Solid-State Redox Solutions: Microfabrication and Electrochemistry†
Dezhi Yang
Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, and State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorLianhuan Han
Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, and State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorYang Yang
Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, and State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorLiu-Bin Zhao
Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, and State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorCheng Zong
Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, and State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorYi-Fan Huang
Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, and State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Dongping Zhan
Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, and State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005 (China)
Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, and State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005 (China)Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Zhong-Qun Tian
Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, and State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorDezhi Yang
Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, and State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorLianhuan Han
Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, and State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorYang Yang
Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, and State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorLiu-Bin Zhao
Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, and State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorCheng Zong
Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, and State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorYi-Fan Huang
Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, and State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Dongping Zhan
Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, and State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005 (China)
Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, and State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005 (China)Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Zhong-Qun Tian
Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, and State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorThis work is supported by the National Science Foundation of China (NSFC, No. 20973142), the NSFC Innovation Group of Interfacial Electrochmistry (No. 21021002), National Project 985 of High Education, and New Faculty Starting Package of Xiamen University.
Graphical Abstract
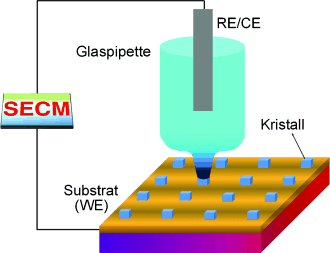
Gemischtvalente Eisenhexacyanide (FeIII, FeII und Preußischblau) können Teile eines NaCl-Kristalgitters unter Bildung fester Lösungen ersetzen. Die Mikrokristalle wurden durch ein speziell entwickeltes elektrochemisches Rasterverfahren mit einer Mikrokapillare (SECM) erhalten. Konfokale Raman-Spektren können in situ ohne Kontakt mit einer Flüssigkeit aufgenommen werden. WE=Arbeitselektrode, RE/CE=Referenz-/Gegenelektrode.
Supporting Information
Detailed facts of importance to specialist readers are published as ”Supporting Information”. Such documents are peer-reviewed, but not copy-edited or typeset. They are made available as submitted by the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| ange_201103386_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf163.4 KB | miscellaneous_information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1J. Korvink, O. Haber, MEMS: A Practical Guide to Design, Analysis, and Applications, William Andrew, New York, 2005.
- 2H. Andersson, A. van den Berg, Lab-on-chips for cellomics: micro and nanotechnologies for life science, Kluwer, London, 2004.
10.1007/978-1-4020-2975-2 Google Scholar
- 3B. J. Feringa, Molecular Switches, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2001.
10.1002/3527600329 Google Scholar
- 4V. Balzani, A. Credi, M. Venturi, Molecular Devices and Machines—A Journey into the Nano World, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2003.
10.1002/3527601600 Google Scholar
- 5W. Zhan, R. M. Crooks, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 9934–9935.
- 6P. J. Kulesza, J. A. Cox, Electroanalysis 1998, 10, 73–80, and reference therein.
- 7P. J. Kulesza, Z. Galus, Electrochim. Acta 1997, 42, 867–872.
- 8C. G. Williams, M. E. Edwards, A. L. Colley, J. V. Macpherson, P. R. Unwin, Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 2486–2495.
- 9For example: M. M. Lohrengel, A. Moehring, M. Pilaski, Electrochim. Acta 2001, 47, 137–141.
- 10J. F. Duncan, H. J. Percival, Aust. J. Chem. 1968, 21, 2175–2188.
- 11S. C. Jain, A. V. R. Warrier, H. K. Sehgal, J. Phys. C 1973, 6, 193–200.
- 12R. Kirmse, R. Bottcher, J. P. Willems, E. J. Reijerse, E. De Boer, J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1991, 87, 3105–3111.
- 13P. V. Sushko, A. L. Shluger, R. C. Baetzold, C. R. A. Catlow, J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2000, 12, 8257–8266.
- 14For example: K. Itaya, I. Uchida, V. D. Neff, Acc. Chem. Res. 1986, 19, 162–168.
- 15H. G. M. Edwards, R. Wolstenholme, D. S. Wilkinson, C. Brooke, M. Pepper, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 2255–2262.
- 16P. J. Gellings, H. J. M. Bouwmeester, The CRC Handbook of Solid State Electrochemistry, CRC Press, New York, 1997.
- 17A. A. Karyakin, Electroanalysis 2001, 13, 813–819.
- 18F. Ricci, G. Palleschi, Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 21, 389–407.
- 19F. Scholz, U. Schröder, R. Gulaboski, Electrochemistry of Immobilized Particles and Droplets, Springer, Heidelberg, 2005.
10.1007/b137048 Google Scholar
- 20 Scanning Electrochemical Microscopy (Eds.: ), Marcel Dekker, New York, 2001.
- 21D. J. Carter, M. I. Ogden, A. L. Rohl, Aust. J. Chem. 2003, 56, 675–678.
- 22K. V. Reddy, T. R. Reddy, S. C. Jain, J. Magn. Reson. 1974, 16, 87–94.
- 23S. C. Jain, K. V. Reddy, T. R. Reddy, J. Chem. Phys. 1975, 62, 4366–4372.
- 24A. K. Visvanath, J. Vetuskey, W. D. Ellenson, M. B. Krogh-Jespersen, H. H. Patterson, Inorg. Chem. 1981, 20, 3493–3499.
- 25N. M. Pinhal, N. V. Vugman, J. Phys. C 1985, 18, 6273–6279.
- 26M. T. Bennebroek, J. Schmidt, R. S. Eachus, M. T. Olm, J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1997, 9, 3227–3240.
- 27R. C. Baetzold, J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 1130–1137.
- 28X. W. Li, R. J. Liu, A. C. Geng, S. P. Yang, G. S. Fu, Chin. Phys. 2005, 14, 404–408.
Citing Literature
This is the
German version
of Angewandte Chemie.
Note for articles published since 1962:
Do not cite this version alone.
Take me to the International Edition version with citable page numbers, DOI, and citation export.
We apologize for the inconvenience.