Real-Time Atomic-Scale Visualization of Reversible Copper Surface Activation during the CO Oxidation Reaction
Corresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Langli Luo
Institute of Molecular Plus, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Sciences, Department of Chemistry, Tianjin University, 92 Weijin Road, Tianjin, 300072 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYao Nian
School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Tianjin University and Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemical Science and Chemical Engineering (Tianjin), Tianjin, 300350 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Shuangbao Wang
School of Physical Science and Technology, Guangxi University, Nanning, 530004 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorZejian Dong
Institute of Molecular Plus, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Sciences, Department of Chemistry, Tianjin University, 92 Weijin Road, Tianjin, 300072 China
Search for more papers by this authorYang He
Environmental Molecular Sciences Laboratory, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, 902 Battelle Blvd, Richland, WA, 99354 USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. You Han
School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Tianjin University and Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemical Science and Chemical Engineering (Tianjin), Tianjin, 300350 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Chongmin Wang
Environmental Molecular Sciences Laboratory, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, 902 Battelle Blvd, Richland, WA, 99354 USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Langli Luo
Institute of Molecular Plus, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Sciences, Department of Chemistry, Tianjin University, 92 Weijin Road, Tianjin, 300072 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYao Nian
School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Tianjin University and Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemical Science and Chemical Engineering (Tianjin), Tianjin, 300350 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Shuangbao Wang
School of Physical Science and Technology, Guangxi University, Nanning, 530004 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorZejian Dong
Institute of Molecular Plus, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Sciences, Department of Chemistry, Tianjin University, 92 Weijin Road, Tianjin, 300072 China
Search for more papers by this authorYang He
Environmental Molecular Sciences Laboratory, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, 902 Battelle Blvd, Richland, WA, 99354 USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. You Han
School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Tianjin University and Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemical Science and Chemical Engineering (Tianjin), Tianjin, 300350 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Chongmin Wang
Environmental Molecular Sciences Laboratory, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, 902 Battelle Blvd, Richland, WA, 99354 USA
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
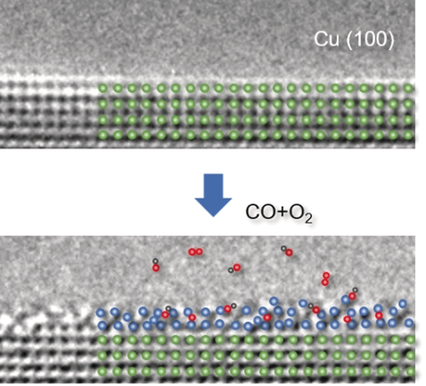
Copper surfer: The atomic-scale surface activation process of copper during CO oxidation was observed through environmental transmission electron microscopy. 2–3 atomic layers of the Cu surface are activated with CO and with the help of O2, which intercalates into Cu lattices. CuOx is also observed and believed to be an active species catalyzing the CO oxidation reaction.
Abstract
By using in situ aberration-corrected environmental transmission electron microscopy, for the first time at atomic level, the dynamic evolution of the Cu surface is captured during CO oxidation. Under reaction conditions, the Cu surface is activated, typically involving 2–3 atomic layers with the formation of a reversible metastable phase that only exists during catalytic reactions. The distinctive role of CO and O2 in the surface activation is revealed, which features CO exposure to lead to surface roughening and consequently formation of low-coordinated Cu atoms, while O2 exposure induces a quasi-crystalline CuOx phase. Supported by DFT calculations, it is shown that crystalline CuOx reversibly transforms into the amorphous phase, acting as an active species to facilitate the interaction of gas reactants and catalyzing CO oxidation.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201915024-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf1.8 MB | Supplementary |
| anie201915024-sup-0001-S01.CuOx_cryst_to_amorph.mp46.9 MB | Supplementary |
| anie201915024-sup-0001-S02._first_O2_dissociation.avi1.8 MB | Supplementary |
| anie201915024-sup-0001-S03.format_desorpt_CO2.avi2.3 MB | Supplementary |
| anie201915024-sup-0001-S04.second_O2_dissociation.avi2.6 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aF. Tao, P. A. Crozier, Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 3487–3539;
- 1bM. Duan, J. Yu, J. Meng, B. Zhu, Y. Wang, Y. Gao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 6464–6469; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 6574–6579.
