Ecological Protection Technology of Spraying Vegetation Concrete on Carbonaceous Rock Slope Experimental Research and Application
Abstract
To solve the environmental protection issue of carbonaceous rock slope, the failure mechanism of carbonaceous rock slope and the protection mechanism of vegetation concrete are analyzed based on the engineering characteristics of carbonaceous rock and vegetation concrete. Therefore, the field test of vegetation concrete was carried out to obtain the optimal dosage of vegetation concrete greening additive. The application of environmental protection technology of vegetation concrete on carbonaceous rock slope is applied in slope engineering of Hebai highway, and the change law of soil fertility was analyzed to verify the effect of ecological protection. The results show that the protection mechanism of vegetation concrete slope protection technology is mainly categorized into two groups, namely, the surface sealing effect of vegetation concrete substrate in the early stage and the plant ecological protection effect in the later stage. The experiment results show that the optimum dosage of green additive for vegetation concrete is ranging from 30 kg/m3 to 40 kg/m3. According to the field application, within one year after the construction of vegetation concrete, the contents of available phosphorus, potassium, and organic matter increased by 70.2%, 24.9%, and 76.8%, respectively. Moreover, the content of alkali hydrolyzed nitrogen decreased by 44.8% and bulk density by 17.4%; the content of total phosphorus changed little. After 60 days of construction, the vegetation coverage rate of the slope can reach more than 95% and there is no obvious soil erosion phenomenon after three times of heavy rainfall.
1. Introduction
With the booming demand for infrastructure construction such as highways and railways, a series of environmental issues have become increasingly prominent. Among them, many exposed rock slopes are bound to be formed in engineering construction activities. Different from the general soil slopes, carbonaceous rock slopes will not only be destroyed by the living environment around the vegetation but also cause soil erosion, which has induced a series of engineering geological disasters, such as landslides and debris flows. Thus, slope ecological protection has attracted attention and has become a hot research issue in recent years [1].
Carbonaceous rock slope is a special kind of rock slope, which is integrated and softens easily underwater interaction. Compared with traditional ecological protection, the carbonaceous rock contains pyrite and other sulfides, which lead to soil acidification after oxidation and hydrolysis. Although conventional vegetation is generally difficult to survive, acid-resistant vegetation can live better. Therefore, in protecting this kind of slope, other than considering the effect of slope protection, acid-resistant plants should also be selected as vegetation restoration items for the ecological protection of carbonaceous rock slopes.
At present, many scholars have achieved some achievements in slope protection [2–5]. Xi et al. [6] used straw fiber as a based material modifier to study the change of shear strength to slope base material under different amounts of straw fiber with cement and obtained the influence law to the changes of the shear strength on the base material. Zhou et al. [7] applied vegetation ecological slope protection technology to protect highway slope and discussed the conservation mechanism between slope vegetation and soil-water interaction. Waldron and McKinnell [8–10] proposed and deduced the mechanical model and theoretical calculation formula of root slope protection. Based on the principle of system engineering, Long et al. [11] established the evaluation index system of ecological slope protection effect and applied it to the practical ecological slope protection engineering of rock slope successfully.
Technically, the particular engineering characteristics of carbonaceous rock determine the particularity of ecological protection methods on carbonaceous rock slopes. This article chose slope engineering of Hebai highway carbonaceous rock as the targeted slope as the case study aims to reveal the failure mechanism of carbonaceous rock slope and the protection mechanism of vegetation concrete based on engineering characteristics of the targeted slope and combined with the technical characteristics of vegetation concrete. Through the experiment on vegetation concrete, the optimum dosage of green additive to vegetation concrete is explored and the ecological slope protection techniques of vegetation concrete are applied on carbonaceous rock slope. Moreover, the change law of soil fertility is concluded and the protective effect of vegetation concrete ecological slope protection is verified, which provides a reference for the slope protection with the same geoconditions.
1.1. Failure Mechanism and Ecological Protection Mechanism of Carbonaceous Rock Slope
Different from the general soil, carbonaceous rocks are swell and soften easily under soil-water interaction, which is sensitive to the environment and easy to disintegrate. According to soil coverage conditions, the failure modes of carbonaceous rock slope can be classified into two types: rock-soil interface sliding and rock-soil internal disintegration [12, 13]. In terms of the rock-soil interface sliding mechanism, excavation of slope should be noticed and the upper loose overburden layer will slide along the interface of rock and soil due to the joint infiltration of groundwater and surface water, particularly during the progressive excavation. The permeability between rock and soil layer is often vulnerable, and the carbonaceous rock is easy to disintegrate and soften by water. Therefore, a certain thickness of weak interlayer will be formed at the interface of rock and soil. When considering rock-soil internal disintegration, the surfaces rock and soil of carbonaceous rock slope disintegrate and soften by water, resulting in rock and soil fragmentation and leading to spalling and collapsing on the slope surface. These two failure modes are mainly affected by water. Therefore, the surface of carbonaceous rock slope should be closed in time after excavation to prevent it from being exposed to the atmosphere for a long time, avoiding the infiltration of surface water into the slope and resulting in the disintegration and softening of carbonaceous rock, which decreases soil strength and slope stability inducing landslide and geological disasters as a consequence.
