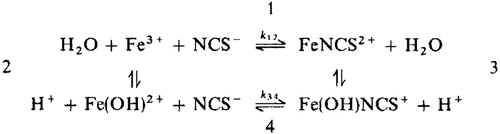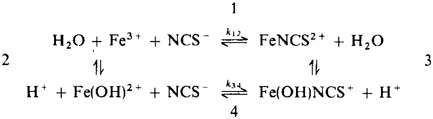Fast Reactions in Solutions at High Pressures III†): The Effect of Pressure on the Reaction of Fe(III)-Ions with Thiocyanate in Water up to 2 kbar at 25°C
Part I and II see [1,2].
Abstract
enStatic experiments of the pressure dependence of equilibrium constants for the equilibria 1 and 2 of the iron(III)-thiocyanate complex formation reaction in water
up to pressures of 2 kbar at T = 25°C and ionic strength of I = 0.2 mol kg−1 (NaClO4) yield reaction volumes of ΔV1 = 8.9 cm3 mol−1 and ΔV2 = 3 cm3 mol−1, respectively.
With the reaction volumes ΔV1 and ΔV2 the pressure dependence of the rate constants k12 and k34 of the reaction were obtained by measuring relaxation times of the reaction up to 2 kbar with a temperature-jump apparatus. The measured volumes of activation of step 1 and 4 are ΔV12≠ ≈︁ 0 cm3 mol−1 and ΔV34≠ = 7.1 cm3 mol−1 at 25°C.
From the relaxation amplitudes of temperature-jump experiments the pressure dependence of the reaction enthalpy ΔH1 of reaction path 1 was evaluated up to 2 kbar. ΔH1 varies with pressure from -15.1 kJ mol−1 at 1 bar to -4.4 kJ mol−1 at 2 kbar.
Abstract
deStatische Untersuchungen der Druckabhängigkeit der Gleichgewichtskonstanten für die Reaktionsschritte 1 und 2 der Eisen(III)-Thiocyanat-Komplexbildungsreaktion
in wäßriger Lösung bei Drücken bis 2 kbar ergaben bei T = 25°C und der Ionenstärke I = 0,2 mol kg−1 (NaClO4) Reaktionsvolumina von ΔV1 = 8,9 cm3 mol−1 bzw. ΔV2 = 3 cm3 mol−1.
Mit Kenntnis der Reaktionsvolumina ΔV1 und ΔV2 konnte aus den Relaxationszeiten, die mit einer Temperatursprung-Methode bis 2 kbar gemessen wurden, die Druckabhängigkeit der Geschwindigkeitskonstanten k12 und k34 der Reaktion ermittelt werden. Es ergaben sich Aktivierungsvolumina für die beiden Reaktionsschritte von ΔV12≠ ≈︁ 0 cm3 mol−1 bzw. ΔV34≠ = 7,1 cm3 mol−1 bei 25°C.
Aus den Relaxationsamplituden von Temperatursprung-Experimenten wurde die Druckabhängigkeit der Reaktionsenthalpie ΔH1 des Reaktionsschrittes 1 bis 2 kbar bestimmt. ΔH1 ändert sich mit dem Druck von -15,1 kJ mol−1 bei 1 bar nach -4,4 kJ mol−1 bei 2 kbar.