An Expanded Palette of Fluorescent COS/H2S-Releasing Donors for H2S Delivery, Detection, and In Vivo Application
Graphical Abstract
Abstract
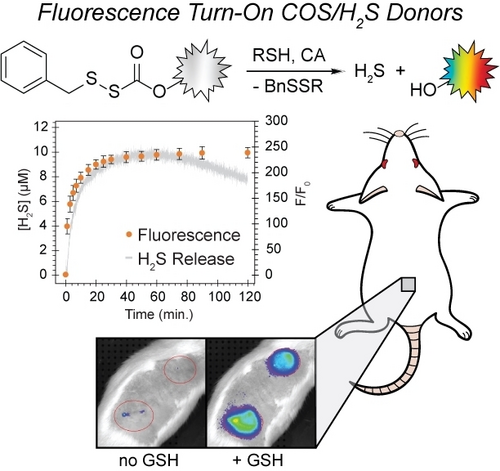
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is an important reactive sulfur species that is involved in many biological functions, and H2S imbalances have been indicated as a potential biomarker for various diseases. Different H2S donors have been developed to deliver H2S directly to biological systems, but few reports include donors with optical responses that allow for tracking of H2S release. Moreover, donor systems that use the same chemistry to deliver H2S across a palette of fluorescent responses remain lacking. Here we report five thiol-activated fluorescence turn-on COS/H2S donors that utilize blue, yellow, orange, red, and near infrared-emitting dyes functionalized with an H2S-releasing sulfenyl thiocarbonate scaffold. Upon treatment with thiols, each donor provides a fluorescence turn-on response (3–310-fold) and high H2S release efficiencies (>60 %). Using combined electrode and fluorescence experiments, we directly correlate the measured H2S release with the fluorescence response. All donors are biocompatible and release H2S in live cell environments. In addition, we demonstrate that the NIR donor allows for imaging H2S release in live rats via subcutaneous injection of the donor loaded into an alginate gel, which to the best of our knowledge is the first in vivo tracking of H2S release from a fluorogenic donor in non-transparent organisms.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the supplementary material of this article.