Synthesis of ZSM-5 Zeolite Nanosheets with Tunable Silanol Nest Contents across an Ultra-wide pH Range and Their Catalytic Validation
Graphical Abstract
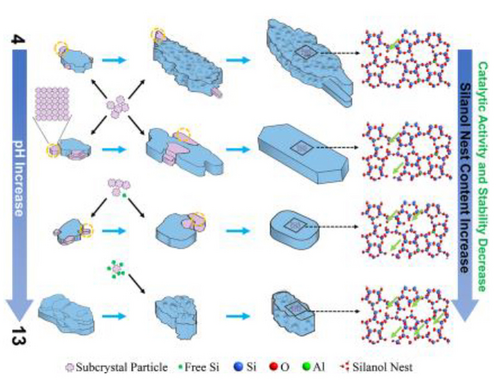
This study presents a method for synthesizing ZSM-5 zeolite nanosheets via aggregation crystallization of zeolite subcrystals within a broad pH range, detailing its crystallization process. pH manipulation enables precise control of silanol nest content, opening new avenues in zeolite engineering. Catalytic results in furfuryl alcohol etherification highlight the positive impact of regulating silanol nest content on catalytic reactions.
Abstract
Zeolite synthesis under acidic conditions has always presented a challenge. In this study, we successfully prepared series of ZSM-5 zeolite nanosheets (Z-5-SCA-X) over a broad pH range (4 to 13) without the need for additional supplements. This achievement was realized through aggregation crystallization of ZSM-5 zeolite subcrystal (Z-5-SC) with highly short-range ordering and ultrasmall size extracted from the synthetic system of ZSM-5 zeolite. Furthermore, the crystallization behavior of Z-5-SC was investigated, revealing its non-classical crystallization process under mildly alkaline and acidic conditions (pH<10), and the combination of classical and non-classical processes under strongly alkaline conditions (pH≥10). What's particularly intriguing is that, the silanol nest content in the resultant Z-5-SCA-X samples appears to be dependent on the pH values during the Z-5-SC crystallization process rather than its crystallinity. Finally, the results of the furfuryl alcohol etherification reaction demonstrate that reducing the concentration of silanol nests significantly enhances the catalytic performance of the Z-5-SCA-X zeolite. The ability to synthesize zeolite in neutral and acidic environments without the additional mineralizing agents not only broadens the current view of traditional zeolite synthesis but also provides a new approach to control the silanol nest content of zeolite catalysts.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.