Unraveling the Interfacial Charge Migration Pathway at the Atomic Level in a Highly Efficient Z-Scheme Photocatalyst
Dr. Pengfei Wang
MOE Key Laboratory of Pollution Processes and Environmental Criteria, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Environmental Remediation and Pollution Control, College of Environmental Science and Engineering, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300350 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYueshuang Mao
MOE Key Laboratory of Pollution Processes and Environmental Criteria, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Environmental Remediation and Pollution Control, College of Environmental Science and Engineering, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300350 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Lina Li
Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility, Shanghai Advanced Research Institute, Shanghai, 201800 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Zhurui Shen
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300350 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorXiao Luo
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Reaction Dynamics, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Kaifeng Wu
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Reaction Dynamics, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Pengfei An
Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility, Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Haitao Wang
MOE Key Laboratory of Pollution Processes and Environmental Criteria, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Environmental Remediation and Pollution Control, College of Environmental Science and Engineering, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300350 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorLina Su
MOE Key Laboratory of Pollution Processes and Environmental Criteria, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Environmental Remediation and Pollution Control, College of Environmental Science and Engineering, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300350 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Yi Li
Department of Chemistry, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Sihui Zhan
MOE Key Laboratory of Pollution Processes and Environmental Criteria, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Environmental Remediation and Pollution Control, College of Environmental Science and Engineering, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300350 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Pengfei Wang
MOE Key Laboratory of Pollution Processes and Environmental Criteria, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Environmental Remediation and Pollution Control, College of Environmental Science and Engineering, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300350 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYueshuang Mao
MOE Key Laboratory of Pollution Processes and Environmental Criteria, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Environmental Remediation and Pollution Control, College of Environmental Science and Engineering, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300350 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Lina Li
Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility, Shanghai Advanced Research Institute, Shanghai, 201800 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Zhurui Shen
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300350 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorXiao Luo
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Reaction Dynamics, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Kaifeng Wu
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Reaction Dynamics, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, 116023 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Pengfei An
Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility, Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Haitao Wang
MOE Key Laboratory of Pollution Processes and Environmental Criteria, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Environmental Remediation and Pollution Control, College of Environmental Science and Engineering, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300350 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorLina Su
MOE Key Laboratory of Pollution Processes and Environmental Criteria, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Environmental Remediation and Pollution Control, College of Environmental Science and Engineering, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300350 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Yi Li
Department of Chemistry, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Sihui Zhan
MOE Key Laboratory of Pollution Processes and Environmental Criteria, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Environmental Remediation and Pollution Control, College of Environmental Science and Engineering, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300350 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorDedicated to the 100th anniversary of Nankai University
Graphical Abstract
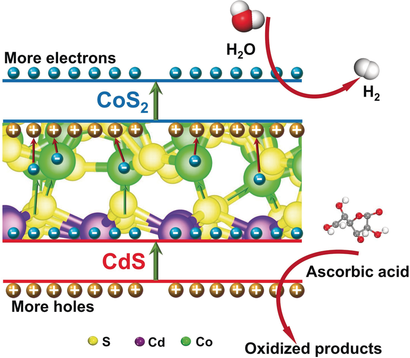
A whole lot of electrons and holes: A highly efficient Z-scheme photocatalyst was constructed from 1D CdS and 2D CoS2. Experimental and theoretical evidence suggests that the transition layer at the interface enables electrons to be transferred from CdS to CoS2, thus resulting in more photogenerated electrons and holes participating in the surface photocatalytic reaction.
Abstract
A highly efficient Z-scheme photocatalytic system constructed with 1D CdS and 2D CoS2 exhibited high photocatalytic hydrogen-evolution activity of 5.54 mmol h−1 g−1 with an apparent quantum efficiency of 10.2 % at 420 nm. More importantly, its interfacial charge migration pathway was unraveled: The electrons are efficiently transferred from CdS to CoS2 through a transition atomic layer connected by Co–S5.8 coordination, thus resulting in more photogenerated carriers participating in surface reactions. Furthermore, the charge-trapping and charge-transfer processes were investigated by transient absorption spectroscopy, which gave an estimated charge-separation yield of approximately 91.5 % and a charge-separated-state lifetime of approximately (5.2±0.5) ns in CdS/CoS2. This study elucidates the key role of interfacial atomic layers in heterojunctions and will facilitate the development of more efficient Z-scheme photocatalytic systems.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201904571-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf2 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aB. Qiu, Q. Zhu, M. Du, L. Fan, M. Xing, J. Zhang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 2684–2688; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 2728–2732;
- 1bY. Wang, X. Liu, J. Liu, B. Han, X. Hu, F. Yang, Z. Xu, Y. Li, S. Jia, Z. Li, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 5765–5771; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 5867–5873;
- 1cJ. Li, X. Wu, W. Pan, G. Zhang, H. Chen, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 491–495; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 500–504;
- 1dJ. Ran, B. Zhu, S. Z. Qiao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 10373–10377; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 10509–10513;
- 1eY. Cao, S. Chen, Q. Luo, H. Yan, Y. Lin, W. Liu, L. Cao, J. Lu, J. Yang, T. Yao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 12191–12196; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 12359–12364;
- 1fH. Li, Y. Sun, Z. Yuan, Y. Zhu, T. Ma, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 3222–3227; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 3276–3281.
