A Crystallographic Charge Density Study of the Partial Covalent Nature of Strong N⋅⋅⋅Br Halogen Bonds
Mihael Eraković
Department of Physical Chemistry, Rudjer Bošković Institute, Bijenička 54, HR-10000 Zagreb, Croatia
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dominik Cinčić
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, University of Zagreb, Horvatovac 102a, HR-10000 Zagreb, Croatia
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Krešimir Molčanov
Department of Physical Chemistry, Rudjer Bošković Institute, Bijenička 54, HR-10000 Zagreb, Croatia
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Vladimir Stilinović
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, University of Zagreb, Horvatovac 102a, HR-10000 Zagreb, Croatia
Search for more papers by this authorMihael Eraković
Department of Physical Chemistry, Rudjer Bošković Institute, Bijenička 54, HR-10000 Zagreb, Croatia
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dominik Cinčić
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, University of Zagreb, Horvatovac 102a, HR-10000 Zagreb, Croatia
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Krešimir Molčanov
Department of Physical Chemistry, Rudjer Bošković Institute, Bijenička 54, HR-10000 Zagreb, Croatia
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Vladimir Stilinović
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, University of Zagreb, Horvatovac 102a, HR-10000 Zagreb, Croatia
Search for more papers by this authorIn memory of Professor Drago Grdenić (1919–2018)
Graphical Abstract
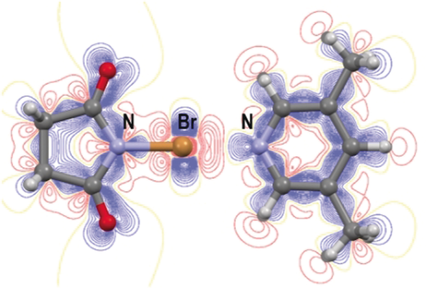
Crystallographic charge density analysis of a strong N−Br⋅⋅⋅N halogen bond in a N-bromosuccinimide and 3,5-dimethylpyridine co-crystal (NBS-lut) reveals a partially covalent character. Comparisons with pure crystalline NBS and the covalent bond in a bis(3-methylpyridine)bromonium cation suggest that there is a continuum of interactions between the intermolecular “non-bonding” halogen bond and a three centre–two electron covalent bond.
Abstract
The covalent nature of strong N−Br⋅⋅⋅N halogen bonds in a cocrystal (2) of N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) with 3,5-dimethylpyridine (lut) was determined from X-ray charge density studies and compared to a weak N−Br⋅⋅⋅O halogen bond in pure crystalline NBS (1) and a covalent bond in bis(3-methylpyridine)bromonium cation (in its perchlorate salt (3). In 2, the donor N−Br bond is elongated by 0.0954 Å, while the Br⋅⋅⋅acceptor distance of 2.3194(4) is 1.08 Å shorter than the sum of the van der Waals radii. A maximum electron density of 0.38 e Å−3 along the Br⋅⋅⋅N halogen bond indicates a considerable covalent contribution to the total interaction. This value is intermediate to 0.067 e Å−3 for the Br⋅⋅⋅O contact in 1, and approximately 0.7 e Å−3 in both N−Br bonds of the bromonium cation in 3. A calculation of the natural bond order charges of the contact atoms, and the σ*(N1−Br) population of NBS as a function of distance between NBS and lut, have shown that charge transfer becomes significant at a Br⋅⋅⋅N distance below about 3 Å.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201908875-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf4.1 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aG. Cavallo, P. Metrangolo, R. Milani, T. Pilati, A. Priimagi, G. Resnati, G. Terraneo, Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 2478–2601;
- 1bG. R. Desiraju, P. S. Ho, L. Kloo, A. C. Legon, R. Marquardt, P. Metrangolo, P. Politzer, G. Resnati, K. Rissanen, Pure Appl. Chem. 2013, 85, 1711–1713;
- 1cA. Farina, S. V. Meille, M. T. Messina, P. Metrangolo, G. Resnati, G. Vecchio, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 2433–2436;
10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19990816)38:16<2433::AID-ANIE2433>3.0.CO;2-D CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google ScholarAngew. Chem. 1999, 111, 2585–2588;10.1002/(SICI)1521-3757(19990816)111:16<2585::AID-ANGE2585>3.0.CO;2-X Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 1dE. Corradi, S. V. Meille, M. T. Messina, P. Metrangolo, G. Resnati, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 1782–1786;
10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(20000515)39:10<1782::AID-ANIE1782>3.0.CO;2-5 CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google ScholarAngew. Chem. 2000, 112, 1852–1856.10.1002/(SICI)1521-3757(20000515)112:10<1852::AID-ANGE1852>3.0.CO;2-7 Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 2
- 2aA. Priimagi, G. Cavallo, P. Metrangolo, G. Resnati, Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2686–2695;
- 2bM. Erdélyi, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3547–3557;
- 2cD. W. Bruce, P. Metrangolo, F. Meyer, T. Pilati, C. Präsang, G. Resnati, G. Terraneo, S. G. Wainwright, A. C. Whitwood, Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 9511–9524;
- 2dM. A. Sinnwell, L. R. MacGillivray, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 3477–3480; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 3538–3541;
- 2eD. Cinčić, T. Friščić, W. Jones, Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 747–753;
- 2fM. Branca, V. Dichiarante, C. Esterhuysen, P. M. J. Szell, Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 11615–11621;
- 2gK. Lisac, F. Topić, M. Arhangelskis, S. Cepić, P. A. Julien, C. W. Nickels, A. J. Morris, T. Friščić, D. Cinčić, Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 61.