- 2
- 2aH. Yoshida, Y. Kuwauchi, J. R. Jinschek, K. Sun, S. Tanaka, M. Kohyama, S. Shimada, M. Haruta, S. Takeda, Science 2012, 335, 317–319;
- 2bT. Avanesian, S. Dai, M. J. Kale, G. W. Graham, X. Pan, P. Christopher, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 4551–4558.
- 3
- 3aJ. Hrbek, F. M. Hoffman, J. B. Park, P. Liu, D. Stacchiola, Y. S. Hoo, S. Ma, A. Nambu, J. A. Rodriguez, M. G. White, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 17272–17273;
- 3bT. Uchiyama, H. Yoshida, Y. Kuwauchi, S. Ichikawa, S. Shimada, M. Haruta, S. Takeda, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 10157–10160; Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 10339–10342.
- 4
- 4aG. C. Chinchen, K. C. Waugh, D. A. Whan, Appl. Catal. 1986, 25, 101–107;
- 4bJ. D. Grunwaldt, A. M. Molenbroek, N. Y. Topsøe, H. Topsøe, B. S. Clausen, J. Catal. 2000, 194, 452–460;
- 4cP. L. Hansen, J. B. Wagner, S. Helveg, J. R. Rostrup-Nielsen, B. S. Clausen, H. Topsøe, Science 2002, 295, 2053–2055;
- 4dJ. Nakamura, Y. Choi, T. Fujitani, Top. Catal. 2003, 22, 277–285.
- 5
- 5aM. Behrens, F. Studt, I. Kasatkin, S. Kühl, M. Hävecker, F. Abild-Pedersen, S. Zander, F. Girgsdies, P. Kurr, B.-L. Kniep, M. Tovar, R. W. Fischer, J. K. Nørskov, R. Schlögl, Science 2012, 336, 893–897;
- 5bT. Lunkenbein, J. Schumann, M. Behrens, R. Schlögl, M. G. Willinger, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 4544–4548; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 4627–4631;
- 5cS. Kuld, M. Thorhauge, H. Falsig, C. F. Elkjær, S. Helveg, I. Chorkendorff, J. Sehested, Science 2016, 352, 969–974;
- 5dS. Kattel, P. J. Ramírez, J. G. Chen, J. A. Rodriguez, P. Liu, Science 2017, 355, 1296–1299.
- 6
- 6aC. W. Li, J. Ciston, M. W. Kanan, Nature 2014, 508, 504–507;
- 6bA. Verdaguer-Casadevall, C. W. Li, T. P. Johansson, S. B. Scott, J. T. McKeown, M. Kumar, I. E. L. Stephens, M. W. Kanan, I. Chorkendorff, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 9808–9811;
- 6cA. Eilert, F. Cavalca, F. S. Roberts, J. Osterwalder, C. Liu, M. Favaro, E. J. Crumlin, H. Ogasawara, D. Friebel, L. G. M. Pettersson, A. Nilsson, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 285–290.
- 7T.-J. Huang, D.-H. Tsai, Catal. Lett. 2003, 87, 173–178.
- 8Z. Zhang, H. Wu, Z. Yu, R. Song, K. Qian, X. Chen, J. Tian, W. Zhang, W. Huang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 4276–4280; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 4320–4324.
- 9
- 9aY. Bu, J. W. H. Niemantsverdriet, H. O. A. Fredriksson, ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 2867–2876;
- 9bB. Eren, C. Heine, H. Bluhm, G. A. Somorjai, M. Salmeron, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 11186–11190.
- 10B. Eren, D. Zherebetskyy, L. L. Patera, C. H. Wu, H. Bluhm, C. Africh, L.-W. Wang, G. A. Somorjai, M. Salmeron, Science 2016, 351, 475–478.
- 11
- 11aG. Zhou, L. Luo, L. Li, J. Ciston, E. A. Stach, J. C. Yang, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 235502;
- 11bG. Zhou, L. Luo, L. Li, J. Ciston, E. A. Stach, W. A. Saidi, J. C. Yang, Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 10862–10864;
- 11cL. Luo, L. Li, J. Ciston, W. A. Saidi, E. A. Stach, J. C. Yang, G. Zhou, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 136104.
- 12
- 12aF. Jensen, F. Besenbacher, E. Laegsgaard, I. I. Stensgaard, Phys. Rev. B 1990, 42, 9206–9209;
- 12bM. Lee, A. J. H. McGaughey, Surf. Sci. 2010, 604, 1425–1431.
- 13L.-N. Wu, Z.-Y. Tian, W. Qin, J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 16733–16740.