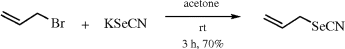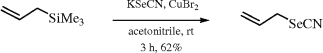Allylselenocyanate
Abstract
[4671-92-5] C4H5SeN (MW 146.95) InChI = 1S/C4H5NSe/c1-2-3-6-4-5/h2H,1,3H2 InChIKey = DSBZIVWXXWRSKF-UHFFFAOYSA-N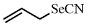
(prototypical allylic selenocyanate for transfer of allyl groups to thiols by deselenylative sigmatropic rearrangement,1, 2 allylation of cysteine-derived proteins,3 precursor to allylselenol4)
Physical Data: bp 31.5 °C (ca. 0.1 Torr).
Solubility: soluble in most organic solvents such as methanol, acetonitrile, and DMF.
Handling, Storage, and Precautions: stable to prolonged storage on the shelf; highly toxic and unpleasant smell; all reactions and handling must be carried out in a well-ventilated hood.
Preparative Methods: the most commonly employed method for the incorporation of the SeCN group into organic compounds involves nucleophilic substitution of appropriate leaving groups with potassium selenocyanate KSeCN (eq 1). Allylselenocyanate prepared in this way can be easily purified by vacuum distillation and readily handled at room temperature.4
Alternatively, allylselenocyanate can be prepared by the reaction of allylsilanes with selenocyanogen (SeCN)2, an effective electrophilic source generated in situ from KSeCN and CuBr2 (eq 2).5 The regioselective α-substitution of SiR3 with SeCN observed in this electrophilic substitution reaction is contrary to the normal γ-substitution featured in reactions of electrophiles with allylsilanes. This anomaly can be attributed to a facile [1,3]-shift of the SeCN group from the more substituted γ-position to the sterically less demanding α-site. Similar [1,3]-shifts have been noted previously for allylic selenides.6