- 3
- 3aK. Raatikainen, J. Huuskonen, M. Lahtinen, P. Metrangolo, K. Rissanen, Chem. Commun. 2009, 2160–2162;
- 3bC. B. Aakeröy, T. K. Wijethunga, M. A. Haj, J. Desper, C. Moore, CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 7218–7225;
- 3cD. Yan, A. Delori, G. O. Lloyd, T. Friščić, G. M. Day, W. Jones, J. Lu, M. Wei, D. G. Evans, X. Duan, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 12483–12486; Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 12691–12694;
- 3dR. W. Troff, T. Mäkelä, F. Topić, A. Valkonen, K. Raatikainen, K. Rissanen, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 1617–1637;
- 3eR. B. Walsh, C. W. Padgett, P. Metrangolo, G. Resnati, T. W. Hanks, W. T. Pennington, Cryst. Growth Des. 2001, 1, 165–175;
- 3fN. Bedeković, V. Stilinović, T. Friščić, D. Cinčić, New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 10584–10591;
- 3gA. Carletta, M. Zbačnik, M. Van Gysel, M. Vitković, N. Tumanov, V. Stilinović, J. Wouters, D. Cinčić, Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 6833–6842.
- 4
- 4aP. Auffinger, F. A. Hays, E. Westhof, P. S. Ho, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 16789–16794;
- 4bJ. Fanfrlík, F. X. Ruiz, A. Kadlčíková, J. Řezáč, A. Cousido-Siah, A. Mitschler, S. Haldar, M. Lepšík, M. H. Kolář, P. Majer, A. D. Podjarny, P. Hobza, ACS Chem. Biol. 2015, 10, 1637–1642.
- 5
- 5aR. S. Mulliken, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1950, 72, 600–608;
- 5bR. S. Mulliken, J. Phys. Chem. 1952, 56, 801–822.
- 6
- 6aT. Brinck, J. S. Murray, P. Politzer, Int. J. Quantum Chem. 1992, 44, 57–64;
- 6bT. Brinck, J. S. Murray, P. Politzer, Int. J. Quantum Chem. 1993, 48, 73–88;
- 6cJ. S. Murray, P. Lane, T. Clark, P. Politzer, J. Mol. Model. 2007, 13, 1033–1038;
- 6dP. Politzer, J. S. Murray, T. Clark, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 7748–7757;
- 6eK. E. Riley, J. S. Murray, J. Fanfrlík, J. Rezáč, R. J. Solá, M. C. Concha, F. M. Ramos, P. Politzer, J. Mol. Model. 2011, 17, 3309–3318;
- 6fT. Clark, M. Hennemann, J. S. Murray, P. Politzer, J. Mol. Model. 2007, 13, 291–296;
- 6gP. Politzer, P. Lane, M. C. Concha, Y. Ma, J. S. Murray, J. Mol. Model. 2007, 13, 305–311;
- 6hP. Politzer, J. S. Murray, T. Clark, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 11178–11189;
- 6iP. Politzer, J. S. Murray, ChemPhysChem 2013, 14, 278–294;
- 6jM. Kolář, J. Hostaš, P. Hobza, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 9987–9996;
- 6kP. Politzer, J. S. Murray, T. Clark, J. Mol. Model. 2015, 21, 52;
- 6lM. H. Kolar, P. Hobza, Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 5155–5187.
