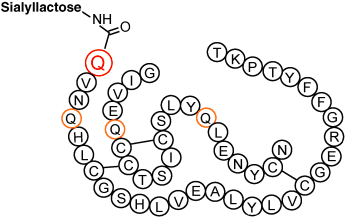
Site-Specific Introduction of Sialic Acid into Insulin†
Masaaki Sato
Division of Biological Sciences, Graduate School of Science, Frontier Research Center for Post-Genomic Science and Technology, Hokkaido University, Kita 21 Nishi 11, Sapporo 001-0021, Japan, Fax: (+81) 11-706-9042
Search for more papers by this authorReiko Sadamoto Dr.
Shionogi Laboratory of Biomolecular Chemistry, Division of Biological Science, Graduate School of Science, Frontier Research Center for Post-Genomic Science and Technology, Hokkaido University, Kita 21 Nishi 11, Sapporo 001-0021, Japan
Search for more papers by this authorKenichi Niikura Dr.
Division of Biological Sciences, Graduate School of Science, Frontier Research Center for Post-Genomic Science and Technology, Hokkaido University, Kita 21 Nishi 11, Sapporo 001-0021, Japan, Fax: (+81) 11-706-9042
Search for more papers by this authorKenji Monde Dr.
Division of Biological Sciences, Graduate School of Science, Frontier Research Center for Post-Genomic Science and Technology, Hokkaido University, Kita 21 Nishi 11, Sapporo 001-0021, Japan, Fax: (+81) 11-706-9042
Search for more papers by this authorHirosato Kondo Dr.
Discovery Research Laboratories, Shionogi & Co., Ltd., Osaka 553-0002, Japan
Search for more papers by this authorShin-Ichiro Nishimura Prof.
Division of Biological Sciences, Graduate School of Science, Frontier Research Center for Post-Genomic Science and Technology, Hokkaido University, Kita 21 Nishi 11, Sapporo 001-0021, Japan, Fax: (+81) 11-706-9042
Japan Bioindustry Association, Sapporo 060-0810, Japan
National Insutitute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Sapporo 062-8517, Japan
Search for more papers by this authorMasaaki Sato
Division of Biological Sciences, Graduate School of Science, Frontier Research Center for Post-Genomic Science and Technology, Hokkaido University, Kita 21 Nishi 11, Sapporo 001-0021, Japan, Fax: (+81) 11-706-9042
Search for more papers by this authorReiko Sadamoto Dr.
Shionogi Laboratory of Biomolecular Chemistry, Division of Biological Science, Graduate School of Science, Frontier Research Center for Post-Genomic Science and Technology, Hokkaido University, Kita 21 Nishi 11, Sapporo 001-0021, Japan
Search for more papers by this authorKenichi Niikura Dr.
Division of Biological Sciences, Graduate School of Science, Frontier Research Center for Post-Genomic Science and Technology, Hokkaido University, Kita 21 Nishi 11, Sapporo 001-0021, Japan, Fax: (+81) 11-706-9042
Search for more papers by this authorKenji Monde Dr.
Division of Biological Sciences, Graduate School of Science, Frontier Research Center for Post-Genomic Science and Technology, Hokkaido University, Kita 21 Nishi 11, Sapporo 001-0021, Japan, Fax: (+81) 11-706-9042
Search for more papers by this authorHirosato Kondo Dr.
Discovery Research Laboratories, Shionogi & Co., Ltd., Osaka 553-0002, Japan
Search for more papers by this authorShin-Ichiro Nishimura Prof.
Division of Biological Sciences, Graduate School of Science, Frontier Research Center for Post-Genomic Science and Technology, Hokkaido University, Kita 21 Nishi 11, Sapporo 001-0021, Japan, Fax: (+81) 11-706-9042
Japan Bioindustry Association, Sapporo 060-0810, Japan
National Insutitute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Sapporo 062-8517, Japan
Search for more papers by this authorThis work was supported partly by a grant for “Research and Development on Glycocluster Controlling Biomolecules” from the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO). M.S. would like to thank Mr. A. Toda, Dr. K. Yamada, Dr. K. Iwata, Mr. T. Ohta, and Dr. H. Nakagawa for helpful discussions.
Graphical Abstract
More gain, less pain: A new long-acting insulin (see structure) was created by the enzymatic introduction of sialyllactose into mutant insulins. The glycosylation site was introduced into the insulin by point mutation without loss of biological activity. The experimental results with mice clearly demonstrated that the introduction of a sialic acid residue is crucial in prolonging glucose-lowering activity in the blood.
