Diagonally Related s- and p-Block Metals Join Forces: Synthesis and Characterization of Complexes with Covalent Beryllium–Aluminum Bonds
Graphical Abstract
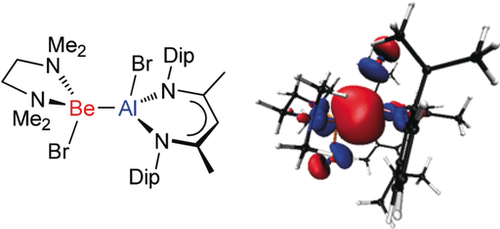
Bondage partners: The first examples of compounds containing beryllium–aluminum bonds are prepared by additions of beryllium–halide bonds, in simple beryllium dihalide adducts, across the metal center of an aluminum(I) heterocycle (see picture, Dip=2,6-diisopropylphenyl). Computational studies reveal the covalent Be-Al bonds to be weakly polarized, and high in s-character.
Abstract
Additions of beryllium–halide bonds in the simple beryllium dihalide adducts, [BeX2(tmeda)] (X=Br or I, tmeda=N,N,N′,N′-tetramethylethylenediamine), across the metal center of a neutral aluminum(I) heterocycle, [:Al(DipNacnac)] (DipNacnac=[(DipNCMe)2CH]−, Dip=2,6-diisopropylphenyl), have yielded the first examples of compounds with beryllium–aluminum bonds, [(DipNacnac)(X)Al-Be(X)(tmeda)]. For sake of comparison, isostructural Mg–Al and Zn–Al analogues of these complexes, viz. [(DipNacnac)(X)Al-M(X)(tmeda)] (M=Mg or Zn, X=I or Br) have been prepared and structurally characterized. DFT calculations reveal all compounds to have high s-character metal–metal bonds, the polarity of which is consistent with the electronegativities of the metals involved. Preliminary reactivity studies of [(DipNacnac)(Br)Al-Be(Br)(tmeda)] are reported.