Decrease in RNA Folding Cooperativity by Deliberate Population of Intermediates in RNA G-Quadruplexes†
Chun Kit Kwok
Department of Chemistry and Center for RNA Molecular Biology, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 16802 (USA) http://research.chem.psu.edu/pcbgroup
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorMadeline E. Sherlock
Department of Chemistry and Center for RNA Molecular Biology, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 16802 (USA) http://research.chem.psu.edu/pcbgroup
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Philip C. Bevilacqua
Department of Chemistry and Center for RNA Molecular Biology, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 16802 (USA) http://research.chem.psu.edu/pcbgroup
Department of Chemistry and Center for RNA Molecular Biology, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 16802 (USA) http://research.chem.psu.edu/pcbgroupSearch for more papers by this authorChun Kit Kwok
Department of Chemistry and Center for RNA Molecular Biology, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 16802 (USA) http://research.chem.psu.edu/pcbgroup
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorMadeline E. Sherlock
Department of Chemistry and Center for RNA Molecular Biology, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 16802 (USA) http://research.chem.psu.edu/pcbgroup
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Philip C. Bevilacqua
Department of Chemistry and Center for RNA Molecular Biology, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 16802 (USA) http://research.chem.psu.edu/pcbgroup
Department of Chemistry and Center for RNA Molecular Biology, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 16802 (USA) http://research.chem.psu.edu/pcbgroupSearch for more papers by this authorThis study was supported by a Human Frontier Science Program (HFSP) Grant RGP0002/2009-C to P.C.B. and Penn State Summer Discovery Grant to M.E.S. We thank Prof. Sarah Assmann, Prof. Bratoljub Milosavljevic, and Dr. Melissa Mullen for helpful discussions.
Graphical Abstract
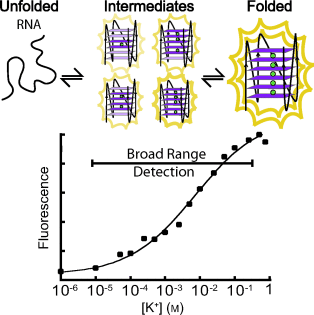
Keeping a broad (RNA) perspective: Conventional biochemical detection systems only have a 100-fold linear response range. The range of potassium concentrations detected by an RNA G-quadruplex sequence can be broadened by intentionally populating multiple intermediate folding states (see scheme). The folding of the RNA G-quadruplexes was monitored by both circular dichroism and intrinsic fluorescence spectroscopy.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie_201206475_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf1.2 MB | miscellaneous_information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aE. M. Moody, P. C. Bevilacqua, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 16285–16293;
- 1bE. M. Moody, J. C. Feerrar, P. C. Bevilacqua, Biochemistry 2004, 43, 7992–7998;
- 1cB. D. Sattin, W. Zhao, K. Travers, S. Chu, D. Herschlag, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 6085–6087;
- 1dS. V. Solomatin, M. Greenfeld, D. Herschlag, Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011, 18, 732–734.
- 2M. Mandal, M. Lee, J. E. Barrick, Z. Weinberg, G. M. Emilsson, W. L. Ruzzo, R. R. Breaker, Science 2004, 306, 275–279.
- 3
- 3aT. V. Erion, S. A. Strobel, RNA 2011, 17, 74–84;
- 3bE. B. Butler, Y. Xiong, J. Wang, S. A. Strobel, Chem. Biol. 2011, 18, 293–298;
- 3cJ. Lipfert, A. Y. L. Sim, D. Herschlag, S. Doniach, RNA 2010, 16, 708–719.
- 4
- 4aD. Koshland, A. Goldbeter, J. Stock, Science 1982, 217, 220–225;
- 4bA. Vallee-Belisle, F. Ricci, K. W. Plaxco, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13802–13807.
- 5M. Cerminara, T. M. Desai, M. Sadqi, V. Munoz, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 8010–8013.
- 6
- 6aA. Vallée-Bélisle, F. Ricci, K. W. Plaxco, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 2876–2879;
- 6bJ. Lin, D. Liu, Anal. Chim. Acta 2000, 408, 49–55;
- 6cA. P. Drabovich, V. Okhonin, M. Berezovski, S. N. Krylov, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 7260–7261.
- 7J. L. Huppert, Biochimie 2008, 90, 1140–1148.
- 8
- 8aY. Sannohe, H. Sugiyama, Curr. Protoc. Nucleic Acid Chem. 2010, Chapter 17, Unit 17.12.11–17;
- 8bK. Halder, J. S. Hartig, Met. Ions Life Sci. 2011, 9, 125–139.
- 9
- 9aN. V. Hud, F. W. Smith, F. A. L. Anet, J. Feigon, Biochemistry 1996, 35, 15383–15390;
- 9bM. A. Mullen, K. J. Olson, P. Dallaire, F. Major, S. M. Assmann, P. C. Bevilacqua, Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 8149–8163;
- 9cA. Y. Q. Zhang, A. Bugaut, S. Balasubramanian, Biochemistry 2011, 50, 7251–7258;
- 9dA. Bugaut, S. Balasubramanian, Biochemistry 2008, 47, 689–697.
- 10S. Takenaka, B. Juskowiak, Anal. Sci. 2011, 27, 1167–1167.
- 11
- 11aK. Halder, M. Wieland, J. S. Hartig, Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 6811–6817;
- 11bA. T. Phan, FEBS J. 2010, 277, 1107–1117;
- 11cA. N. Lane, J. B. Chaires, R. D. Gray, J. O. Trent, Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 5482–5515.
- 12
- 12aV. Víglaský, K. Tlučková, L. Bauer, Eur. Biophys. J. 2011, 40, 29–37;
- 12bM. A. Mullen, S. M. Assmann, P. C. Bevilacqua, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 812–815;
- 12cM. Vorlíčková, I. Kejnovská, J. Sagi, D. Renčiuk, K. Bednářová, J. Motlová, J. Kypr, Methods 2012, 57, 64–75.
- 13
- 13aM. A. Mendez, V. A. Szalai, Biopolymers 2009, 91, 841–850;
- 13bN. T. Dao, R. Haselsberger, M.-E. Michel-Beyerle, A. T. Phan, FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 3969–3977.
- 14The sequences chosen herein are either directly from a known gene, such as in the case of G2w2, G2m2, G2s2, and G4m1, or are closely related to these and representative of classes known to exist in genes.
- 15UA-rich loops led to Hill constants approaching unity, which may be because of the formation of intermediates involving base-pairing of the G residues with residues in the loops.
- 16
- 16aS. A. Woodson, Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2010, 39, 61–77;
- 16bT. R. Weikl, M. Palassini, K. A. Dill, Protein Sci. 2004, 13, 822–829.
- 17Notably, we previously reported folding intermediates in related G3 sequences, which were observed by CD spectroscopy of three-state titrations, the presence of intermediates on native gels, and RNase T1 protection.
- 18D. A. Doyle, J. M. Cabral, R. A. Pfuetzner, A. Kuo, J. M. Gulbis, S. L. Cohen, B. T. Chait, R. MacKinnon, Science 1998, 280, 69–77.
- 19D. Y. Vargas, K. Shah, M. Batish, M. Levandoski, S. Sinha, S. A. E. Marras, P. Schedl, S. Tyagi, Cell 2011, 147, 1054–1065.
- 20
- 20aJ. Liu, Z. Cao, Y. Lu, Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 1948–1998;
- 20bW. Mok, Y. Li, Sensors 2008, 8, 7050–7084.