High-Rate CO2 Electroreduction to C2+ Products over a Copper-Copper Iodide Catalyst
Hefei Li
State Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Dalian National Laboratory for Clean Energy, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Tianfu Liu
State Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Dalian National Laboratory for Clean Energy, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Search for more papers by this authorPengfei Wei
State Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Dalian National Laboratory for Clean Energy, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorLong Lin
State Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Dalian National Laboratory for Clean Energy, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Dunfeng Gao
State Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Dalian National Laboratory for Clean Energy, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Guoxiong Wang
State Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Dalian National Laboratory for Clean Energy, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Xinhe Bao
State Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Dalian National Laboratory for Clean Energy, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Search for more papers by this authorHefei Li
State Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Dalian National Laboratory for Clean Energy, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Tianfu Liu
State Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Dalian National Laboratory for Clean Energy, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Search for more papers by this authorPengfei Wei
State Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Dalian National Laboratory for Clean Energy, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorLong Lin
State Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Dalian National Laboratory for Clean Energy, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Dunfeng Gao
State Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Dalian National Laboratory for Clean Energy, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Guoxiong Wang
State Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Dalian National Laboratory for Clean Energy, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Xinhe Bao
State Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Dalian National Laboratory for Clean Energy, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
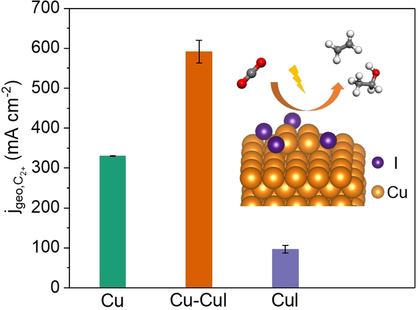
A Cu-CuI composite catalyst achieves a remarkable C2+ partial current density of 591 mA cm−2 at −1.0 V vs. RHE, substantially higher than Cu or CuI alone. It is ascribed to the presence of residual Cu+ and adsorbed iodine species which improve CO adsorption and facilitate C−C coupling during CO2 electroreduction.
Abstract
Electrochemical CO2 reduction reaction (CO2RR) to multicarbon hydrocarbon and oxygenate (C2+) products with high energy density and wide availability is of great importance, as it provides a promising way to achieve the renewable energy storage and close the carbon cycle. Herein we design a Cu-CuI composite catalyst with abundant Cu0/Cu+ interfaces by physically mixing Cu nanoparticles and CuI powders. The composite catalyst achieves a remarkable C2+ partial current density of 591 mA cm−2 at −1.0 V vs. reversible hydrogen electrode in a flow cell, substantially higher than Cu (329 mA cm−2) and CuI (96 mA cm−2) counterparts. Induced by alkaline electrolyte and applied potential, the Cu-CuI composite catalyst undergoes significant reconstruction under CO2RR conditions. The high-rate C2+ production over Cu-CuI is ascribed to the presence of residual Cu+ and adsorbed iodine species which improve CO adsorption and facilitate C−C coupling.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202102657-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf1.7 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aY. Y. Birdja, E. Pérez-Gallent, M. C. Figueiredo, A. J. Göttle, F. Calle-Vallejo, M. T. M. Koper, Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 732–745;
- 1bM. G. Kibria, J. P. Edwards, C. M. Gabardo, C. T. Dinh, A. Seifitokaldani, D. Sinton, E. H. Sargent, Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1807166;
- 1cA. Vasileff, Y. Zheng, S. Z. Qiao, Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1700759.
- 2
- 2aM. B. Ross, P. De Luna, Y. Li, C.-T. Dinh, D. Kim, P. Yang, E. H. Sargent, Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 648–658;
- 2bR. M. Arán-Ais, D. Gao, B. Roldan Cuenya, Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 2906–2917.
- 3
- 3aH. Xie, T. Y. Wang, J. S. Liang, Q. Li, S. H. Sun, Nano Today 2018, 21, 41–54;
- 3bC. W. Li, J. Ciston, M. W. Kanan, Nature 2014, 508, 504–507.