To improve the safety and stability of the carbonaceous rock slope, the measures of timely closing the slope surface after excavation are taken to prevent the disintegration and softening of the carbonaceous rock slope. Currently, the carbon rock slope is usually protected by hanging net shotcrete, which takes advantage of fast construction, low cost, quick sealing of slope surface, and avoiding the exposure of carbonaceous rocks for a long time. However, its disadvantages are also very prominent. As can be seen from Figure 1, this technique has nothing to do with the ecosystem and its antienvironmentally friendly to the surrounding environment. As shown in Figure 2, the nonsynchronous deformation of the slope and the concrete protective layer on the slope surface occurred after construction, which led to the cracking and spalling of the concrete on the surface. With the seeping of rainwater, the damage is intensified, affecting the durability of the protection. Thus, the method of hanging net and shotcrete can not be considered as a long-term protection technique for carbonaceous rock slope protection issues.


As a new type of ecological slope protection technique, ecological slope protection technique by spraying vegetation concrete adopts specific matrix soil formula and mixed green seed ratio for slope ecological protection. It is mainly composed of cement, sandy loam, organic matter, green additives, etc. This technique has the advantages of rapid planting of common soil and also possesses the characteristics of surface sealing and strong erosion resistance of hanging net shotcrete, which is very suitable for ecological protection engineering of carbonaceous rock slope.
The vegetation concrete matrix can provide a good living environment for plants on the rocky slope; hence, the environmental protection issues of rock slope are solved. In carbonaceous rock, the slope can be evergreen all over the year; herbaceous and shrub seeds are used according to a certain proportion, mainly including acid-resistant Sophora flavescens and bermudagrass. It is supported by different vegetation in different periods. In the early stage, the greening and protection functions were realized by herbaceous plants. With the growth of shrub plants, the ecological community of shrub grass combination and multiple plant growth was finally formed so that the ecological environment of the slope was restored, the soil and water loss was restrained to a certain extent, and the slope was effectively protected.
The protection mechanism of spraying vegetation concrete ecological slope mainly includes two stages: (1) the early stage with the surface sealing effect of vegetation concrete matrix; (2) the later stage with ecological protection effect on plants. In terms of the surface sealing effect in the early stage, the carbonaceous rock slope should be closed in time after excavation to restrain the slope disintegration and softening. Through vegetation concrete spraying and sowing construction, a layer of vegetation concrete covering layer is formed on the slope surface; then, the overburden layer can produce a certain strength in a short time and has strong antierosion performance, which can make the excavated carbonaceous rock slope surface be closed in time and resist large rain erosion and prevent soil erosion. While analyzing the environmental protection effect on plants in the later stage, the protective effect of vegetation concrete mainly depends on the surface sealing effect of vegetation concrete substrate. When the vegetation covers the whole slope, the ecological protection effect of vegetation is highlighted. The ecological protection is mainly reflected in rainfall interception, splash erosion weakening, and root reinforcement. In the process of rainfall, some rainwater will be intercepted by plant branches and leaves when it reaches the slope. Moreover, the reevaporation of water into the atmosphere or falling to the slope can form surface runoff, while vegetation can inhibit the surface runoff and weaken the splash erosion of raindrops, which plays a role in controlling soil and water loss. The reinforcement effect of plant roots is a key factor to maintain the stability of the slope surface through avoiding soils erosion by rainfall splash achieving a long-term slope stability condition and environmental sustainability.
2. Experimental Investigations on Vegetation Concrete
Technically, the stability of the slope should be considered in the first place, and then the corresponding supported forms should be adopted according to the design requirements and local environment. Then, according to the characteristics of the local environment and climate, testing schemes were designed and experiments were carried out according to local conditions. The greening effect is analyzed eventually.
