Nickel-Catalyzed α-Arylation of Ketones with Phenol Derivatives†
We thank Dr. Yasutomo Segawa and Dr. Hideto Ito for assistance with X-ray crystal structure analysis. Dr. Keiko Kuwata (ITbM) is acknowledged for HRMS measurements. We thank Prof. Cathleen M. Crudden for discussions. This work was supported by the Funding Program for Next Generation World-Leading Researchers from JSPS (220GR049 to K.I.), a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas “Molecular Activation Directed toward Straightforward Synthesis” (25105720 to J.Y.), KAKENHI (25708005 to J.Y.) from MEXT, and a JSPS research fellowship for young scientists (to K.M.). ITbM is supported by the World Premier International Research Center (WPI) Initiative (Japan).
Graphical Abstract
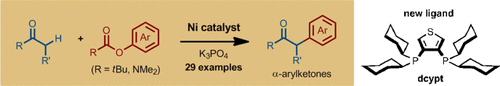
The nickel-catalyzed α-arylation of ketones with readily available phenol derivatives (esters and carbamates) provides access to useful α-arylketones. The use of 3,4-bis(dicyclohexylphosphino)thiophene (dcypt) as an air-stable ligand enables this transformation. The intermediate of an assumed CO oxidative addition was isolated and characterized by X-ray crystal-structure analysis.
Abstract
The nickel-catalyzed α-arylation of ketones with readily available phenol derivatives (esters and carbamates) provides access to useful α-arylketones. For this transformation, 3,4-bis(dicyclohexylphosphino)thiophene (dcypt) was identified as a new, enabling, air-stable ligand for this transformation. The intermediate of an assumed CO oxidative addition was isolated and characterized by X-ray crystal-structure analysis.