Catalytic Enantioselective Synthesis of α-Chiral Azaheteroaryl Ethylamines by Asymmetric Protonation
Dr. Chao Xu
EaStCHEM, School of Chemistry, University of St Andrews, North Haugh, St Andrews, Fife, KY16 9ST UK
Search for more papers by this authorCalum W. Muir
Department of Pure and Applied Chemistry, University of Strathclyde, 295 Cathedral Street, Glasgow, G1 1XL UK
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Andrew G. Leach
School of Pharmacy and Biomolecular Sciences, Liverpool John Moores University, Byrom Street, Liverpool, L3 3AF UK
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Alan R. Kennedy
Department of Pure and Applied Chemistry, University of Strathclyde, 295 Cathedral Street, Glasgow, G1 1XL UK
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Allan J. B. Watson
EaStCHEM, School of Chemistry, University of St Andrews, North Haugh, St Andrews, Fife, KY16 9ST UK
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Chao Xu
EaStCHEM, School of Chemistry, University of St Andrews, North Haugh, St Andrews, Fife, KY16 9ST UK
Search for more papers by this authorCalum W. Muir
Department of Pure and Applied Chemistry, University of Strathclyde, 295 Cathedral Street, Glasgow, G1 1XL UK
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Andrew G. Leach
School of Pharmacy and Biomolecular Sciences, Liverpool John Moores University, Byrom Street, Liverpool, L3 3AF UK
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Alan R. Kennedy
Department of Pure and Applied Chemistry, University of Strathclyde, 295 Cathedral Street, Glasgow, G1 1XL UK
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Allan J. B. Watson
EaStCHEM, School of Chemistry, University of St Andrews, North Haugh, St Andrews, Fife, KY16 9ST UK
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
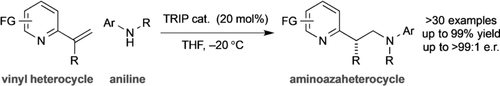
The direct enantioselective synthesis of chiral azaheteroaryl ethylamines from vinyl-substituted N-heterocycles and anilines is reported. A chiral phosphoric acid catalyst promotes dearomatizing aza-Michael addition to generate a prochiral exocyclic aryl enamine, which undergoes asymmetric protonation upon rearomatization, giving the products in high selectivity.
Abstract
The direct enantioselective synthesis of chiral azaheteroaryl ethylamines from vinyl-substituted N-heterocycles and anilines is reported. A chiral phosphoric acid (CPA) catalyst promotes dearomatizing aza-Michael addition to give a prochiral exocyclic aryl enamine, which undergoes asymmetric protonation upon rearomatization. The reaction accommodates a broad range of N-heterocycles, nucleophiles, and substituents on the prochiral centre, generating the products in high enantioselectivity. DFT studies support a facile nucleophilic addition based on catalyst-induced LUMO lowering, with site-selective, rate-limiting, intramolecular asymmetric proton transfer from the ion-paired prochiral intermediate.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201806956-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf14.7 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1For general information, see:
- 1aNational Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Database; CID=1001, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/1001 (accessed April 12, 2018);
- 1b The Merck Index—An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals, 13th ed. ), Merck and Co., New Jersey, 2001.
- 2For a review on the general use of azaarenes in asymmetric catalysis, see: D. Best, H. W. Lam, J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 831–845.
