An Integrated Dual-Functional Nanotool Capable of Studying Single-Cell Epigenetics and Programmable Gene Regulation
Xiao-Mei Shi
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYi-Tong Xu
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorBing Wang
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorZheng Li
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorSi-Yuan Yu
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorHang Dong
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Wei-Wei Zhao
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Dechen Jiang
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Hong-Yuan Chen
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Jing-Juan Xu
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorXiao-Mei Shi
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYi-Tong Xu
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorBing Wang
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorZheng Li
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorSi-Yuan Yu
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorHang Dong
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Wei-Wei Zhao
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Dechen Jiang
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Hong-Yuan Chen
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Jing-Juan Xu
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
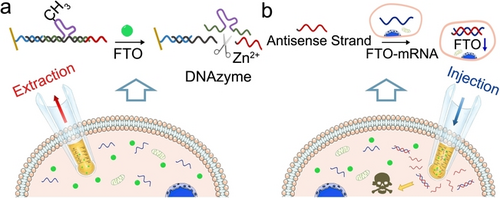
An integrated iontronic nanotool was developed for the study of single-cell epigenetics and programmable gene regulation. With the nanotool, an N6-methyladenine (m6A)-modified deoxyribozyme (DNAzyme) was used for profiling a representative m6 A-modifying enzyme, fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO), which also released a DNA sequence that could be programmed as an antisense strand against intracellular FTO-mRNA.
Abstract
Single-cell epigenetics is envisioned to decipher manifold epigenetic phenomena and to contribute to our accurate knowledge about basic epigenetic mechanisms. Engineered nanopipette technology has gained momentum in single-cell studies; however, solutions to epigenetic questions remain unachieved. This study addresses the challenge by exploring N6-methyladenine (m6A)-bearing deoxyribozyme (DNAzyme) confined within a nanopipette for profiling a representative m6A-modifying enzyme, fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO). Electroosmotic intracellular extraction of FTO could remove the m6A and cause DNAzyme cleavage, leading to the altered ionic current signal. Because the cleavage can release a DNA sequence, we simultaneously program it as an antisense strand against FTO-mRNA, intracellular injection of which has been shown to induce early stage apoptosis. This nanotool thus features the dual functions of studying single-cell epigenetics and programmable gene regulation.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the Supporting Information of this article.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202302930-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf1.3 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aW. A. Flavahan, E. Gaskell, B. E. Bernstein, Science 2017, 357, eaal2380;
- 1bD. Smeeth, S. Beck, E. G. Karam, M. Pluess, Lancet Psychiatry 2021, 8, 620–629.
- 2
- 2aG. Egger, G. Liang, A. Aparicio, P. A. Jones, Nature 2004, 429, 457–463;
- 2bA. D. Goldberg, C. D. Allis, E. Bernstein, Cell 2007, 128, 635–638.
- 3
- 3aC. M. Wei, A. Gershowitz, B. Moss, Nature 1975, 257, 251–253;
- 3bS. Horowitz, A. Horowitz, T. W. Nilsen, T. W. Munns, F. M. Rottman, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 5667–5671;
- 3cP. Narayan, F. M. Rottman, Science 1988, 242, 1159–1162;
- 3dJ. E. Harper, S. M. Miceli, R. J. Roberts, J. L. Manley, Nucleic Acids Res. 1990, 18, 5735–5741;
- 3eY. Q. Wang, S. Y. Zhang, W. D. Jia, P. P. Fan, L. Y. Wang, X. Y. Li, J. L. Chen, Z. Y. Cao, X. Y. Du, Y. Liu, K. F. Wang, C. Z. Hu, J. Y. Zhang, J. Hu, P. K. Zhang, H. Y. Chen, S. Huang, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2022, 17, 976–983.
- 4
- 4aG. F. Jia, Y. Fu, Q. Dai, G. Q. Zheng, Y. Yang, C. Q. Yi, T. Lindahl, T. Pan, Y. G. Yang, C. He, Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 885–887;
- 4bY. Fu, G. F. Jia, X. Q. Pang, R. N. Wang, X. Wang, C. J. Li, S. Smemo, Q. Dai, K. A. Bailey, M. A. Nobrega, K. L. Han, Q. Cui, Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1798;
- 4cG. Q. Zheng, J. A. Dahl, Y. M. Niu, P. Fedorcsak, C. M. Huang, C. J. Li, C. B. Vagbo, Y. Shi, W. L. Wang, S. H. Song, Z. K. Lu, R. P. G. Bosmans, Q. Dai, Y. J. Hao, X. Yang, W. M. Zhao, W. M. Tong, X. J. Wang, F. Bogdan, K. Furu, Y. Fu, G. F. Jia, X. Zhao, J. Liu, H. E. Krokan, A. Klungland, Y. G. Yang, C. He, Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 18–29.
