Highlight
Copper-Catalyzed Regio- and Enantioselective Hydroamination of Alkenes with Hydroxylamines
Dr. Kevin D. Hesp,
Corresponding Author
Dr. Kevin D. Hesp
Worldwide Medicinal Chemistry, Pfizer, Inc. Eastern Point Rd., Groton, CT 06340 (USA)
Worldwide Medicinal Chemistry, Pfizer, Inc. Eastern Point Rd., Groton, CT 06340 (USA)Search for more papers by this authorDr. Kevin D. Hesp,
Corresponding Author
Dr. Kevin D. Hesp
Worldwide Medicinal Chemistry, Pfizer, Inc. Eastern Point Rd., Groton, CT 06340 (USA)
Worldwide Medicinal Chemistry, Pfizer, Inc. Eastern Point Rd., Groton, CT 06340 (USA)Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
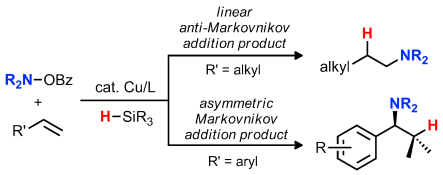
Adding value: The catalytic hydroamination of alkenes with amines holds promise to rapidly deliver value-added chiral amines from simple and accessible starting materials. The use of mild, Cu-catalyzed electrophilic amination strategies for the regioselective preparation of both linear and chiral branched amines is highlighted.
References
- 1
- 1a Chiral Amine Synthesis (Ed: ), Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2010;
- 1bM. T. Robak, M. A. Herbage, J. A. Ellman, Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 3600;
- 1cJ.-H. Xie, S.-F. Zhu, Q.-L. Zhou, Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 1713.
- 2For reviews, see:
- 2aT. E. Müller, M. Beller, Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 675;
- 2bT. E. Müller, K. C. Hultzsch, M. Yus, F. Foubelo, M. Tada, Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 3795;
- 2cK. D. Hesp, M. Stradiotto, ChemCatChem 2010, 2, 1192;
- 2dJ. F. Hartwig, Organotransition Metal Chemistry: From Bonding to Catalysis, University Science Books, Sausalito, CA, 2010, p. 700;
- 2eJ. Hannedouche, E. Schulz, Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 4972;
- 2fM. Beller, J. Seayad, A. Tillack, H. Jiao, Angew. Chem. 2004, 116, 3448;
10.1002/ange.200300616 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 3368.
- 3For lead references on asymmetric intermolecular hydroaminations, see:
- 3aS. Pan, K. Endo, T. Shibata, Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 780;
- 3bC. S. Sevov, J. Zhou, J. F. Hartwig, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 11960;
- 3cJ. R. Zhou, J. F. Hartwig, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 1345;
- 3dK. L. Butler, M. Tragni, R. A. Widenhoefer, Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 5265; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 5175.
- 4For lead references on anti-Markovnikov hydroaminations, see:
- 4aM. Beller, H. Trauthwein, M. Eichberger, C. Breindl, J. Herwig, T. E. Müller, O. R. Thiel, Chem. Eur. J. 1999, 5, 1306;
10.1002/(SICI)1521-3765(19990401)5:4<1306::AID-CHEM1306>3.0.CO;2-4 CAS Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 4bM. Utsunomiya, R. Kuwano, M. Kawatsura, J. F. Hartwig, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 5608;
- 4cM. Utsunomiya, J. F. Hartwig, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 2702;
- 4dC. Brinkmann, A. G. M. Barrett, M. S. Hill, P. A. Procopiou, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 2193.
- 5For reviews and lead references on the preparation and use of electrophilic nitrogen sources in synthesis, see:
- 5aA. M. Berman, J. S. Johnson, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 5680;
- 5bE. Erdik, M. Ay, Chem. Rev. 1989, 89, 1947;
- 5cT. J. Barker, E. R. Jarvo, Synthesis 2011, 3958;
- 5dG. Lalic, R. P. Rucker, Synlett 2013, 269.
- 6R. P. Rucker, A. M. Whittaker, H. Dang, G. Lalic, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 6571.
- 7Y. Miki, K. Hirano, T. Satoh, M. Miura, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 125, 11030;
10.1002/ange.201304365 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 10830.
- 8S. Zhu, N. Niljianskul, S. L. Buchwald, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 15746.
- 9N. Matsuda, K. Hirano, T. Satoh, M. Miura, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 4934.
- 10For seminal reports on the asymmetric synthesis of branched amines by hydroamination of terminal alkyl olefins, see:
- 10aZ. B. Zhang, S. D. Lee, R. A. Widenhoefer, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 5372;
- 10bA. L. Reznichenko, H. N. Nguyen, K. A. Hultzsch, Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 9168;
10.1002/ange.201004570 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 8984.