Epidithiodiketopiperazine Biosynthesis: A Four-Enzyme Cascade Converts Glutathione Conjugates into Transannular Disulfide Bridges†
Dr. Daniel H. Scharf
Depts. of Molecular and Applied Microbiology, Biomolecular Chemistry, and Bio Pilot Plant, Leibniz Institute for Natural Product Research and Infection Biology, HKI, Beutenbergstrasse 11a, 07745 Jena (Germany)
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorPranatchareeya Chankhamjon
Depts. of Molecular and Applied Microbiology, Biomolecular Chemistry, and Bio Pilot Plant, Leibniz Institute for Natural Product Research and Infection Biology, HKI, Beutenbergstrasse 11a, 07745 Jena (Germany)
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Kirstin Scherlach
Depts. of Molecular and Applied Microbiology, Biomolecular Chemistry, and Bio Pilot Plant, Leibniz Institute for Natural Product Research and Infection Biology, HKI, Beutenbergstrasse 11a, 07745 Jena (Germany)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Thorsten Heinekamp
Depts. of Molecular and Applied Microbiology, Biomolecular Chemistry, and Bio Pilot Plant, Leibniz Institute for Natural Product Research and Infection Biology, HKI, Beutenbergstrasse 11a, 07745 Jena (Germany)
Search for more papers by this authorKarsten Willing
Depts. of Molecular and Applied Microbiology, Biomolecular Chemistry, and Bio Pilot Plant, Leibniz Institute for Natural Product Research and Infection Biology, HKI, Beutenbergstrasse 11a, 07745 Jena (Germany)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Axel A. Brakhage
Depts. of Molecular and Applied Microbiology, Biomolecular Chemistry, and Bio Pilot Plant, Leibniz Institute for Natural Product Research and Infection Biology, HKI, Beutenbergstrasse 11a, 07745 Jena (Germany)
Friedrich Schiller University, Jena (Germany)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Christian Hertweck
Depts. of Molecular and Applied Microbiology, Biomolecular Chemistry, and Bio Pilot Plant, Leibniz Institute for Natural Product Research and Infection Biology, HKI, Beutenbergstrasse 11a, 07745 Jena (Germany)
Friedrich Schiller University, Jena (Germany)
Depts. of Molecular and Applied Microbiology, Biomolecular Chemistry, and Bio Pilot Plant, Leibniz Institute for Natural Product Research and Infection Biology, HKI, Beutenbergstrasse 11a, 07745 Jena (Germany)Search for more papers by this authorDr. Daniel H. Scharf
Depts. of Molecular and Applied Microbiology, Biomolecular Chemistry, and Bio Pilot Plant, Leibniz Institute for Natural Product Research and Infection Biology, HKI, Beutenbergstrasse 11a, 07745 Jena (Germany)
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorPranatchareeya Chankhamjon
Depts. of Molecular and Applied Microbiology, Biomolecular Chemistry, and Bio Pilot Plant, Leibniz Institute for Natural Product Research and Infection Biology, HKI, Beutenbergstrasse 11a, 07745 Jena (Germany)
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Kirstin Scherlach
Depts. of Molecular and Applied Microbiology, Biomolecular Chemistry, and Bio Pilot Plant, Leibniz Institute for Natural Product Research and Infection Biology, HKI, Beutenbergstrasse 11a, 07745 Jena (Germany)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Thorsten Heinekamp
Depts. of Molecular and Applied Microbiology, Biomolecular Chemistry, and Bio Pilot Plant, Leibniz Institute for Natural Product Research and Infection Biology, HKI, Beutenbergstrasse 11a, 07745 Jena (Germany)
Search for more papers by this authorKarsten Willing
Depts. of Molecular and Applied Microbiology, Biomolecular Chemistry, and Bio Pilot Plant, Leibniz Institute for Natural Product Research and Infection Biology, HKI, Beutenbergstrasse 11a, 07745 Jena (Germany)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Axel A. Brakhage
Depts. of Molecular and Applied Microbiology, Biomolecular Chemistry, and Bio Pilot Plant, Leibniz Institute for Natural Product Research and Infection Biology, HKI, Beutenbergstrasse 11a, 07745 Jena (Germany)
Friedrich Schiller University, Jena (Germany)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Christian Hertweck
Depts. of Molecular and Applied Microbiology, Biomolecular Chemistry, and Bio Pilot Plant, Leibniz Institute for Natural Product Research and Infection Biology, HKI, Beutenbergstrasse 11a, 07745 Jena (Germany)
Friedrich Schiller University, Jena (Germany)
Depts. of Molecular and Applied Microbiology, Biomolecular Chemistry, and Bio Pilot Plant, Leibniz Institute for Natural Product Research and Infection Biology, HKI, Beutenbergstrasse 11a, 07745 Jena (Germany)Search for more papers by this authorWe thank A. Perner for MS measurements, M. Poetsch for MALDI measurements, S. Fricke and C. Schult for technical assistance, P. Berthel for performing fermentations, M. Steinacker for downstream processing, P. Hortschansky for support in protein production, and A. Thywißen for providing the fluorescence microscope picture for the table of contents entry. This work was supported by the “Pakt für Forschung und Innovation” of the Free State of Thuringia and the BMBF, and the International Leibniz Research School for Biomolecular and Microbial Interactions (ILRS), as part of the excellence graduate school Jena School for Microbial Communication (JSMC).