3. Testing Material
According to the climate characteristics of Guangxi and the acid soil characteristics of carbonaceous rocks, plants were selected for the experiment, including bermudagrass (pH = 5.5∼7.5), bahiagrass (pH = 5.0∼7.0), molasses grass (pH = 5.5∼7.0), ryegrass (pH = 6.0∼7.0), pigeon pea (pH = 5.0∼7.0), and Leucaena leucocephala (pH = 5.0∼8.0). Among them, bermudagrass, bahiagrass, molasses grass, and ryegrass are herbaceous plants, while Leucaena leucocephala and pigeon pea are shrubs to achieve a grass shrub combination. The greening effect of green in four seasons meets the requirements of ecological restoration.
Vegetation concrete includes sandy loam soil, green additives, cement, and organic matter. By making use of local sandy loam soil, green additives are mainly used to regulate soil pH conditions. It not only enhances soil porosity regulating substrate bacteria balance but also provides nutrients for plant growth, maintaining ecological balance to the microbial community. The ordinary Portland cement is selected as cement and the organic matter was fermented pine sawdust.
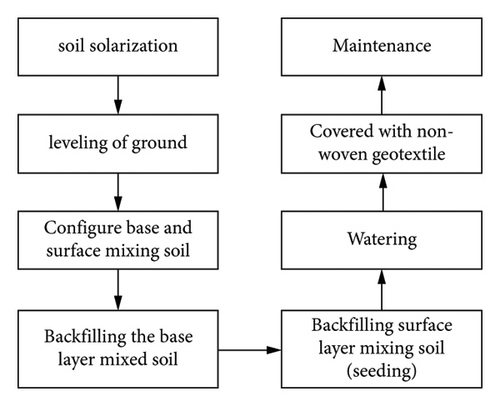
4. Testing Procedures and Schemes
This experiment mainly analyzes the growth of various plants with different amounts of greening additives. The flowchart of testing procedures is present in Figure 3 and Table 1 lists the testing scheme under the mixed sowing plan. It carries out the comparative test of different greening additive dosages, analyzes the influence law of greening additive dosages on plant growth, and obtains the optimal dosage of greening additive. It provides a reference for the actual construction of a vegetation concrete slope protection project.
| Group | Green additive dosage (kg/m3) | Cement consumption (kg/m3) | Seed rate(g/m2) | Planting mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0 | 0 | 100 | Bermudagrass: 10 g/m2. Bahiagrass: 20 g/m2. Molasses grass: 10 g/m2. Ryegrass: 20 g/m2. Leucaena leucocephala: 15 g/m2. Cajanus cajan: 15 g/m2. | Mixed sowing |
| A1 | 0 | 80 | ||
| A2 | 10 | |||
| A3 | 20 | |||
| A4 | 30 | |||
| A5 | 40 | |||
| A6 | 50 | |||
| A7 | 60 | |||
| A8 | 70 |
5. Experiment Results Analysis
Through the contrast test of vegetation concrete with different amounts of greening additives, after five months, the growth status of vegetation with different amounts of greening additives is shown in Figure 4. It can be seen that the vegetation growth of A0 and A1 groups without greening additive is the worst; especially, the A0 sample with a cement content of 100 kg/m3 has the lowest plant density, with dry and yellow leaves. This reveals that soil is hardened due to the incorporation of cement when no greening additive is added and the growth of plant roots is hindered with soil-water retention getting worse. Moreover, the higher the cement content is, the more unfavorable the soil environment is to plant growth.
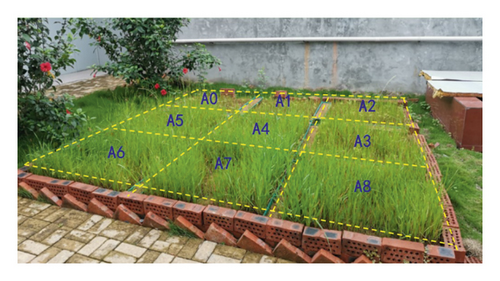
Based on the field construction experience of vegetation concrete, in the commonly used ratio of vegetation concrete, the distribution ratio of 1 m3 sandy loam, 60 kg/m3 organic matter: 80 kg/m3 cement, is constant; comparative tests were conducted under different dosages of greening additives. Comparing groups from A2 to A8 can be found that with the increase of greening additives amount, the overall plant density shows an increasing trend. Among them, under A4 and A5 testing scheme, the plant density is relatively high and the vegetation grows luxuriantly, revealing the best growth conditions. Thus, it can be concluded that the greening effect is best with the mixing amount of greening additive in the vegetation concrete ratio in the range from 30 kg/m3 to 40 kg/m3. Meanwhile, with the increase of greening additive content, the growth status of plants under A6 to A8 conditions did not change significantly, and the plant density did not increase significantly. This shows that the amount of greening additive has a range of influences on plant growth. When exceeding this amount, the effect decreases. For the sake of economy, the optimum amount of greening additive should be selected for the greening construction of vegetation concrete. Therefore, the greening effect is the best when the amount of greening additives is 30 kg/m3–40 kg/m3. It is worth noting that the test is designed for the rainy climate characteristics in Guangxi to ensure the antierosion effect; the cement dosage is relatively large. For fewer rain areas in the north, the amount of cement should be adjusted according to the local rainfall, and the optimal dosage of greening additives may be slightly different.