- 5
- 5aT. Nawy, Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 1060;
- 5bP. Cheung, F. Vallania, M. Dvorak, S. E. Chang, S. Schaffert, M. Donato, A. M. Rao, R. Mao, P. J. Utz, P. Khatri, A. J. Kuo, Clin. Immunol. 2018, 196, 40–48.
- 6
- 6aN. T. N. Phan, X. C. Li, A. G. Ewing, Nat. Chem. Rev. 2017, 1, 0048;
- 6bY. L. Zhao, S. S. You, A. Zhang, J. H. Lee, J. Huang, C. M. Lieber, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 783–790;
- 6cR. J. Yu, Y. L. Ying, R. Gao, Y. T. Long, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 3706–3714;
- 6dW. Zhu, C. Gu, J. Dunevall, L. Ren, X. Zhou, A. G. Ewing, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 4238–4242;
- 6eX. M. Shi, Y. T. Xu, B. Y. Zhou, B. Wang, S. Y. Yu, W. W. Zhao, D. C. Jiang, H. Y. Chen, J. J. Xu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202215801.
- 7
- 7aP. Actis, S. Tokar, J. Clausmeyer, B. Babakinejad, S. Mikhaleva, R. Cornut, Y. Takahashi, A. Lopez Cordoba, P. Novak, A. I. Shevchuck, J. A. Dougan, S. G. Kazarian, P. V. Gorelkin, A. S. Erofeev, I. V. Yaminsky, P. R. Unwin, W. Schuhmann, D. Klenerman, D. A. Rusakov, E. V. Sviderskaya, Y. E. Korchev, ACS Nano 2014, 8, 875–884;
- 7bX. W. Zhang, Q. F. Qiu, H. Jiang, F. L. Zhang, Y. L. Liu, C. Amatore, W. H. Huang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 12997–13000;
- 7cY. Li, K. Hu, Y. Yu, S. A. Rotenberg, C. Amatore, M. V. Mirkin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 13055–13062;
- 7dR. R. Pan, M. C. Xu, J. D. Burgess, D. C. Jiang, H. Y. Chen, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4087–4092;
- 7eK. K. Hu, Y. Li, S. A. Rotenberg, C. Amatore, M. V. Mirkin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 4564–4568;
- 7fX. W. Zhang, A. Oleinick, H. Jiang, Q. L. Liao, Q. F. Qiu, I. Svir, Y. L. Liu, C. Amatore, W. H. Huang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 7753–7756;
- 7gQ. W. Yue, X. C. Li, F. Wu, W. L. Ji, Y. Zhang, P. Yu, M. N. Zhang, W. J. Ma, M. Wang, L. Q. Mao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 11061–11065.
- 8Y. L. Wang, R. Jin, N. Sojic, D. C. Jiang, H. Y. Chen, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 10416–10420.
- 9
- 9aY. F. Ruan, F. Z. Chen, Y. T. Xu, T. Y. Zhang, S. Y. Yu, W. W. Zhao, D. C. Jiang, H. Y. Chen, J. J. Xu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 25762–25765;
- 9bH. Y. Wang, Y. T. Xu, B. Wang, S. Y. Yu, X. M. Shi, W. W. Zhao, D. C. Jiang, H. Y. Chen, J. J. Xu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202212752.
- 10
- 10aT. Y. Zhang, S. Y. Yu, B. Wang, Y. T. Xu, X. M. Shi, W. W. Zhao, D. C. Jiang, H. Y. Chen, J. J. Xu, Research 2022, 9859101;
- 10bH. Y. Wang, Y. F. Ruan, L. B. Zhu, X. M. Shi, W. W. Zhao, H. Y. Chen, J. J. Xu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 13244–13250;
- 10cJ. Song, C. H. Xu, S. Z. Huang, W. Lei, Y. F. Ruan, H. J. Lu, W. Zhao, J. J. Xu, H. Y. Chen, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 13226–13230;
- 10dP. Hu, Y. Zhang, D. D. Wang, G. H. Qi, Y. D. Jin, Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 4240–4245;
- 10eH. L. Liu, Q. C. Jiang, J. Pang, Z. Y. Jiang, J. Cao, L. N. Ji, X. H. Xia, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1703847;
- 10fY. T. Xu, Y. F. Ruan, H. Y. Wang, S. Y. Yu, X. D. Yu, W. W. Zhao, H. Y. Zhao, H. Y. Chen, J. J. Xu, Small 2021, 17, 2100503;
- 10gX. M. Shi, Y. F. Ruan, H. Y. Wang, W. W. Zhao, J. J. Xu, H. Y. Chen, CCS Chem. 2020, 2, 2359–2367.
