Titelbild: Real-Time Live Imaging of Osteoclast Activation via Cathepsin K Activity in Bone Diseases (Angew. Chem. 6/2024)
Graphical Abstract
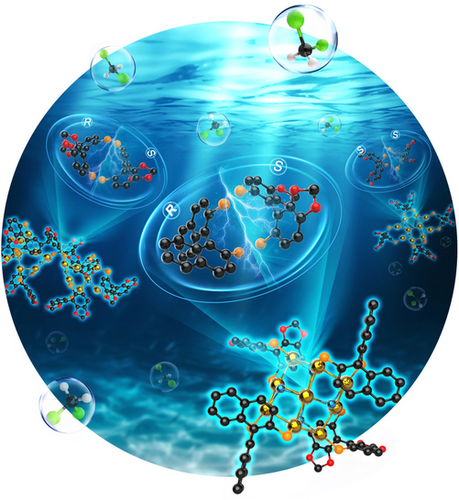
A novel fluorogenic probe for imaging osteoclasts, the major culprit in pathologic bone destruction, is unveiled by Jong Seung Kim, Serk In Park et al. in their Research Article (e202318459). This probe shows enhanced physicochemical properties for real-time intravital deep-tissue imaging of osteoclasts in the long bones of various mouse models, facilitating the development of therapeutic strategies. The discovery marks a significant advance in molecular imaging, opening new avenues in osteoclast-related bone disease research and drug discoveries.
A novel fluorogenic probe for imaging osteoclasts, the major culprit in pathologic bone destruction, is unveiled by Jong Seung Kim, Serk In Park et al. in their Research Article (e202318459). This probe shows enhanced physicochemical properties for real-time intravital deep-tissue imaging of osteoclasts in the long bones of various mouse models, facilitating the development of therapeutic strategies. The discovery marks a significant advance in molecular imaging, opening new avenues in osteoclast-related bone disease research and drug discoveries.
MXenes
Supramolecular Chemistry
Bioimaging