“Sandwich” Diimine-Copper Catalysts for C−H Functionalization by Carbene Insertion
Dr. Kristine Klimovica
Department of Chemistry, University of Houston, 3585 Cullen Blvd., Houston, TX, USA
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Julius X. Heidlas
Department of Chemistry, University of Houston, 3585 Cullen Blvd., Houston, TX, USA
Search for more papers by this authorIrvin Romero
Department of Chemistry, University of Houston, 3585 Cullen Blvd., Houston, TX, USA
Search for more papers by this authorThanh V. Le
Department of Chemistry, University of Houston, 3585 Cullen Blvd., Houston, TX, USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Olafs Daugulis
Department of Chemistry, University of Houston, 3585 Cullen Blvd., Houston, TX, USA
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Kristine Klimovica
Department of Chemistry, University of Houston, 3585 Cullen Blvd., Houston, TX, USA
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Julius X. Heidlas
Department of Chemistry, University of Houston, 3585 Cullen Blvd., Houston, TX, USA
Search for more papers by this authorIrvin Romero
Department of Chemistry, University of Houston, 3585 Cullen Blvd., Houston, TX, USA
Search for more papers by this authorThanh V. Le
Department of Chemistry, University of Houston, 3585 Cullen Blvd., Houston, TX, USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Olafs Daugulis
Department of Chemistry, University of Houston, 3585 Cullen Blvd., Houston, TX, USA
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
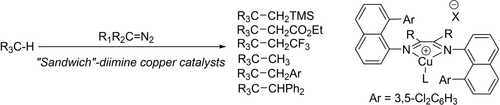
A new catalyst platform for C(sp3)−H bond functionalization has been discovered. “Sandwich” diimine-copper(I) complexes catalyze reactions of alkane, ether, and amine C−H bonds with a large panel of diazo compounds. Additionally, the first metal-catalyzed C(sp3)−H methylation by CH2N2 is disclosed. The electrophilicity and extreme steric bulk of these catalysts are likely reasons for their efficiency.
Abstract
We report here “sandwich” diimine-copper(I) catalysts for C(sp3)−H bond functionalization. Reactions of alkanes and ethers with trimethylsilyldiazomethane, ethyl diazoacetate, and trifluoromethyl-diazomethane have been demonstrated. We also report C(sp3)−H bond methylation, benzylation, and diphenylmethylation by diazomethane, aryldiazomethanes, and diphenyldiazomethane. These reactions are rare examples of base-metal catalyzed, intermolecular C(sp3)−H functionalizations by employing unactivated diazo compounds. Electrophilicity and unique steric environment of “sandwich”-copper catalysts are likely reasons for their catalytic efficiency.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202200334-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf6.5 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aO. Baudoin, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 17798–17809; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 17950–17961;
- 1bP. Gandeepan, T. Müller, D. Zell, G. Cera, S. Warratz, L. Ackermann, Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 2192–2452;
- 1cJ. Das, S. Guin, D. Maiti, Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 10887–10909;
- 1dZ. Chen, M.-Y. Rong, J. Nie, X.-F. Zhu, B.-F. Shi, J.-A. Ma, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 4921–4942;
- 1eJ. C. K. Chu, T. Rovis, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 62–101; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 64–105;
- 1fJ. F. Hartwig, M. A. Larsen, ACS Cent. Sci. 2016, 2, 281–292;
- 1gX. Tang, X. Jia, Z. Huang, Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 288–299;
- 1hT. G. Saint-Denis, R.-Y. Zhu, G. Chen, Q.-F. Wu, J.-Q. Yu, Science 2018, 359, eaao4798;
- 1iW. R. Gutekunst, P. S. Baran, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1976–1991.
- 2
- 2aY. Xia, D. Qiu, J. Wang, Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 13810–13889;
- 2bC. Damiano, P. Sonzini, E. Gallo, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 4867–4905;
- 2cC. N. Slattery, A. Ford, A. R. Maguire, Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 6681–6705;
- 2dM. P. Doyle, R. Duffy, M. Ratnikov, L. Zhou, Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 704–724;
- 2eM. M. Díaz-Requejo, P. J. Pérez, Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 3379–3394;
- 2fM. M. Díaz-Requejo, P. J. Pérez, Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 879–885;
- 2gA. Caballero, M. M. Díaz-Requejo, M. R. Fructos, A. Olmos, J. Urbano, P. J. Pérez, Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 20295–20307;
- 2hX. Zhao, Y. Zhang, J. Wang, Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 10162–10173;
- 2iW. Kirmse, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 1088–1093; Angew. Chem. 2003, 115, 1120–1125.
- 3
- 3aH. M. L. Davies, J. Org. Chem. 2019, 84, 12722–12745;
- 3bH. M. L. Davies, J. R. Denton, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 3061–3071;
- 3cJ.-L. Shih, P.-A. Chen, J. A. May, Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2016, 12, 985–999;
- 3dA. DeAngelis, R. Panish, J. M. Fox, Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 115–127.
- 4Selected examples:
- 4aJ. Fu, Z. Ren, J. Bacsa, D. G. Musaev, H. M. L. Davies, Nature 2018, 564, 395–399;
- 4bP. Lu, A. Mailyan, Z. Gu, D. M. Guptill, H. Wang, H. M. L. Davies, A. Zakarian, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 17738–17749.
- 5
- 5aL. T. Scott, G. J. DeCicco, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1974, 96, 322–323;
- 5bM. M. Díaz-Requejo, T. R. Belderraín, M. C. Nicasio, S. Trofimenko, P. J. Pérez, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 896–897;
- 5cR. Gava, A. Olmos, B. Noverges, T. Varea, E. Álvarez, T. R. Belderrain, A. Caballero, G. Asensio, P. J. Pérez, ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 3726–3730;
- 5dJ. A. Flores, V. Badarinarayana, S. Singh, C. J. Lovely, H. V. R. Dias, Dalton Trans. 2009, 7648–7652.
