Hierarchical Nanosheet-Based MoS2 Nanotubes Fabricated by an Anion-Exchange Reaction of MoO3–Amine Hybrid Nanowires†
Sifei Zhuo
Department of Chemistry, School of Science, Tianjin University and The Co-Innovation Center of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering of Tianjin, Tianjin 300072 (China)
These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorYou Xu
Department of Chemistry, School of Science, Tianjin University and The Co-Innovation Center of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering of Tianjin, Tianjin 300072 (China)
These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorWeiwei Zhao
Department of Chemistry, School of Science, Tianjin University and The Co-Innovation Center of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering of Tianjin, Tianjin 300072 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorJin Zhang
Department of Chemistry, School of Science, Tianjin University and The Co-Innovation Center of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering of Tianjin, Tianjin 300072 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Bin Zhang
Department of Chemistry, School of Science, Tianjin University and The Co-Innovation Center of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering of Tianjin, Tianjin 300072 (China)
Department of Chemistry, School of Science, Tianjin University and The Co-Innovation Center of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering of Tianjin, Tianjin 300072 (China)Search for more papers by this authorSifei Zhuo
Department of Chemistry, School of Science, Tianjin University and The Co-Innovation Center of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering of Tianjin, Tianjin 300072 (China)
These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorYou Xu
Department of Chemistry, School of Science, Tianjin University and The Co-Innovation Center of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering of Tianjin, Tianjin 300072 (China)
These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorWeiwei Zhao
Department of Chemistry, School of Science, Tianjin University and The Co-Innovation Center of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering of Tianjin, Tianjin 300072 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorJin Zhang
Department of Chemistry, School of Science, Tianjin University and The Co-Innovation Center of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering of Tianjin, Tianjin 300072 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Bin Zhang
Department of Chemistry, School of Science, Tianjin University and The Co-Innovation Center of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering of Tianjin, Tianjin 300072 (China)
Department of Chemistry, School of Science, Tianjin University and The Co-Innovation Center of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering of Tianjin, Tianjin 300072 (China)Search for more papers by this authorThis research was supported financially by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 20901057 and No. 11074185), the National Basic Research Program of China (2009CB939901), and the Innovation Foundation of Tianjin University.
Graphical Abstract
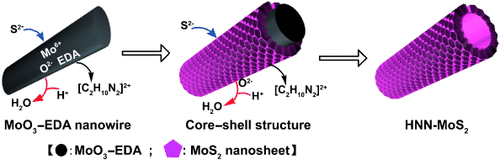
Moving onward and outward: MoO3–ethylenediamine (EDA) inorganic–organic hybrid nanowires were successfully transformed into hierarchical nanosheet-based MoS2 nanotubes (HNN-MoS2) by anion exchange with S2− anions at elevated temperature (see picture). The resulting nanotubes were highly active catalysts for photoelectrochemical hydrogen evolution by water splitting.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie_201303480_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf892.3 KB | miscellaneous_information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1S. Iijima, Nature 1991, 354, 56.
- 2
- 2aO. Y. Gutiérrez, A. Hrabar, J. Hein, Y. Yu, J. Han, J. A. Lercher, J. Catal. 2012, 295, 155;
- 2bM. Polyakov, S. Indris, S. Schwamborn, A. Mazheika, M. Poisot, L. Kienle, W. Bensch, M. Muhler, W. Grünert, J. Catal. 2008, 260, 236;
- 2cT. Drescher, F. Niefind, W. Bensch, W. Grünert, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 18896;
- 2dQ. Gao, C. Giordano, M. Antonietti, Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 11910; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 11740.
- 3
- 3aB. Seger, A. B. Laursen, P. C. K. Vesborg, T. Pedersen, O. Hansen, S. Dahl, I. Chorkendorff, Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 9262; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 9128;
- 3bY. Hou, A. B. Laursen, J. Zhang, G. Zhang, Y. Zhu, X. Wang, S. Dahl, I. Chorkendorff, Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 3709; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3621;
- 3cW. Zhou, Z. Yin, Y. Du, X. Huang, Z. Zeng, Z. Fan, H. Liu, J. Wang, H. Zhang, Small 2013, 9, 140;
- 3dX. Zong, H. Yan, G. Wu, G. Ma, F. Wen, L. Wang, C. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 7176;
- 3eF. A. Frame, F. E. Osterloh, J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 10628;
- 3fD. Merki, S. Fierro, H. Vrubel, X. Hu, Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 1262;
- 3gD. Merki, H. Vrubel, L. Rovelli, S. Fierro, X. Hu, Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 2515.
- 4M. S. Fuhrer, J. Hone, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 146.
- 5M. Chhowalla, G. A. Amaratunga, Nature 2000, 407, 164.
- 6
- 6aJ. Chen, N. Kuriyama, H. Yuan, H. T. Takeshita, T. Sakai, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 11813;
- 6bL. Ye, C. Wu, W. Guo, Y. Xie, Chem. Commun. 2006, 4738.
