceuticals’, Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 61.
- 25G. Llauradó Maury, D. Méndez Rodríguez, S. Hendrix, J. C. Escalona Arranz, Y. Fung Boix, A. O. Pacheco, J. García Díaz, H. J. Morris-Quevedo, A. Ferrer Dubois, E. I. Aleman, ‘Antioxidants in plants: A valorization potential emphasizing the need for the conservation of plant biodiversity in Cuba’, Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1048.
- 26L. Cassidy, F. Fernandez, J. B. Johnson, M. Naiker, A. G. Owoola, D. A. Broszczak, ‘Oxidative stress in Alzheimer's disease: A review on emergent natural polyphenolic therapeutics’, Complement. Ther. Med. 2020, 49, 102294.
- 27V. Sindhi, V. Gupta, K. Sharma, S. Bhatnagar, R. Kumari, N. Dhaka, ‘Potential applications of antioxidants–A review’, J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 7, 828–835.
- 28R. Singh, S. Sharma, P. Singh, ‘Antioxidants: Their Health Benefits and Plant Sources’, Phytochemicals of Nutraceutical Importance 2014, 248. .
10.1079/9781780643632.0248 Google Scholar
- 29M. S. Swallah, H. Sun, R. Affoh, H. Fu, H. Yu, ‘Antioxidant potential overviews of secondary metabolites (polyphenols) in fruits’, Int. J. Food Sci. 2020, 2020.
- 30J. O. Unuofin, S. L. Lebelo, ‘Antioxidant effects and mechanisms of medicinal plants and their bioactive compounds for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes: an updated review’, Oxid. Met. 2020, 2020.
- 31C. Castro-López, J. M. Ventura-Sobrevilla, M. D. González-Hernández, R. Rojas, J. A. Ascacio-Valdés, C. N. Aguilar, G. C. Martínez-Ávila, ‘Impact of extraction techniques on antioxidant capacities and phytochemical composition of polyphenol-rich extracts’, Food Chem. 2017, 237, 1139–1148.
- 32H.-X. Zhao, H.-S. Zhang, S.-F. Yang, ‘Phenolic compounds and its antioxidant activities in ethanolic extracts from seven cultivars of Chinese jujube’, Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2014, 3, 183–190.
10.1016/j.fshw.2014.12.005 Google Scholar
- 33K. Güçlü, M. Özyürek, S. E. K. Çelik, E. Erçağ, ‘The cupric ion reducing antioxidant capacity (CUPRAC) and polyphenolic content of some herbal teas’.
- 34R. Apak, K. Güçlü, M. Özyürek, S. Esin Karademir, E. Erçağ, ‘The cupric ion reducing antioxidant capacity and polyphenolic content of some herbal teas’, Int. J. Food Sci. 2006, 57, 292–304.
- 35R. Diwan, A. Shinde, N. Malpathak, ‘Phytochemical composition and antioxidant potential of Ruta graveolens L. in vitro culture lines’, J. Bot. 2012, 2012.
- 36V. M. Nurchi, R. Cappai, G. Crisponi, G. Sanna, G. Alberti, R. Biesuz, S. Gama, ‘Chelating agents in soil remediation: A new method for a pragmatic choice of the right chelator’, Front. Chem. 2020, 991.
- 37İ. Gulcin, S. H. Alwasel, ‘Metal Ions, Metal Chelators and Metal Chelating Assay as Antioxidant Method’, Processes 2022, 10, 132.
- 38S. Adusei, J. K. Otchere, P. Oteng, R. Q. Mensah, E. Tei-Mensah, ‘Phytochemical analysis, antioxidant and metal chelating capacity of Tetrapleura tetraptera’, Heliyon 2019, 5, e02762.
- 39S. Ahmed, S. T. Khan, M. K. Zargaham, A. U. Khan, S. Khan, A. Hussain, J. Uddin, A. Khan, A. Al-Harrasi, ‘Potential therapeutic natural products against Alzheimer's disease with Reference of Acetylcholinesterase’, Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 139, 111609.
- 40P. Taslimi, C. Caglayan, İ. Gulcin, ‘The impact of some natural phenolic compounds on carbonic anhydrase, acetylcholinesterase, butyrylcholinesterase, and α-glycosidase enzymes: An antidiabetic, anticholinergic, and antiepileptic study’, J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2017, 31, e21995.
- 41P. Upadhyaya, V. Seth, M. Ahmad, ‘Therapy of Alzheimers disease: an update’, Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. y 2010, 4, 408–421.
- 42B. McGleenon, K. Dynan, A. Passmore, ‘Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors in Alzheimer's disease’, Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1999, 48, 471.
