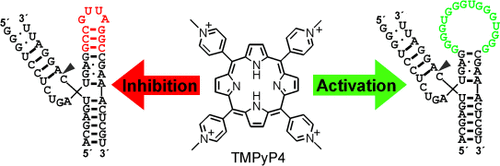
Turning Inhibitors into Activators: A Hammerhead Ribozyme Controlled by a Guanine Quadruplex†
Markus Wieland
University of Konstanz, Department of Chemistry, Universitätsstrasse 10, 78457 Konstanz, Germany, Fax: (+49) 7531-885-140
Search for more papers by this authorJörg S. Hartig Prof. Dr.
University of Konstanz, Department of Chemistry, Universitätsstrasse 10, 78457 Konstanz, Germany, Fax: (+49) 7531-885-140
Search for more papers by this authorMarkus Wieland
University of Konstanz, Department of Chemistry, Universitätsstrasse 10, 78457 Konstanz, Germany, Fax: (+49) 7531-885-140
Search for more papers by this authorJörg S. Hartig Prof. Dr.
University of Konstanz, Department of Chemistry, Universitätsstrasse 10, 78457 Konstanz, Germany, Fax: (+49) 7531-885-140
Search for more papers by this authorJ.S.H. gratefully acknowledges the Volkswagen Foundation for funding a Lichtenberg Professorship. We thank the Department of Chemistry at the University of Konstanz for support.
Graphical Abstract
Modular design of functional RNAs can be used to tailor molecular properties. Guanosine-rich sequences were introduced as switching devices for functional nucleic acids. TMPyP4 (see picture) was identified as the strongest ribozyme inhibitor known to date. When quadruplex-forming, G-rich sequences were attached to the ribozyme, the TMPyP4-mediated response was inverted from inhibition to activation of the ribozyme reaction.
Supporting Information
Supporting information for this article is available on the WWW under http://www.wiley-vch.de/contents/jc_2002/2006/z600909_s.pdf or from the author.
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1M. A. Keniry, Biopolymers 2000, 56, 123.
10.1002/1097-0282(2000/2001)56:3<123::AID-BIP10010>3.0.CO;2-3 CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 2T. Simonsson, Biol. Chem. 2001, 382, 621.
- 3R. H. Shafer, I. Smirnov, Biopolymers 2000, 56, 209.
10.1002/1097-0282(2000/2001)56:3<209::AID-BIP10018>3.0.CO;2-Y CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 4H. Arthanari, P. H. Bolton, Chem. Biol. 2001, 8, 221.
- 5S. Neidle, G. N. Parkinson, Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2003, 13, 275.
- 6T. R. Cech, Angew. Chem. 2000, 112, 34;
10.1002/(SICI)1521-3757(20000103)112:1<34::AID-ANGE34>3.0.CO;2-2 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 34.10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(20000103)39:1<34::AID-ANIE34>3.0.CO;2-N CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 7A. Siddiqui-Jain, C. L. Grand, D. J. Bearss, L. H. Hurley, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11593.
- 8J. Dai, T. S. Dexheimer, D. Chen, M. Carver, A. Ambrus, R. A. Jones, D. Yang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 1096.
- 9S. Rankin, A. P. Reszka, J. Huppert, M. Zloh, G. N. Parkinson, A. K. Todd, S. Ladame, S. Balasubramanian, S. Neidle, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 10584.
- 10J. C. Darnell, K. B. Jensen, P. Jin, V. Brown, S. T. Warren, R. B. Darnell, Cell 2001, 107, 489.
- 11S. Bonnal, C. Schaeffer, L. Creancier, S. Clamens, H. Moine, A. C. Prats, S. Vagner, J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 39330.
- 12S. M. Kerwin, Curr. Pharm. Des. 2000, 6, 441.
- 13A. Rangan, O. Y. Fedoroff, L. H. Hurley, J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 4640.
- 14B. Pan, Y. Xiong, K. Shi, M. Sundaralingam, Structure 2003, 11, 1423.
- 15H. Liu, A. Matsugami, M. Katahira, S. Uesugi, J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 322, 955.
- 16S. Verma, N. K. Vaish, F. Eckstein, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 1997, 1, 532.
- 17T. K. Stage-Zimmermann, O. C. Uhlenbeck, RNA 1998, 4, 875.
- 18A. Jenne, J. S. Hartig, N. Piganeau, A. Tauer, D. A. Samarsky, M. R. Green, J. Davies, M. Famulok, Nat. Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 56.
- 19R. J. Fiel, J. C. Howard, E. H. Mark, N. Datta Gupta, Nucleic Acids Res. 1979, 6, 3093.
- 20M. Koizumi, G. A. Soukup, J. N. Kerr, R. R. Breaker, Nat. Struct. Biol 1999, 6, 1062.
- 21J. Tang, R. R. Breaker, Chem. Biol. 1997, 4, 453.
- 22J. S. Hartig, M. Famulok, Angew. Chem. 2002, 114, 4440;
10.1002/1521-3757(20021115)114:22<4440::AID-ANGE4440>3.0.CO;2-X Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 4263.10.1002/1521-3773(20021115)41:22<4263::AID-ANIE4263>3.0.CO;2-7 CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 23J. S. Hartig, S. H. Najafi-Shoushtari, I. Grune, A. Yan, A. D. Ellington, M. Famulok, Nat. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 717.
- 24T. Tuschl, F. Eckstein, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 6991.
- 25V. Dapic, P. J. Bates, J. O. Trent, A. Rodger, S. D. Thomas, D. M. Miller, Biochemistry 2002, 41, 3676.
- 26K. J. Hertel, A. Pardi, O. C. Uhlenbeck, M. Koizumi, E. Ohtsuka, S. Uesugi, R. Cedergren, F. Eckstein, W. L. Gerlach, R. Hodgson, et al., Nucleic Acids Res. 1992, 20, 3252.
- 27H. W. Pley, K. M. Flaherty, D. B. McKay, Nature 1994, 372, 68.
- 28W. G. Scott, J. T. Finch, A. Klug, Cell 1995, 81, 991.
- 29T. K. Stage, K. J. Hertel, O. C. Uhlenbeck, RNA 1995, 1, 95.
- 30J. B. Murray, J. R. Arnold, Biochem. J. 1996, 317, 855.
- 31Q. Vicens, E. Westhof, ChemBioChem 2003, 4, 1018.
- 32R. Penchovsky, R. R. Breaker, Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 1424.
- 33W. C. Winkler, R. R. Breaker, Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 59, 487.
- 34E. Izbicka, L. D. Barnes, A. K. Robinson, K. K. Davidson, R. A. Lawrence, G. T. Hannibal, Anticancer Res. 2001, 21, 1899.
- 35S. Y. Rha, E. Izbicka, R. Lawrence, K. Davidson, D. Sun, M. P. Moyer, G. D. Roodman, L. Hurley, D. Von Hoff, Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 987.
- 36C. L. Grand, H. Han, R. M. Munoz, S. Weitman, D. D. Von Hoff, L. H. Hurley, D. J. Bearss, Mol. Cancer Ther. 2002, 1, 565.
- 37L. R. Kelland, Eur. J. Cancer 2005, 41, 971.