- 11
- 11aJ. Wang, S. S. Yu, Q. Wu, X. Gong, S. Z. He, J. H. Shang, X. Q. Liu, F. Wang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 10766–10774;
- 11bL. L. Shi, W. B. Wu, Y. K. Duan, L. Xu, S. Li, X. H. Gao, B. Liu, ACS Nano 2021, 15, 1841–1849;
- 11cX. J. Wang, G. Kim, J. L. Chu, T. J. Song, Z. L. Yang, W. J. Guo, X. L. Shao, M. L. Oelze, K. C. Li, Y. Lu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 5812–5819;
- 11dW. J. Wang, N. S. R. Satyavolu, Z. K. Wu, J. R. Zhang, J. J. Zhu, Y. Lu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 6798–6802.
- 12
- 12aY. Sun, S. Chen, X. Y. Chen, Y. L. Xu, S. Y. Zhang, Q. Y. Ouyang, G. F. Yang, H. B. Li, Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1323;
- 12bL. Shi, C. L. Mu, T. Gao, W. X. Chai, A. Z. Sheng, T. S. Chen, J. Yang, X. L. Zhu, G. X. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 8239–8243;
- 12cX. C. Li, T. Y. Zhai, P. C. Gao, H. L. Cheng, R. Z. Hou, X. D. Lou, F. Xia, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 40;
- 12dM. Ali, R. Neumann, W. Ensinger, ACS Nano 2010, 4, 7267–7274;
- 12eC. Wei, A. J. Bard, S. W. Feldberg, Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, 4627–4633;
- 12fY. F. Wu, D. Y. Wang, I. Willner, Y. Tian, L. Jiang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 7790–7794.
- 13Q. Wang, K. Y. Tan, H. Wang, J. H. Shang, Y. Q. Wan, X. Q. Liu, X. C. Weng, F. A. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 6895–6904.
- 14Z. Siwy, E. Heins, C. C. Harrell, P. Kohli, C. R. Martin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 10850–10851.
- 15
- 15aW. W. Zhao, J. J. Xu, H. Y. Chen, Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 7421–7441;
- 15bP. C. Gao, D. G. Wang, C. Che, Q. Ma, X. Q. Wu, Y. J. Chen, H. Q. Xu, X. C. Li, Y. Lin, D. F. Ding, X. D. Lou, F. Xia, Nat. Protoc. 2021, 16, 4201–4226.
- 16
- 16aT. Rahman, T. Masui, T. Ichiki, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 54, 04DL08;
- 16bT. M. Herne, M. J. Tarlov, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 8916–8920.
- 17
- 17aS. Peng, W. Xiao, D. Ju, B. Sun, N. Hou, Q. Liu, Y. Wang, H. Zhao, C. Gao, S. Zhang, R. Cao, P. Li, H. Huang, Y. Ma, Y. Wang, W. Lai, Z. Ma, W. Zhang, S. Huang, H. Wang, Z. Zhang, L. Zhao, T. Cai, Y. L. Zhao, F. Wang, Y. Nie, G. Zhi, Y. G. Yang, E. E. Zhang, N. Huang, Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaau7116;
- 17bN. Svensen, S. R. Jaffrey, Cell Chem. Biol. 2016, 23, 415–425;
- 17cY. Huang, J. Yan, Q. Li, J. Li, S. Gong, H. Zhou, J. Gan, H. Jiang, G. F. Jia, C. Luo, C. G. Yang, Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 373–384.
- 18R. K. Saiki, PCR Protoc. 1990, 2, 13–20.
- 19
- 19aM. G. Tian, J. Sun, B. L. Dong, W. Y. Lin, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 16506–16510;
- 19bL. C. Crowley, B. J. Marfell, N. J. Water-house, Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2016, 9, prot087205;
10.1101/pdb.prot087205 Google Scholar
- 19cM. M. Ho, A. V. Ng, S. Lam, J. Y. Hung, Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 4827–4833.
- 20D. D. Young, M. O. Lively, A. Deiters, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 6183–6193.
- 21
- 21aY. L. Wang, J. Y. Pang, Q. Y. Wang, L. C. Yan, L. T. Wang, Z. Xing, C. M. Wang, J. F. Zhang, L. Dong, Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2004929;
- 21bD. R. Scoles, P. Meera, M. D. Schneider, S. Paul, W. Dansithong, K. P. Figueroa, G. Hung, F. Rigo, C. F. Bennett, T. S. Otis, S. M. Pulst, Nature 2017, 544, 362–366.