Polymer-Based Muscle Expansion and Contraction†
M.J.S. acknowledges funding from the University of Alberta (the Department of Chemistry and the Faculty of Science), the Natural Science and Engineering Research Council (NSERC), the Canada Foundation for Innovation (CFI), the Alberta Advanced Education & Technology Small Equipment Grants Program (AET/SEGP) and Grand Challenges Canada. M.J.S. acknowledges Mark McDermott for the use of the thermal evaporator.
Graphical Abstract
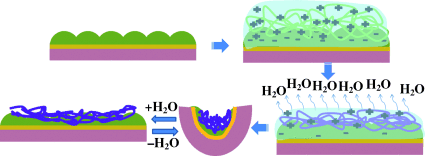
Weight lifting: A polymer-based device capable of lifting many times its own mass was fabricated by drying a solution of the polycation poly(diallyldimethyl ammonium chloride) (pDADMAC) on a surface coated with charged poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-based microgels. Upon drying of the pDADMAC solution on the microgel-modified surface, it bends. Flexible surfaces then curl up into scroll-like structures, which can be opened up at high humidity.