Arsenate Respiratory Reductase
Abstract
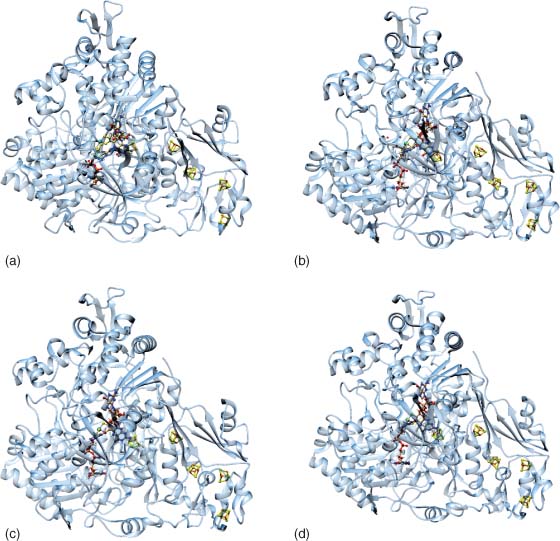
The arsenate respiratory reductase serves as the terminal electron acceptor in dissimilatory arsenate reduction. The enzyme, Arr, is a heterodimer with a large catalytic subunit, ArrA, and a smaller electron transfer subunit, ArrB. It was initially purified from Chrysiogenes arsenatis and subsequently from the Firmicute Bacillus selenitireducens, and genetically characterized from Shewanella sp. strain ANA-3. The crystal structure of ArrAB has been determined for the enzyme from ANA-3 as the complex (1.6 Å resolution), bound to arsenate (1.8 Å resolution), bound to arsenite (1.8 Å resolution), and bound to an inhibitor, phosphate (1.7 Å resolution). ArrA has two metal binding domains, the molybdopterin binding domain, which contains a cysteine residue that coordinates to the Mo, and a [4Fe–4S] cluster binding domain. ArrB has four [4Fe–4S] cluster binding domains. The rapid turnover exhibited by Arr from Shewanella sp. ANA-3 (kcat of 9810 s−1) suggest it is an efficient enzyme limited by diffusion.