Ferroelectricity Driven by Twisting of Silicate Tetrahedral Chains†
Corresponding Author
Prof. Hiroki Taniguchi
Materials and Structures Laboratory, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Yokohama 226-8503 (Japan)
Current address: Department of Physics, Nagoya University, Furo-cho, Chikusa, Nagoya 464-8602 (Japan)
Materials and Structures Laboratory, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Yokohama 226-8503 (Japan)Search for more papers by this authorDr. Akihide Kuwabara
Nanostructures Research Laboratory (Japan) Fine Ceramics Center, Nagoya 456-8587 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Jungeun Kim
Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute, Sayo-gun, Hyogo 679-5198 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorYounghun Kim
Graduate School of Frontier Sciences, The University of Tokyo, Kashiwa, Chiba 277-8561 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Hiroki Moriwake
Nanostructures Research Laboratory (Japan) Fine Ceramics Center, Nagoya 456-8587 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Sungwng Kim
Department of Energy Science, Sungkyunkwan University, Jangan-Gu, Suwon 440-746 (Korea)
Search for more papers by this authorTakuya Hoshiyama
Department of Materials Science, Osaka Prefecture University, Sakai, Osaka 599-8531 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorTsukasa Koyama
Department of Materials Science, Osaka Prefecture University, Sakai, Osaka 599-8531 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Shigeo Mori
Department of Materials Science, Osaka Prefecture University, Sakai, Osaka 599-8531 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Masaki Takata
Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute, Sayo-gun, Hyogo 679-5198 (Japan)
Graduate School of Frontier Sciences, The University of Tokyo, Kashiwa, Chiba 277-8561 (Japan)
RIKEN Harima Institute, Sayo-gun, Hyogo 679-5148 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Hideo Hosono
Materials and Structures Laboratory, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Yokohama 226-8503 (Japan)
Frontier Research Center, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Yokohama 226-8503 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Yoshiyuki Inaguma
Faculty of Science, Gakushuin University, Toshima-ku, Tokyo 171-8588 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Mitsuru Itoh
Materials and Structures Laboratory, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Yokohama 226-8503 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Hiroki Taniguchi
Materials and Structures Laboratory, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Yokohama 226-8503 (Japan)
Current address: Department of Physics, Nagoya University, Furo-cho, Chikusa, Nagoya 464-8602 (Japan)
Materials and Structures Laboratory, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Yokohama 226-8503 (Japan)Search for more papers by this authorDr. Akihide Kuwabara
Nanostructures Research Laboratory (Japan) Fine Ceramics Center, Nagoya 456-8587 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Jungeun Kim
Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute, Sayo-gun, Hyogo 679-5198 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorYounghun Kim
Graduate School of Frontier Sciences, The University of Tokyo, Kashiwa, Chiba 277-8561 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Hiroki Moriwake
Nanostructures Research Laboratory (Japan) Fine Ceramics Center, Nagoya 456-8587 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Sungwng Kim
Department of Energy Science, Sungkyunkwan University, Jangan-Gu, Suwon 440-746 (Korea)
Search for more papers by this authorTakuya Hoshiyama
Department of Materials Science, Osaka Prefecture University, Sakai, Osaka 599-8531 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorTsukasa Koyama
Department of Materials Science, Osaka Prefecture University, Sakai, Osaka 599-8531 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Shigeo Mori
Department of Materials Science, Osaka Prefecture University, Sakai, Osaka 599-8531 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Masaki Takata
Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute, Sayo-gun, Hyogo 679-5198 (Japan)
Graduate School of Frontier Sciences, The University of Tokyo, Kashiwa, Chiba 277-8561 (Japan)
RIKEN Harima Institute, Sayo-gun, Hyogo 679-5148 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Hideo Hosono
Materials and Structures Laboratory, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Yokohama 226-8503 (Japan)
Frontier Research Center, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Yokohama 226-8503 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Yoshiyuki Inaguma
Faculty of Science, Gakushuin University, Toshima-ku, Tokyo 171-8588 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Mitsuru Itoh
Materials and Structures Laboratory, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Yokohama 226-8503 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorThis work was supported by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan through a Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists (B, grant number 24760543) and Scientific Research (C, grant number 24560833), Hitachi Metals—Materials Science Foundation, and MEXT Element Strategy Initiative Project.
