Cobalt- and Manganese-Catalyzed Direct Amination of Azoles under Mild Reaction Conditions and the Mechanistic Details†
Ji Young Kim
Department of Chemistry and Molecular-Level Interface Research Center, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Daejeon 305-701 (Republic of Korea), Fax: (+82) 42-350-2810
Search for more papers by this authorSeung Hwan Cho
Department of Chemistry and Molecular-Level Interface Research Center, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Daejeon 305-701 (Republic of Korea), Fax: (+82) 42-350-2810
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Jomy Joseph
Department of Chemistry and Molecular-Level Interface Research Center, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Daejeon 305-701 (Republic of Korea), Fax: (+82) 42-350-2810
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Sukbok Chang
Department of Chemistry and Molecular-Level Interface Research Center, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Daejeon 305-701 (Republic of Korea), Fax: (+82) 42-350-2810
Department of Chemistry and Molecular-Level Interface Research Center, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Daejeon 305-701 (Republic of Korea), Fax: (+82) 42-350-2810Search for more papers by this authorJi Young Kim
Department of Chemistry and Molecular-Level Interface Research Center, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Daejeon 305-701 (Republic of Korea), Fax: (+82) 42-350-2810
Search for more papers by this authorSeung Hwan Cho
Department of Chemistry and Molecular-Level Interface Research Center, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Daejeon 305-701 (Republic of Korea), Fax: (+82) 42-350-2810
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Jomy Joseph
Department of Chemistry and Molecular-Level Interface Research Center, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Daejeon 305-701 (Republic of Korea), Fax: (+82) 42-350-2810
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Sukbok Chang
Department of Chemistry and Molecular-Level Interface Research Center, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Daejeon 305-701 (Republic of Korea), Fax: (+82) 42-350-2810
Department of Chemistry and Molecular-Level Interface Research Center, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Daejeon 305-701 (Republic of Korea), Fax: (+82) 42-350-2810Search for more papers by this authorThis research was supported by the Korea Research Foundation Grant (KRF-2008-C00024, Star Faculty Program), and MIRC (NRF-2010-0001957).
Graphical Abstract
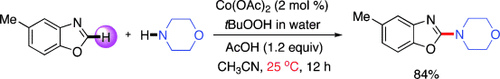
A bonding moment: A new cobalt- or manganese-catalyzed amination of azoles has been developed using peroxide and an acid additive to couple various types of azoles with ammonia, and primary or secondary amines (see scheme). The catalyst loadings are low, the optimal reaction conditions are mild, and the substrate scope is broad. The product azoles are an important pharmacophore of high biological activity.
Supporting Information
Detailed facts of importance to specialist readers are published as ”Supporting Information”. Such documents are peer-reviewed, but not copy-edited or typeset. They are made available as submitted by the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie_201005922_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf2.1 MB | miscellaneous_information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aR. Hili, A. K. Yudin, Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006, 2, 284;
- 1b Amino Group Chemistry, From Synthesis to the Life Sciences (Ed.: ), Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2007.
- 2For recent reviews on copper-mediated N-arylation reactions, see:
- 2aS. V. Ley, A. W. Thomas, Angew. Chem. 2003, 115, 5558;
10.1002/ange.200300594 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 5400;
- 2bG. Evano, N. Blanchard, M. Toumi, Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 3054.
- 3
- 3aD. S. Surry, S. L. Buchwald, Angew. Chem. 2008, 120, 6438;
10.1002/ange.200800497 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 6338;
- 3bJ. F. Hartwig, Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1534.
- 4M. Kim, S. Chang, Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 1640.
- 5
- 5aP. Y. S. Lam, S. Deudon, K. M. Averill, R. Li, M. Y. He, P. DeShong, C. G. Clark, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 7600;
- 5bJ. P. Collman, M. Zhong, Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 1233;
- 5cH. Rao, H. Fu, Y. Jiang, Y. Zhao, Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 1134; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 1114.
- 6F. Collet, R. H. Dodd, P. Dauban, Chem. Commun. 2009, 5061.
