N-(Aminoiminomethyl)-carbamic Acid, 1,1-Dimethylethyl Ester (Boc-guanidine)
Abstract
[219511-71-4] C6H13N3O2 (MW 159.19)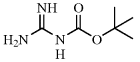
InChI = 1S/C6H13N3O2/c1-6(2,3)11-5(10)9-4(7)8/h1-3H3,(H4,7,8,9,10)
InChIKey = UMOZLQVSOVNSCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
(used as guanidinylating agent and for synthesis of 2-aminoimidazoles)
Physical Data: mp 196–197 °C.1
Solubility: soluble in most alcohols, esters (e.g., ethyl acetate), ketones (e.g., acetone), acetonitrile, and dichloromethane. Not soluble in diethyl ether and hexane.
Purification: for most applications, Boc-guanidine may be used as obtained after synthesis. Possible impurities are di- and tri-Boc-guanidine. Further purification is possible by crystallization from ethyl acetate and light petroleum.1
Preparative Method: the original synthesis was reported by Buchinska.1 A modified protocol for handling of larger quantities is as follows. To a cooled (0 °C) solution of guanidine hydrochloride (5 equiv, 275 mmol, 26.3 g) in aqueous sodium hydroxide (50 mL, 5.5 equiv, 303 mmol, 12.1 g) a solution of di-tert-butyl dicarbonate (1 equiv, 55 mmol, 12.0 g) in dioxane (100 mL) was added slowly (8 h). The reaction mixture was stirred for 20 h at room temperature. After extraction with ethyl acetate, the combined organic phases were dried (MgSO4) and the solvent evaporated under reduced pressure. The resulting colorless crystals were dried in vacuo to yield 97% of Boc-guanidine (8.51 g, purity ca. 90%).1, 2.
Handling, Storage, and Precautions: avoid contact with acids because of decomposition of the Boc-protecting group to CO2 and isobutylene as by-products. In aqueous solution, the Boc group is stable under basic conditions and inert to many nucleophilic reagents.3 Stability tests of di-Boc-guanidine (which should behave in a similar manner) were performed in solutions of acetonitrile and water with HOAc, TFA, and HCl 10% each. After 13 h reaction time, decomposition of di-Boc-guanidine to the extent of 25–35% (HOAc), 40–50% (TFA) and 85–95% (HCl) was observed.