- 4
- 4aS. Nitopi, E. Bertheussen, S. B. Scott, X. Liu, A. K. Engstfeld, S. Horch, B. Seger, I. E. L. Stephens, K. Chan, C. Hahn, J. K. Norskov, T. F. Jaramillo, I. Chorkendorff, Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 7610–7672;
- 4bF. Li, A. Thevenon, A. Rosas-Hernández, Z. Wang, Y. Li, C. M. Gabardo, A. Ozden, C. T. Dinh, J. Li, Y. Wang, J. P. Edwards, Y. Xu, C. McCallum, L. Tao, Z.-Q. Liang, M. Luo, X. Wang, H. Li, C. P. O'Brien, C.-S. Tan, D.-H. Nam, R. Quintero-Bermudez, T.-T. Zhuang, Y. C. Li, Z. Han, R. D. Britt, D. Sinton, T. Agapie, J. C. Peters, E. H. Sargent, Nature 2020, 577, 509–513;
- 4cM. Zhong, K. Tran, Y. Min, C. Wang, Z. Wang, C. T. Dinh, P. De Luna, Z. Yu, A. S. Rasouli, P. Brodersen, S. Sun, O. Voznyy, C. S. Tan, M. Askerka, F. Che, M. Liu, A. Seifitokaldani, Y. Pang, S. C. Lo, A. Ip, Z. Ulissi, E. H. Sargent, Nature 2020, 581, 178–183;
- 4dP. De Luna, R. Quintero-Bermudez, C.-T. Dinh, M. B. Ross, O. S. Bushuyev, P. Todorović, T. Regier, S. O. Kelley, P. Yang, E. H. Sargent, Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 103–110.
- 5
- 5aQ. Lu, F. Jiao, Nano Energy 2016, 29, 439–456;
- 5bC. T. Dinh, T. Burdyny, M. G. Kibria, A. Seifitokaldani, C. M. Gabardo, F. P. G. de Arquer, A. Kiani, J. P. Edwards, P. De Luna, O. S. Bushuyev, C. Q. Zou, R. Quintero-Bermudez, Y. J. Pang, D. Sinton, E. H. Sargent, Science 2018, 360, 783–787;
- 5cS. Shen, X. Peng, L. Song, Y. Qiu, C. Li, L. Zhuo, J. He, J. Ren, X. Liu, J. Luo, Small 2019, 15, 1902229;
- 5dX. Wang, Z. Y. Wang, F. P. G. de Arquer, C. T. Dinh, A. Ozden, Y. G. C. Li, D. H. Nam, J. Li, Y. S. Liu, J. Wicks, Z. T. Chen, M. F. Chi, B. Chen, Y. Wang, J. Tam, J. Y. Howe, A. Proppe, P. Todorovic, F. W. Li, T. T. Zhuang, C. M. Gabardo, A. R. Kirmani, C. McCallum, S. F. Hung, Y. W. Lum, M. C. Luo, Y. M. Min, A. N. Xu, C. P. O'Brien, B. Stephen, B. Sun, A. H. Ip, L. J. Richter, S. O. Kelley, D. Sinton, E. H. Sargent, Nat. Energy 2020, 5, 478–486;
- 5eC. G. Morales-Guio, E. R. Cave, S. A. Nitopi, J. T. Feaster, L. Wang, K. P. Kuhl, A. Jackson, N. C. Johnson, D. N. Abram, T. Hatsukade, C. Hahn, T. F. Jaramillo, Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 764–771;
- 5fW. C. Ma, S. J. Xie, T. T. Liu, Q. Y. Fan, J. Y. Ye, F. F. Sun, Z. Jiang, Q. H. Zhang, J. Cheng, Y. Wang, Nat. Catal. 2020, 3, 478–487.