References
- 1
- 1aO. Pillai, R. Panchagnula, Drug Discovery Today 2001, 6, 1056–1061;
- 1bD. E. DeWitt, I. B. Hirsch, JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2003, 289, 2254–2264;
- 1cD. E. DeWitt, D. C. Dugdale, JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2003, 289, 2265–2269.
- 2M. Schmidt, K. R. Babu, N. Khanna, S. Marten, U. Rinas, J. Biotechnol. 1999, 68, 71–83.
- 3E. Gershonov, Y. Shechter, M. Fridkin, Diabetes 1999, 48, 1437–1442.
- 4
- 4aJ. Markussen, P. Hougaard, U. Ribel, A. R. Sorensen, E. Sorensen, Protein Eng. 1987, 1, 205–213;
- 4bJ. Markussen, I. Diers, A. Engesgaard, M. T. Hansen, P. Hougaard, L. Langkjaer, K. Norris, U. Ribel, A. R. Sorensen, E. Sorensen, H. O. Voigt, Protein Eng. 1987, 1, 215–223;
- 4cJ. Markussen, I. Diers, P. Hougaard, L. Langkjaer, K. Norris, L. Snel, A. R. Sorensen, E. Sorensen, H. O. Voigt, Protein Eng. 1988, 2, 157–166.
- 5J. Markussen, S. Havelund, P. Kurtzhals, A. S. Andersen, J. Halstrom, E. Hasselager, U. D. Larsen, U. Ribel, L. Schaffer, K. Vad, I. Jonassen, Diabetologia 1996, 39, 281–288.
- 6
- 6aE. Gershonov, I. Goldwaser, M. Fridkin, Y. Shechter, J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 2530–2537;
- 6bP. Kurtzhals, B. Kiehr, A. R. Sorensen, J. Pharm. Sci. 1995, 84, 1164–1168.
- 7G. Walsh, Protein Biochemistry and Biotechnology, Wiley, Chichester, 2002, p. 30.
- 8
- 8aJ. C. Egrie, E. Dwyer, J. K. Browne, A. Hitz, M. A. Lykos, Exp. Hematol. 2003, 31, 290–299;
- 8bJ. C. Egrie, J. K. Browne, Br. J. Cancer 2001, 84 (Suppl. 1), 3–10.
- 9
- 9aM. Brownlee, A. Cerami, Science 1979, 206, 1190–1191;
- 9bT. Uchio, M. Baudys, F. Liu, S. C. Song, S. W. Kim, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 1999, 35, 289–306;
- 9cE. J. Bilsky, R. D. Egleton, S. A. Mitchell, M. M. Palian, P. Davis, J. D. Huber, H. Jones, H. I. Yamamura, J. Janders, T. P. Davis, F. Porreca, V. J. Hruby, R. Polt, J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 2586–2590;
- 9dD. Macmillan, R. M. Bill, K. A. Sage, D. Fern, S. L. Flitsch, Chem. Biol. 2001, 8, 133–145.
- 10
- 10aJ. E. Folk, P. W. Cole, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1966, 122, 244–264;
- 10bT. Ohtsuka, M. Ota, N. Nio, M. Motoki, Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2000, 64, 2608–2613.
- 11
- 11aH. J. Gross, R. Brossmer, Glycoconjugate J. 1995, 12, 739–746;
- 11bA. Nagpurkar, D. Hunt, S. Mookerjea, Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1996, 28, 1337–1348
- 11cE. R. Sjoberg, H. Kitagawa, J. Glushka, H. van Halbeek, J. C. Paulson, J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 7450–7459.
- 12T. Ohta, N. Miura, N. Fujitani, F. Nakajima, K. Niikura, R. Sadamoto, C.-T. Guo, T. Suzuki, Y. Suzuki, K. Monde, S.-I. Nishimura, Angew. Chem. 2003, 115, 5344–5347;
10.1002/ange.200351640 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 5186–5189.
- 13D. Ramos, P. Rollin, W. Klaffke, J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 2948–2956.
- 14G. I. Bell, R. L. Pictet, W. J. Rutter, B. Cordell, E. Tischer, H. M. Goodman, Nature 1980, 284, 26–32.
- 15K. D. Hinds, S. W. Kim, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2002, 54, 505–530.
- 16R. B. Mackin, Protein Expression Purif. 1999, 15, 308–313.
- 17P. Jonasson, J. Nilsson, E. Samuelsson, T. Moks, S. Stahl, M. Uhlen, Eur. J. Biochem. 1996, 236, 656–661.
- 18D. J. Cowley, R. B. Mackin, FEBS Lett. 1997, 402, 124–130.