- 6
- 6aD. Zhu, L. Chen, H. Fan, Q. Yaoa, S. Zhu, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 908–950;
- 6bB. D. Bergstrom, L. A. Nickerson, J. T. Shaw, L. W. Souza, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 6864–6878; Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 6940–6954;
- 6cD. Morton, S. B. Blakey, ChemCatChem 2015, 7, 577–578;
- 6dC. Soldi, K. N. Lamb, R. A. Squitieri, M. González-López, M. J. Di Maso, J. T. Shaw, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 15142–15145;
- 6eA. R. Reddy, C.-Y. Zhou, Z. Guo, J. Wei, C.-M. Che, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 14175–14180; Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 14399–14404;
- 6fX. Wen, Y. Wang, X. P. Zhang, Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 5082–5086;
- 6gL. W. Souza, R. A. Squitieri, C. A. Dimirjian, B. M. Hodur, L. A. Nickerson, C. N. Penrod, J. Cordova, J. C. Fettinger, J. T. Shaw, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 15213–15216; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 15433–15436;
- 6hD. Zhu, J. Ma, K. Luo, H. Fu, L. Zhang, S. Zhu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 8452–8456; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 8592–8596;
- 6iH.-X. Wang, Q. Wan, K.-H. Low, C.-Y. Zhou, J.-S. Huang, J.-L. Zhang, C.-M. Che, Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 2243–2259;
- 6jZ. Liu, S. Cao, W. Yu, J. Wu, F. Yi, E. A. Anderson, X. Bi, Chem 2020, 6, 2110–2124.
- 7
- 7aJ. Zhang, X. Huang, R. K. Zhang, F. H. Arnold, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 9798–9802;
- 7bJ. H. Atherton, R. Fields, J. Chem. Soc. C 1968, 2276–2278;
- 7cP. K. Mykhailiuk, Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 12718–12755;
- 7dS. Hyde, J. Veliks, B. Liégault, D. Grassi, M. Taillefer, V. Gouverneur, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 3785–3789; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 3849–3853.
- 8K. Klimovica, K. Kirschbaum, O. Daugulis, Organometallics 2016, 35, 2938–2943.
- 9
- 9aD. Zhang, E. T. Nadres, M. Brookhart, O. Daugulis, Organometallics 2013, 32, 5136–5143;
- 9bT. Vaidya, K. Klimovica, A. LaPointe, I. Keresztes, E. B. Lobkovsky, O. Daugulis, G. W. Coates, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 7213–7216;
- 9cK. E. Allen, J. Campos, O. Daugulis, M. Brookhart, ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 456–464.
- 10
- 10aX. Dai, T. H. Warren, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 10085–10094;
- 10bB. F. Straub, P. Hofmann, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 1288–1290;
10.1002/1521-3773(20010401)40:7<1288::AID-ANIE1288>3.0.CO;2-6 CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google ScholarAngew. Chem. 2001, 113, 1328–1330;
- 10cJ. Barluenga, L. A. López, O. Löber, M. Tomás, S. García-Granda, C. Alvarez-Rúa, J. Borge, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 3392–3394;
10.1002/1521-3773(20010917)40:18<3392::AID-ANIE3392>3.0.CO;2-Y CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google ScholarAngew. Chem. 2001, 113, 3495–3497;
- 10dP. Hofmann, I. V. Shishkov, F. Rominger, Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 11755–11762.
- 11Reaction of a more electrophilic carbene source ethyl diazoacetate with dioxane catalyzed by a hydrotris(3-mesityl)pyrazolylborate Cu complex gave C−H insertion product in 20 % yield. Please see ref. [5b].
- 12C. G. Espino, K. W. Fiori, M. Kim, J. Du Bois, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 15378–15379.
- 13K. Matsuoka, N. Komami, M. Kojima, T. Mita, K. Suzuki, S. Maeda, T. Yoshino, S. Matsunaga, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 103–108.
- 14For enantioselective, engineered cytochrome P450 enzyme-catalyzed amine α-C−H trifluoroethylation please see ref. [7a].
- 15E. J. Barreiro, A. E. Kümmerle, C. A. M. Fraga, Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5215–5246.
- 16Non-selective photochemical insertions of methylene into C−H bonds are known. Addition of transition metal, such as rhodium, shuts down C−H insertion reactivity in favor of ylide formation.
- 16aH. Meerwein, H. Rathjen, H. Werner, Chem. Ber. 1942, 75, 1610–1622;
10.1002/cber.19420751229 Google Scholar
- 16bW. Kirmse, P. V. Chiem, V. Schurig, Tetrahedron Lett. 1985, 26, 197–200;
- 16cG. A. Olah, H. Doggweiler, J. D. Felberg, J. Org. Chem. 1984, 49, 2116–2120.
- 17
- 17aA. Caballero, M. M. Díaz-Requejo, S. Trofimenko, T. R. Belderraín, P. J. Pérez, Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 2848–2852.
- 17bReactions of TMSCHN2 with dioxane give higher yields if lower catalyst loadings are employed. Please see Table S-1 in Supporting Information.
- 17cM. Besora, A. A. C. Braga, W. M. C. Sameera, J. Urbano, M. R. Fructos, P. J. Pérez, F. Maseras, J. Organomet. Chem. 2015, 784, 2–12;
- 17dJ. R. Jagannathan, J. C. Fettinger, J. T. Shaw, A. K. Franz, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 11674–11679.