- 7
- 7aP. Müller, C. Fruit, Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 2905;
- 7bP. Dauban, R. H. Dodd, Synlett 2003, 1571;
- 7cH. M. L. Davies, J. R. Manning, Nature 2008, 451, 417.
- 8
- 8aW. C. P. Tsang, N. Zheng, S. L. Buchwald, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 14560;
- 8bB.-J. Li, S.-L. Tian, Z. Fang, Z.-J. Shi, Angew. Chem. 2008, 120, 1131; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 1115;
- 8cJ. A. Jordan-Hore, C. C. C. Johansson, M. Gulias, E. M. Beck, M. J. Gaunt, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 16184;
- 8dT.-S. Mei, X. Wang, J.-Q. Yu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 10806.
- 9
- 9aX. Chen, X.-S. Hao, C. E. Goodhue, J.-Q. Yu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 6790;
- 9bH.-Y. Thu, W.-Y. Yu, C.-M. Che, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 9048.
- 10aT. Hamada, X. Ye, S. S. Stahl, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 833;
- 10bA. E. King, L. M. Huffman, A. Casitas, M. Costas, X. Ribas, S. S. Stahl, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 12068.
- 11A. Armstrong, J. C. Collins, Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 2332;
10.1002/ange.200906750 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 2282.
- 12aD. Monguchi, T. Fujiwara, H. Furukawa, A. Mori, Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 1607;
- 12bQ. Wang, S. L. Schreiber, Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 5178.
- 13T. Kawano, K. Hirano, T. Satoh, M. Miura, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 6900.
- 14
- 14aS. Ko, Y. Na, S. Chang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 750;
- 14bJ. M. Lee, Y. Na, H. Han, S. Chang, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2004, 33, 302;
- 14cS. H. Cho, S. J. Hwang, S. Chang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 9254;
- 14dS. J. Hwang, S. H. Cho, S. Chang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 16158;
- 14eM. Kim, J. Kwak, S. Chang, Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 9097; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 8935;
- 14fS. H. Kim, S. Chang, Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 1868;
- 14gJ. Kim, S. Chang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 10272.
- 15S. H. Cho, J. Y. Kim, S. Y. Lee, S. Chang, Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 9291; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 9127.
- 16
- 16aS. Chiba, Z. Cao, S. A. A. E. Bialy, K. Narasaka, Chem. Lett. 2006, 35, 18;
- 16bI. B. Seiple, S. Su, R. A. Rodriguez, R. Gianatassio, Y. Fujiwara, A. L. Sobel, P. S. Baran, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 13194.
- 17
- 17aE. J. Y. Scott, J. Phys. Chem. 1970, 74, 1174;
- 17bR. P. Houghton, C. R. Rice, Polyhedron 1996, 15, 1893.
- 18
- 18aN. A. Johnson, E. S. Gould, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1973, 95, 5198;
- 18bD. T. Sawyer, A. Sobkowiak, T. Matsushita, Acc. Chem. Res. 1996, 29, 409.
- 19A similar result was obtained in the Ag-mediated amination reaction of benzothiazoles (Ref [15]). Additional investigations on the effects of Lewis acid additives are now underway.
- 20
- 20aH. L. Yale, K. Losee, J. Med. Chem. 1966, 9, 478;
- 20bS. A. F. Rostom, M. A. Shalaby, M. A. El-Demellawy, Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 38, 959.
- 21The direct amination with 1-methylbenzimidazole or 4,5-dimethylthiazole was unsuccessful under Co or Mn catalysis conditions, and the starting materials were recovered unchanged.
- 22See the Supporting Information for details.
- 23Analogous to the putative 2-aminobenzoxazolidine intermediate 7, oxidation of carbinolamine or hemiacetal species by metal/peroxide oxidant systems has been invoked for the oxidative amidation or esterification of aldehydes with amines or alcohols:
- 23aR. Gopinath, B. K. Patel, Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 577;
- 23bW.-J. Yoo, C.-J. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 13064;
- 23cK. Ekoue-Kovi, C. Wolf, Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 3429.
- 24Y.-X. Chen, L.-F. Qian, W. Zhang, B. Han, Angew. Chem. 2008, 120, 9470; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 9330.