- 43T. T. Bui, T. H. Nguyen, ‘Natural product for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease’, J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 28, 413–423.
- 44M. J. R. Howes, N. S. Perry, P. J. Houghton, ‘Plants with traditional uses and activities, relevant to the management of Alzheimer's disease and other cognitive disorders’, Phytother. Res.: An International Journal Devoted to Pharmacological and Toxicological Evaluation of Natural Product Derivatives 2003, 17, 1–18.
- 45S. Zolghadri, A. Bahrami, M. T. Hassan Khan, J. Munoz-Munoz, F. Garcia-Molina, F. Garcia-Canovas, A. A. Saboury, ‘A comprehensive review on tyrosinase inhibitors’, J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 279–309.
- 46M. N. Masum, K. Yamauchi, T. Mitsunaga, ‘Tyrosinase inhibitors from natural and synthetic sources as skin-lightening agents’, Rev. Agric. Sci. 2019, 7, 41–58.
10.7831/ras.7.41 Google Scholar
- 47A. Di Petrillo, A. M. González-Paramás, B. Era, R. Medda, F. Pintus, C. Santos-Buelga, A. Fais, ‘Tyrosinase inhibition and antioxidant properties of Asphodelus microcarpus extracts’, BMC complement. med. ther. 2016, 16, 1–9.
- 48L. Ali, S. Khan, M. Nazir, N. Raiz, S. Naz, G. Zengin, M. Mukhtar, S. Parveen, N. Shazmeen, M. Saleem, ‘Chemical profiling, in vitro biological activities and Pearson correlation between phenolic contents and antioxidant activities of Caragana brachyantha Rech. f’, S. Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 140, 189–193.
- 49H. B. B. Ag, ‘Pharmacology of α-glucosidase inhibition’, Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 1994, 24, 3–10.
- 50A. Bhatia, B. Singh, R. Arora, S. Arora, ‘In vitro evaluation of the α-glucosidase inhibitory potential of methanolic extracts of traditionally used antidiabetic plants’, BMC complement. med. ther. 2019, 19, 1–9.
- 51C. Lankatillake, S. Luo, M. Flavel, G. B. Lenon, H. Gill, T. Huynh, D. A. Dias, ‘Screening natural product extracts for potential enzyme inhibitors: protocols, and the standardisation of the usage of blanks in α-amylase, α-glucosidase and lipase assays’, Plant Methods 2021, 17, 1–19.
- 52A. Ota, N. P. Ulrih, ‘An overview of herbal products and secondary metabolites used for management of type two diabetes’, Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 436.
- 53W. Jia, W. Gao, L. Tang, ‘Antidiabetic herbal drugs officially approved in China’, Phytother. Res.: An International Journal Devoted to Pharmacological and Toxicological Evaluation of Natural Product Derivatives 2003, 17, 1127–1134.
- 54F. Salimi, M. Fattahi, J. Hamzei, ‘Phenolic contents, composition and antioxidant activity of essential oils obtained from Iranian populations of Apium graveolens, and their canonical correlation with environmental factors’, Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2022, 101, 104394.
- 55G. T. Vo, Z. Liu, O. Chou, B. Zhong, C. J. Barrow, F. R. Dunshea, H. A. Suleria, ‘Screening of phenolic compounds in australian grown grapes and their potential antioxidant activities’, Food Biosci. 2022, 47, 101644.
- 56J. Yang, X. Wang, C. Zhang, L. Ma, T. Wei, Y. Zhao, X. Peng, ‘Comparative study of inhibition mechanisms of structurally different flavonoid compounds on α-glucosidase and synergistic effect with acarbose’, Food Chem. 2021, 347, 129056.
- 57U. Hossain, A. K. Das, S. Ghosh, P. C. Sil, ‘An overview on the role of bioactive α-glucosidase inhibitors in ameliorating diabetic complications’, Food and chem. toxicol. 2020, 145, 111738.
- 58M. J. Balunas, A. D. Kinghorn, ‘Drug discovery from medicinal plants’, Life Sci. 2005, 78, 431–441.
- 59G. Sliwoski, S. Kothiwale, J. Meiler, E. W. Lowe, ‘Computational methods in drug discovery’, Pharmacol. Rev. 2014, 66, 334–395.
- 60J. Fan, A. Fu, L. Zhang, ‘Progress in molecular docking’, Quant. Biol. 2019, 7, 83–89.
- 61D. J. A. Studio, ‘Discovery Studio’, 2008.
- 62M. Grundman, P. Delaney, ‘Antioxidant strategies for Alzheimer's disease’, Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2002, 61, 191–202.