The Oxidation of Thiols by Flavoprotein Oxidases: a Biocatalytic Route to Reactive Thiocarbonyls†
This work was carried out within the BE-Basic R&D Program, for which an FES subsidy was granted from the Dutch Ministry of Economic Affairs, Agriculture, and Innovation (EL&I).
Graphical Abstract
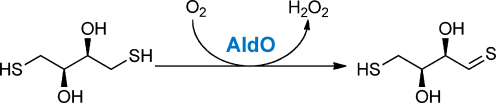
An all-around player: Numerous classical flavin-dependent alcohol oxidases, such as alditol oxidase (AldO), which are well-known for their activity towards CO and CN bonds, can also catalyze the oxidation of thiols (see picture). This method provides a potential biocatalytic route to reactive thiocarbonyl compounds.
Abstract
Flavoprotein oxidases are a diverse class of biocatalysts, most of which catalyze the oxidation of CO, CN, or CC bonds. Flavoprotein oxidases that are known to catalyze the oxidation of CS bonds are rare, being limited to enzymes that catalyze the oxidative cleavage of thioethers. Herein, we report that various flavoprotein oxidases, previously thought to solely act on alcohols, also catalyze the oxidation of thiols to thiocarbonyls. These results highlight the versatility of enzymatic catalysis and provide a potential biocatalytic route to reactive thiocarbonyl compounds, which have a variety of applications in synthetic organic chemistry.