Chemical-Reaction-Induced Hot Electron Flows on Platinum Colloid Nanoparticles under Hydrogen Oxidation: Impact of Nanoparticle Size†
The work was supported by IBS-R004-G4, Republic of Korea, and by the Director, Office of Science, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, Division of Chemical Science, Geological and Biosciences of the US Department of Energy under contract DE-AC02-05CH11231.
Graphical Abstract
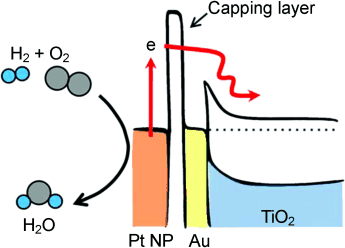
Catalytic nanodiodes: Chemically induced hot electron flows on Pt nanoparticles were measured using Au/TiO2 nanodiodes (see picture) and showed the correlation of chemicurrent with catalytic activity. The catalytic nanodiodes with smaller Pt nanoparticles lead to higher chemicurrent, and the temperature dependence is similar to that of the turnover frequency.
Abstract
Generation of hot electron flows and the catalytic activity of Pt nanoparticles (NPs) with different sizes were investigated using catalytic nanodiodes. We show that smaller Pt NPs lead to higher chemicurrent yield, which is associated with the shorter travel length for the hot electrons, compared with their inelastic mean free path. We also show the impact of capping on charge carrier transfer between Pt NPs and their support.