- 6
- 6aY. Zhou, F. Che, M. Liu, C. Zou, Z. Liang, P. De Luna, H. Yuan, J. Li, Z. Wang, H. Xie, H. Li, P. Chen, E. Bladt, R. Quintero-Bermudez, T. K. Sham, S. Bals, J. Hofkens, D. Sinton, G. Chen, E. H. Sargent, Nat. Chem. 2018, 10, 974–980;
- 6bH. Mistry, A. S. Varela, C. S. Bonifacio, I. Zegkinoglou, I. Sinev, Y. W. Choi, K. Kisslinger, E. A. Stach, J. C. Yang, P. Strasser, B. Roldan Cuenya, Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12123;
- 6cR. M. Arán-Ais, F. Scholten, S. Kunze, R. Rizo, B. Roldan Cuenya, Nat. Energy 2020, 5, 317–325;
- 6dQ. Zhu, X. Sun, D. Yang, J. Ma, X. Kang, L. Zheng, J. Zhang, Z. Wu, B. Han, Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3851.
- 7H. Xiao, W. A. Goddard III, T. Cheng, Y. Liu, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 6685–6688.
- 8
- 8aA. Vasileff, Y. Zhu, X. Zhi, Y. Zhao, L. Ge, H. M. Chen, Y. Zheng, S. Z. Qiao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 19649–19653; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 19817–19821;
- 8bW. Zhang, C. Huang, Q. Xiao, L. Yu, L. Shuai, P. An, J. Zhang, M. Qiu, Z. Ren, Y. Yu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 11417–11427;
- 8cC. B. Chen, Y. F. Li, S. Yu, S. Louisia, J. B. Jin, M. F. Li, M. B. Ross, P. D. Yang, Joule 2020, 4, 1688–1699;
- 8dT.-T. Zhuang, Y. Pang, Z.-Q. Liang, Z. Wang, Y. Li, C.-S. Tan, J. Li, C. T. Dinh, P. De Luna, P.-L. Hsieh, T. Burdyny, H.-H. Li, M. Liu, Y. Wang, F. Li, A. Proppe, A. Johnston, D.-H. Nam, Z.-Y. Wu, Y.-R. Zheng, A. H. Ip, H. Tan, L.-J. Chen, S.-H. Yu, S. O. Kelley, D. Sinton, E. H. Sargent, Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 946–951.
- 9
- 9aD. Gao, F. Scholten, B. Roldan Cuenya, ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 5112–5120;
- 9bD. Gao, I. Sinev, F. Scholten, R. M. Aran-Ais, N. J. Divins, K. Kvashnina, J. Timoshenko, B. Roldan Cuenya, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 17047–17053; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 17203–17209.
- 10F. D. Speck, S. Cherevko, Electrochem. Commun. 2020, 115, 106739.
- 11
- 11aX. Chang, T. Wang, Z. J. Zhao, P. Yang, J. Greeley, R. Mu, G. Zhang, Z. Gong, Z. Luo, J. Chen, Y. Cui, G. A. Ozin, J. Gong, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 15415–15419; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 15641–15645;
- 11bT. C. Chou, C. C. Chang, H. L. Yu, W. Y. Yu, C. L. Dong, J. J. Velasco-Velez, C. H. Chuang, L. C. Chen, J. F. Lee, J. M. Chen, H. L. Wu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 2857–2867;
- 11cP. P. Yang, X. L. Zhang, F. Y. Gao, Y. R. Zheng, Z. Z. Niu, X. Yu, R. Liu, Z. Z. Wu, S. Qin, L. P. Chi, Y. Duan, T. Ma, X. S. Zheng, J. F. Zhu, H. J. Wang, M. R. Gao, S. H. Yu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 6400–6408.
- 12H. Bai, T. Cheng, S. Li, Z. Zhou, H. Yang, J. Li, M. Xie, J. Ye, Y. Ji, Y. Li, Z. Zhou, S. Sun, B. Zhang, H. Peng, Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 62–68.
- 13A. Bagger, W. Ju, A. S. Varela, P. Strasser, J. Rossmeisl, ChemPhysChem 2017, 18, 3266–3273.
- 14I. T. McCrum, S. A. Akhade, M. J. Janik, Electrochim. Acta 2015, 173, 302–309.
- 15B. Hammer, J. K. Norskov, Nature 1995, 376, 238–240.