- 7
- 7aC. Zhang, Z. Wang, Z. Guo, X. W. Lou, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 3765;
- 7bL. Yang, S. Wang, J. Mao, J. Deng, Q. Gao, Y. Tang, O. G. Schmidt, Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1180;
- 7cK. Chang, W. Chen, ACS Nano 2011, 5, 4720;
- 7dY. Liang, R. Feng, S. Yang, H. Ma, J. Liang, J. Chen, Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 640;
- 7eH. Liu, D. Su, R. Zhou, B. Sun, G. Wang, S. Z. Qiao, Adv. Energy Mater. 2012, 2, 970;
- 7fX. L. Li, Y. D. Li, J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 13893.
- 8G. Ma, H. Peng, J. Mu, H. Huang, X. Zhou, Z. Lei, J. Power Sources 2013, 229, 72.
- 9
- 9aA. Yella, M. Kappl, M. Panthöfer, W. Tremel, Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 2629;
10.1002/ange.200902481 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 2575;
- 9bJ. Tannous, F. Dassenoy, B. Vacher, T. Le Mogne, A. Bruhacs, W. Tremel, Tribol. Lett. 2011, 41, 55;
- 9cY. Tian, Y. He, Y. Zhu, Mater. Chem. Phys. 2004, 87, 87;
- 9dH. S. S. Ramakrishna Matte, A. Gomathi, A. K. Manna, D. J. Late, R. Datta, S. K. Pati, C. N. R. Rao, Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 4153;
10.1002/ange.201000009 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 4059;
- 9eM. Nath, A. Govindaraj, C. N. R. Rao, Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 283.
- 10
- 10aM. Hershfinkel, L. A. Gheber, V. Volterra, J. L. Hutchison, R. Tenne, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 1914;
- 10bY. Feldman, E. Wasserman, D. J. Srolovitz, R. Tenne, Science 1995, 267, 222.
- 11D. H. Son, S. M. Hughes, Y. Yin, A. P. Alivisatos, Science 2004, 306, 1009.
- 12
- 12aE. Muthuswamy, S. L. Brock, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 15849;
- 12bR. D. Robinson, B. Sadtler, D. O. Demchenko, C. K. Erdonmez, L. W. Wang, A. P. Alivisatos, Science 2007, 317, 355;
- 12cK. Miszta, D. Dorfs, A. Genovese, M. R. Kim, L. Manna, ACS Nano 2011, 5, 7176.
- 13
- 13aJ. B. Rivest, P. K. Jain, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 89;
- 13bJ. Yao, S. Schachermeyer, Y. Yin, W. Zhong, Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 402;
- 13cY. Liu, J. Goebl, Y. Yin, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2610.
- 14
- 14aH. Tong, Y. J. Zhu, L. X. Yang, L. Li, L. Zhang, Angew. Chem. 2006, 118, 7903; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 7739;
- 14bH.-W. Liang, J.-W. Liu, H.-S. Qian, S.-H. Yu, Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, DOI: .
- 15aY. Yu, J. Zhang, X. Wu, W. Zhao, B. Zhang, Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 921; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 897;
- 15bX. Wu, Y. Yu, Y. Liu, Y. Xu, C. Liu, B. Zhang, Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 3265; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 3211.
- 16
- 16aY. Hou, F. Zuo, A. Dagg, P. Feng, Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 6464;
- 16bY. Hou, F. Zuo, A. Dagg, P. Feng, Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 1286; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 1248;
- 16cA. Kongkanand, R. M. Domínguez, P. V. Kamat, Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 676;
- 16dS. Chen, J. Duan, M. Jaroniec, S. Z. Qiao, J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, DOI: .
- 17Q. Gao, S. Wang, H. Fang, J. Weng, Y. Zhang, J. Mao, Y. Tang, J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 4709.
- 18C. Zhang, H. B. Wu, Z. Guo, X. W. Lou, Electrochem. Commun. 2012, 20, 7.
- 19
- 19aY. Feldman, V. Lyakhovitskaya, R. Tenne, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 4176;
- 19bZ. Chen, D. Cummins, B. N. Reinecke, E. Clark, M. K. Sunkara, T. F. Jaramillo, Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 4168.
- 20
- 20aE. Benavente, M. A. Santa Ana, F. Mendizábal, G. González, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2002, 224, 87;
- 20bK. K. Kam, B. A. Parkinson, J. Phys. Chem. 1982, 86, 463.
- 21T. F. Jaramillo, K. P. Jørgensen, J. Bonde, J. H. Nielsen, S. Horch, I. Chorkendorff, Science 2007, 317, 100.
- 22
- 22aJ. Kim, S. Byun, A. J. Smith, J. Yu, J. Huang, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 1227;
- 22bY. Li, H. Wang, L. Xie, Y. Liang, G. Hong, H. Dai, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 7296.