High Performance Memristors Based on Imine-Linked Covalent Organic Frameworks Obtained Using a Protonation Modification Strategy
Graphical Abstract
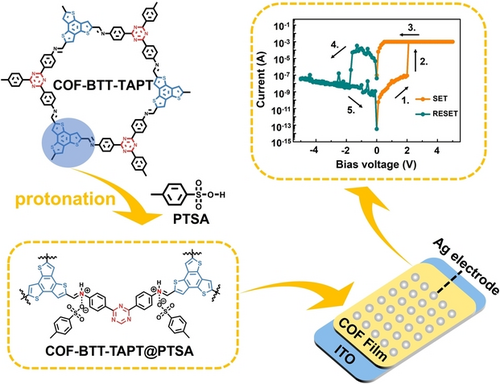
A protonation-modification strategy has been employed to modify imine-linked donor-acceptor (D-A) type covalent organic frameworks (COFs), significantly improving the electron delocalization capabilities of the imine bonds and constructing advanced memory devices. The obtained novel COF-BTT-TAPT@PTSA thin film-based rewritable memristors exhibit high ON/OFF current ratio (ca. 105) and unprecedented endurance (more than 1300 number of cycles).
Abstract
Imine-linked covalent organic frameworks (COFs) are garnering substantial interest in resistive random-access memory, attributed to their superior crystallinity, excellent chemical and thermal stability, and modifiable molecular structures. However, the development of high-performance COF-based memristors impeded by challenges such as low conjugation degree of imine bonds and poor electron delocalization ability. Herein, we report a protonation strategy to modify the imine bonds of donor-acceptor (D-A) type COFs. This modification significantly enhances the electron delocalization capability of imine bonds, lowers the energy barriers for electron injection from electrodes, and stabilizes the conductive charge transfer state, thus markedly improving device performance. The protonated COF-BTT-BPy and COF-BTT-TAPT thin films-based memristors show remarkable device performance with a high ON/OFF current ratio of 105, a low driving voltage, and outstanding endurance exceeding 600 and 1300 cycles, respectively, which is nearly twice the durability of analogous non-protonated COFs-based memristors. Notably, the protonated COF-BTT-TAPT-based memristor exhibit the highest number of cycles reported at present. This work not only unprecedentedly enhances the performance of COF-based memristors, but also provides a universal and promising approach for the molecular design and potential application of D-A type imine-linked COFs.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.