- 2
- 2aJ. Li, G. Zhan, Y. Yu, L. Zhang, Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11480;
- 2bF. Chen, H. Huang, L. Guo, Y. Zhang, T. Ma, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201901361; Angew. Chem. 2019, https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201901361;
- 2cH. Yu, J. Li, Y. Zhang, S. Yang, K. Han, F. Dong, T. Ma, H. Huang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 3880–3884; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 3920–3924.
- 3S. J. A. Moniz, S. A. Shevlin, D. J. Martin, Z. Guo, J. W. Tang, Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 731.
- 4D. J. Martin, P. J. T. Reardon, S. J. A. Moniz, J. Tang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 12568.
- 5A. J. Bard, J. Photochem. 1979, 10, 59.
- 6
- 6aJ. Low, C. Jiang, B. Cheng, S. Wageh, A. A. Al-Ghamdi, J. Yu, Small Methods 2017, 1, 1700080;
- 6bM. Riedel, J. Wersig, A. Ruff, W. Schuhmann, A. Zouni, F. Lisdat, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 801–805; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 811–815.
- 7J. Hu, D. Chen, Z. Mo, N. Li, Q. Xu, H. Li, J. He, H. Xu, J. Lu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 2073–2077; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 2095–2099.
- 8L. Wang, X. Zheng, L. Chen, Y. Xiong, H. Xu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 3454–3458; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 3512–3516.
- 9Z. Jiang, W. Wan, H. Li, S. Yuan, H. Zhao, P. Wong, Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706108.
- 10J. Low, J. Yu, M. Jaroniec, S. Wageh, A. A. Al-Ghamdi, Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1601694.
- 11Y. Chen, S. Zhao, X. Wang, Q. Peng, R. Lin, Y. Wang, R. Shen, X. Cao, L. Zhang, G. Zhou, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 4286.
- 12S. Gao, X. Jiao, Z. Sun, W. Zhang, Y. Sun, C. Wang, Q. Hu, X. Zu, F. Yang, S. Yang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 698–702; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 708–712.
- 13N. Kornienko, J. Resasco, N. Becknell, C. Jiang, Y. Liu, K. Nie, X. Sun, J. Guo, S. R. Leone, P. Yang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 7448.
- 14P. Cai, J. Huang, J. Chen, Z. Wen, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 4858–4861; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 4936–4939.
- 15K. Mudiyanselage, S. D. Senanayake, L. Feria, S. Kundu, A. E. Baber, J. Graciani, A. B. Vidal, S. Agnoli, J. Evans, R. Chang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 5101–5105; Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 5205–5209.
- 16J. Liu, E. Hua, J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 25827.
- 17P. Wang, Z. Shen, Y. Xia, H. Wang, L. Zheng, W. Xi, S. Zhan, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1807013.
- 18M. Xie, X. Fu, L. Jing, L. Peng, Y. Feng, H. Fu, Adv. Energy Mater. 2014, 4, 1300995.
- 19J. Su, X. X. Zou, G. D. Li, X. Wei, C. Yan, Y. N. Wang, J. Zhao, L. J. Zhou, J. S. Chen, J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 8064.
- 20B. C. M. Martindale, G. A. M. Hutton, C. A. Caputo, S. Prantl, R. Godin, J. R. Durrant, E. Reisner, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 6459–6463; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 6559–6563.
- 21
- 21aK. Wu, H. Zhu, T. Lian, Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 851;
- 21bK. Wu, Z. Chen, H. Lv, H. Zhu, C. L. Hill, T. Lian, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 7708;
- 21cK. Wu, H. Zhu, Z. Liu, W. Rodríguez-Córdoba, T. Lian, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 10337.