- 3For selected examples, see:
- 3aQ. Hu, A. Kondoh, M. Terada, Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 4348–4351;
- 3bG. Bertuzzi, D. Pecorari, L. Bernardi, M. Fochi, Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 3977–3980;
- 3cS. Yu, H. L. Sang, S. Ge, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 15896–15900; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 16112–16116;
- 3dM. Meazza, F. Tur, N. Hammer, K. A. Jørgensen, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 1634–1638; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 1656–1660;
- 3eJ. Izquierdo, A. Landa, I. Bastida, R. López, M. Oiarbide, C. Palomo, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 3282–3285;
- 3fY.-Y. Wang, K. Kanomata, T. Korenaga, M. Terada, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 927–931; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 939–943;
- 3gH. B. Hepburn, P. Melchiorre, Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 3520–3523;
- 3hA. Saxena, B. Choi, H. W. Lam, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 8428–8431;
- 3iH.-W. Sun, Y.-H. Liao, Z.-J. Wu, H.-Y. Wang, X.-M. Zhang, W.-C. Yuan, Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 3991–3996;
- 3jG. Pattison, G. Piraux, H. W. Lam, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 14373–14375;
- 3kL. Rupnicki, A. Saxena, H. W. Lam, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 10386–10387;
- 3lA. Baschieri, L. Bernardi, A. Ricci, S. Suresh, M. F. A. Adamo, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 9342–9345; Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 9506–9509.
- 4For a review on asymmetric hydrogenation of enamines, see: J.-H. Xie, S.-F. Zhu, Q.-L. Zhou, Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 1713–1760.
- 5T. E. Müller, K. C. Hultzsch, M. Yus, H. Foubelo, M. Tada, Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 3795–3892.
- 6During the preparation of this manuscript, two catalytic enantioselective preparations of α-stereocentres using a combined CPA/photoredox catalysis approach were reported; see:
- 6aR. S. J. Proctor, H. J. Davis, R. J. Phipps, Science 2018, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aar6376;
- 6bY. Yin, Y. Dai, H. Jia, J. Li, L. Bu, B. Qiao, X. Zhao, Z. Jiang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 6083–6087.
- 7For examples, see:
- 7aH. E. Reich, R. Levine, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1955, 77, 5434–5436;
- 7bH. E. Reich, R. Levine, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1955, 77, 4913–4915.
- 8For a recent CPA-catalysed conjugate addition of a nucleophilic carbon radical to vinyl azaheterocycles, see Ref. [6b].
- 9For previous organocatalysed conjugate additions to vinyl heterocycles, see Refs. [3b] and [3e].
- 10For reviews on the use of chiral counterions in catalysis, see:
- 10aT. Akiyama, K. Mori, Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 9277–9306;
- 10bM. Mahlau, B. List, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 518–533; Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 540–556;
- 10cK. Brak, E. N. Jacobsen, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 534–561; Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 558–588;
- 10dD. Kampen, C. M. Reisinger, B. List, Top. Curr. Chem. 2010, 291, 395–456;
- 10eT. Akiyama, Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 5744–5758.
- 11For reviews on asymmetric protonation, see:
- 11aJ. T. Mohr, A. Y. Hong, B. M. Stoltz, Nat. Chem. 2009, 1, 359–369;
- 11bS. Oudeyer, J.-F. Brière, V. Levacher, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 6103–6119;
- 11cJ. P. Phelan, J. A. Ellman, Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2016, 12, 1203–1228.
- 12For a recent demonstration of CPA-catalysed enantioselective olefin functionalization, see: N. Tsuji, J. L. Kennemur, T. Buyck, S. Lee, S. Prévost, P. S. J. Kaib, D. Bykov, C. Farès, B. List, Science 2018, 359, 1501–1505.
- 13For a review, see: J. T. M. Correia, Synlett 2015, 26, 416–417.
- 14L. P. Masic, Curr. Med. Chem. 2006, 13, 3627–3648.
- 15For examples, see: R. J. D. Hatley, S. J. F. Macdonald, R. J. Slack, J. Le, S. B. Ludbrook, P. T. Lukey, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 3298–3321; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 3354–3379.
- 16C. A. Hunter, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 5310–5324; Angew. Chem. 2004, 116, 5424–5439.
- 17M. J. Frisch et al., Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford CT, 2009.
- 18Y. Zhao, D. G. Truhlar, Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 157–167.
- 19Y. Zhao, D. G. Truhlar, Theor. Chem. Acc. 2008, 120, 215–241.
- 20J. Tomasi, B. Mennucci, R. Cammi, Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 2999–3094.
- 21P. C. Hariharan, J. A. Pople, Theor. Chim. Acta 1973, 28, 213–222.