Graphical Abstract
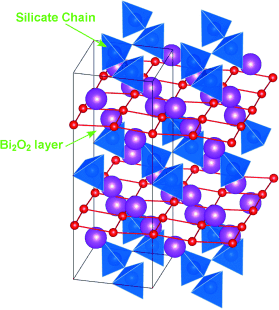
A lead-free ferroelectric: The occurrence of ferroelectricity is demonstrated in a silicate-based compound (Bi2SiO5, see picture), by direct observation of polarization switching. The mechanism of ferroelectricity in Bi2SiO5 has been studied by Raman scattering, transmission electron microscopy, X-ray powder diffraction, and first-principles calculations. The observed ferroelectricity stems from twisting of the one-dimensional SiO4 tetrahedral chain.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie_201302188_sm_figure_3.mov5 MB | figure_3 |
| anie_201302188_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf264.6 KB | miscellaneous_information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1G. H. Haertling, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1999, 82, 797–818.
- 2
- 2aW. Cochran, Adv. Phys. 1960, 9, 387;
- 2bW. Cochran, Adv. Phys. 1961, 10, 401;
- 2cJ. F. Scott, Rev. Mod. Phys. 1974, 46, 83.
- 3
- 3aR. E. Cohen, Nature 1992, 358, 136–138;
- 3bY. Kuroiwa, S. Aoyagi, A. Sawada, J. Harada, E. Nishibori, M. Takata, M. Sakata, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 217601;
- 3cH. Taniguchi, H. P. Soon, T. Shimizu, H. Moriwake, Y. J. Shan, M. Itoh, Phys. Rev. B 2001, 84, 174106.
- 4M. R. Dolgos, U. Adem, A. Manjon-Sanz, X. Wan, T. P. Comyn, T. Stevenson, J. Bennett, A. J. Bell, T. T. Tran, P. S. Halasyamani, J. B. Claridge, M. J. Rosseinsky, Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 10928;
10.1002/ange.201203884 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 10770.
- 5
- 5aR. Seshadri, N. A. Hill, Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 2892–2899;
- 5bJ. B. Neaton, C. Ederer, U. V. Waghmare, N. A. Spaldin, K. M. Rabe, Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 014113.
- 6
- 6aY. Saito, H. Takao, T. Tani, T. Nonoyama, K. Takatori, T. Homma, T. Nagaya, M. Nakamura, Nature 2004, 432, 84–87;
- 6bP. K. Panda, J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 5049–5062.
- 7J. Ketterer, V. Krämer, N. Jb. Miner. Mh. 1986, H.1, 13–18.
- 8H. Taniguchi, Y. J. Shan, H. Mori, M. Itoh, Phys. Rev. B 2007, 76, 212103.
- 9R. E. Cohen, H. Krakauer, Phys. Rev. B 1990, 42, 6416–6423.
- 10D. M. Hatch, S. Ghose, Chem. Minerals 1991, 17, 554.
- 11F. Liebau, Structural chemistry of silicates: structure, bonding, and classification 1–6, Springer, Berlin, 1985.
10.1007/978-3-642-50076-3 Google Scholar
- 12
- 12aG. Kresse, D. Joubert, Phys. Rev. B 1998, 59, 1758–1775;
- 12bD. M. Ceperley, B. J. Alder, Phys. Rev. Lett. 1980, 45, 566–569;
- 12cG. Kresse, J. Furthmüller, Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 11169–11186.
- 13H. J. Monkhorst, J. D. Pack, Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188.
- 14
- 14aK. Parlinski, Z. Q. Li, Y. Kawazoe, Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 78, 4063;
- 14bA. Togo, F. Oba, I. Tanaka, Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 134106.
- 15
- 15aX. Gonze, C. Lee, Phys. Rev. B 1997, 55, 10355;
- 15bY. Wang, J. J. Wang, W. Y. Wang, Z. G. Mei, S. L. Shang, L. Q. Chen, Z. K. Liu, J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2010, 22, 202201.
- 16M. Gajdoš, K. Hummer, G. Kresse, J. Furthmüller, F. Bechstedt, Phys. Rev. B 2006, 73, 045112.
- 17R. D. King-Smith, D. Vanderbilt, Phys. Rev. B 1993, 47, 1651–1654; D. Vanderbilt, R. D. King-Smith, Phys. Rev. B 1993, 48, 4442–4455.
- 18E. Nishibori, M. Takata, K. Kato, M. Sakata, Y. Kubota, S. Aoyagi, Y. Kuroiwa, M. Yamakata, N. Ikeda, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2001, 467–468, 1045–1048.
- 19K. Momma, F. Izumi, J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2011, 44, 1272.