- 7
- 7aL. P. Wolters, F. M. Bickelhaupt, ChemistryOpen 2012, 1, 96–105;
- 7bS. V. Rosokha, C. L. Stern, J. T. Ritzert, Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 8774–8788;
- 7cB. Pinter, N. Nagels, W. A. Herrebout, F. De Proft, Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 519–530;
- 7dS. M. Huber, J. D. Scanlon, E. Jimenez-Izal, J. M. Ugalde, I. Infante, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 10350–10357;
- 7eM. Huber, E. Jimenez-Izal, J. M. Ugalde, I. Infante, Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 7708–7710;
- 7fP. Wolters, P. Schyman, M. J. Pavan, W. L. Jorgensen, F. M. Bickelhaupt, S. Kozuch, Wiley Interdiscip. Rev.: Comput. Mol. Sci. 2014, 4, 523–540;
- 7gC. Wang, D. Danovich, Y. Mo, S. Shaik, J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2014, 10, 3726–3737;
- 7hL. P. Wolters, N. W. G. Smits, C. Fonseca Guerra, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 1585–1592;
- 7iS. W. Robinson, C. L. Mustoe, N. G. White, A. Brown, A. L. Thompson, P. Kennepohl, P. Beer, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 499–507;
- 7jV. Oliveira, E. Kraka, D. Cremer, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 33031–33046;
- 7kV. Oliveira, E. Kraka, D. Cremer, Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 488–502.
- 8
- 8aC. Weinberger, R. Hines, M. Zeller, S. V. Rosokha, Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 8060–8063;
- 8bS. K. Nayak, G. Terraneo, Q. Piacevoli, F. Bertolotti, P. Scilabra, J. T. Brown, S. V. Rosokha, G. Resnati, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 12456–12459; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 12586–12589.
- 9E. Aubert, E. Espinosa, I. Nicolas, O. Jeannin, M. Fourmigué, Faraday Discuss. 2017, 203, 389–406.
- 10J. Crugeiras, A. Rios, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 30961–30971.
- 11
- 11aM. E. Brezgunova, E. Aubert, S. Dahaoui, P. Fertey, S. Lebegue, C. Jelsch, J. G. Angyan, E. Espinosa, Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 12, 5373–5386;
- 11bR. Shukla, N. Claiser, M. Souhassou, C. Lecomte, S. J. Balkrishna, S. Kumar, D. Chopra, IUCrJ 2018, 5, 647–653;
- 11cR. Wang, D. Hartnick, U. Englert, Z. Kristallogr. 2018, 233, 733–744;
- 11dA. Forni, D. Franchini, F. Dapiaggi, S. Pieraccini, M. Sironi, P. Scilabra, T. Pilati, K. I. Petko, G. Resnati, Y. L. Yagupolkii, Cryst. Growth Des. 2019, 19, 1621–1631.
- 12
- 12aK. Raatikainen, K. Rissanen, CrystEngComm 2011, 13, 6972–6977;
- 12bK. Raatikainen, K. Rissanen, Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 1235–1239;
- 12cO. Makhotkina, J. Lieffrig, O. Jeannin, M. Fourmigué, E. Aubert, E. Espinosa, Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 3464–3473;
- 12dJ. Mavračić, D. Cinčić, B. Kaitner, CrystEngComm 2016, 18, 3343–3346;
- 12eV. Stilinović, G. Horvat, T. Hrenar, V. Nemec, D. Cinčić, Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 5244–5257;
- 12fM. Eraković, V. Nemec, T. Lež, I. Porupski, V. Stilinović, D. Cinčić, Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 1182–1190;
- 12gP. Metrangolo, G. Resnati, T. Pilati, S. Biella, Struct. Bonding 2008, 126, 105–136.
- 13
- 13aG. Zundel, H. Metzger, Z. Phys. Chem. 1968, 58, 225–254;
- 13bK. Molčanov, C. Jelsch, E. Wenger, J. Stare, A. Ø. Madsen, B. Kojić-Prodić, CrystEngComm 2017, 19, 3898–3901.
- 14J. Emsley, Chem. Soc. Rev. 1980, 9, 91–124.
- 15P. Munshi, T. N. Guru Row, Crystallogr. Rev. 2005, 11, 199–241.