Graphical Abstract
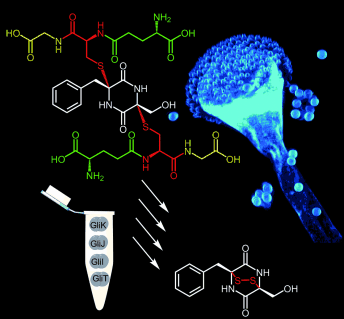
Enzyme quartet: Isolation of the first sulfur-bearing intermediate of the gliotoxin pathway in Aspergillus fumigatus and successful in vitro conversion of the bisglutathione adduct into an intact epidithiodiketopiperazine by a four-enzyme cascade (including glutamyltransferase GliK and dipeptidase GliJ) revealed an outstanding adaptation of a primary metabolic pathway into natural product biosynthesis that is widespread in fungi.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie_201305059_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf5.7 MB | miscellaneous_information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1A. D. Borthwick, Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 3641–3716.
- 2D. M. Gardiner, P. Waring, B. J. Howlett, Microbiology 2005, 151, 1021–1032.
- 3D. M. Vigushin, N. Mirsaidi, G. Brooke, C. Sun, P. Pace, L. Inman, C. J. Moody, R. C. Coombes, Med. Oncol. 2004, 21, 21–30.
- 4P. Waring, A. Sjaarda, Q. H. Lin, Biochem. Pharmacol. 1995, 49, 1195–1201.
- 5D. H. Scharf, T. Heinekamp, N. Remme, P. Hortschansky, A. A. Brakhage, C. Hertweck, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 467–472.
- 6C. J. Balibar, C. T. Walsh, Biochemistry 2006, 45, 15029–15038.
- 7C. Kupfahl, T. Heinekamp, G. Geginat, T. Ruppert, A. Hartl, H. Hof, A. A. Brakhage, Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 62, 292–302.
- 8R. A. Cramer, Jr., M. P. Gamcsik, R. M. Brooking, L. K. Najvar, W. R. Kirkpatrick, T. F. Patterson, C. J. Balibar, J. R. Graybill, J. R. Perfect, S. N. Abraham, W. J. Steinbach, Eukaryotic Cell 2006, 5, 972–980.
- 9S. Spikes, R. Xu, C. K. Nguyen, G. Chamilos, D. P. Kontoyiannis, R. H. Jacobson, D. E. Ejzykowicz, L. Y. Chiang, S. G. Filler, G. S. May, J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 479–486.
- 10D. H. Scharf, N. Remme, A. Habel, P. Chankhamjon, K. Scherlach, T. Heinekamp, P. Hortschansky, A. A. Brakhage, C. Hertweck, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 12322–12325.
- 11C. Davis, S. Carberry, M. Schrettl, I. Singh, J. C. Stephens, S. M. Barry, K. Kavanagh, G. L. Challis, D. Brougham, S. Doyle, Chem. Biol. 2011, 18, 542–552.
- 12D. H. Scharf, P. Chankhamjon, K. Scherlach, T. Heinekamp, M. Roth, A. A. Brakhage, C. Hertweck, Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 10211–10215;
10.1002/ange.201205041 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 10064–10068.
- 13D. H. Scharf, N. Remme, T. Heinekamp, P. Hortschansky, A. A. Brakhage, C. Hertweck, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 10136–10141.
- 14For an independent study on GliT see: M. Schrettl, S. Carberry, K. Kavanagh, H. Haas, G. W. Jones, J. O’Brien, A. Nolan, J. Stephens, O. Fenelon, S. Doyle, PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e 1000952.
- 15E. Szewczyk, T. Nayak, C. E. Oakley, H. Edgerton, Y. Xiong, N. Taheri-Talesh, S. A. Osmani, B. R. Oakley, Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 3111–3120.
- 16N. M. Llewellyn, Y. Li, J. B. Spencer, Chem. Biol. 2007, 14, 379–386.
- 17H. Kaur, D. Ganguli, A. K. Bachhawat, J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 8920–8931.
- 18A. Pastore, G. Federici, E. Bertini, F. Piemonte, Clin. Chim. Acta 2003, 333, 19–39.
- 19A. Braunshausen, F. P. Seebeck, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 1757–1759.
- 20M. F. Freeman, K. A. Moshos, M. J. Bodner, R. Li, C. A. Townsend, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11128–11133.
- 21F. P. Seebeck, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 6632–6633.
- 22N. J. Patron, R. F. Waller, A. J. Cozijnsen, D. C. Straney, D. M. Gardiner, W. C. Nierman, B. J. Howlett, BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 174.