6. Application of Vegetation Concrete Ecological Slope Protection Technique on Carbonaceous Rock Slope
6.1. Project Overview
A slope along the Hechi-Baise expressway link is chosen for the experiment, as shown in Figure 5, where the slope is covered by carbonaceous rock and its lithology is strongly weathered mudstone, black, carbonaceous, thin-to-medium-thick layered structure with broken rock mass and developed local joints and fissures. The terrain at the top of the slope is steep, with broken rock layers, numerous structural planes, and poor integrity. Given the long-term exposure of carbonaceous rocks to the air, it is easy to disintegrate and soften when exposed to water. If effective sealing measures are not taken, the stability of the slope will be achieved and adversely affected. Considering the engineering characteristics of carbonaceous rock, the protection effect of conventional soil spraying or net spraying concrete technology is not good. In this case, the technique of spraying vegetation concrete is selected for greening protection of the slope and it is supported by bolt plus lattice beam structure.

6.2. Sprayed Vegetation Concrete Ecological Slope Protection Materials and Construction Technology
The proportion of vegetation concrete and the number of various materials used in this project are shown in Table 2. According to the climate characteristics of Guangxi and the acidic soil of carbonaceous rocks, plants such as dog bud root, ryegrass, Eragrostis curvula, alfalfa, Leucaena leucocephala, Eupolyphaga seu steleophaga, Sophora flavescens, and Magnolia officinalis were selected. The main construction procedures of sprayed vegetation concrete ecological slope protection are as follows: clean the slope ⟶ anchor ⟶ install diamond metal mesh ⟶ spray vegetation concrete base ⟶ spray vegetation concrete surface ⟶ cover nonwoven geotextile ⟶ spray water for maintenance. Among them, the vegetation concrete base contains no plant seeds, and the spraying thickness is 9 cm, while the surface vegetation concrete is mixed with plant seeds, and the spraying thickness is 1 cm. Upon completion of construction, Covering nonwoven fabrics for water spray irrigation and curing, the curing period is 60 days.
| Material | unit | Quantity | Use | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vegetation concrete matrix | Sandy loam | m3 | 1 | Provide soil environment |
| Greening additive | kg/m3 | 40 | Provide nutrients and microbial colonies needed by plants and adjust soil pH value | |
| P.O42.5 cement | kg/m3 | 100 | Improve soil strength and antiscouring ability | |
| Organic matter (sawdust) | kg/m3 | 60 | Improve soil porosity | |
| Slope anchoring material | Galvanized diamond metal mesh | m2/100m2 | 110 | Enhance the adhesion ability of vegetation concrete slope |
| Anchor rod HRB400Φ16 mm × 80 cm | kg/100m2 | 164.32 | Fixed wire mesh | |
| M30 mortar | m3/100m2 | 0.172 | Fixed bolt | |
| Grass seed (cold and warm season grass mixture) | kg/100m2 | 5 | Planting greening | |
| Maintenance consumables | Nonwoven geotextile | m2/100m2 | 110 | Soil moisture and water conservation |
| Water | m3/100m2 | 60 | Provide water for plant growth | |
6.3. Change Analysis of Fertility Index of Vegetation Concrete
Through on-site sampling and testing, the fertility indexes of vegetation concrete, such as total phosphorus, available phosphorus, alkali hydrolyzable nitrogen, available potassium, organic matter content, and soil bulk density, were analyzed to explore the change law of each fertility index in vegetation concrete. It can be seen from Figure 6 that the fertility indexes of vegetation concrete have changed within one year after construction, The contents of available phosphorus, available potassium, and organic matter increased by 70.2%, 24.9%, and 76.8%, respectively. However, the content of alkali hydrolyzed nitrogen decreased by 44.8%, and the bulk density decreased from 1.655 g/cm3 to 1.367 g/cm3, with a decrease of 17.4%. While the change in total phosphorus content was small, and the increase was only 5.3%.
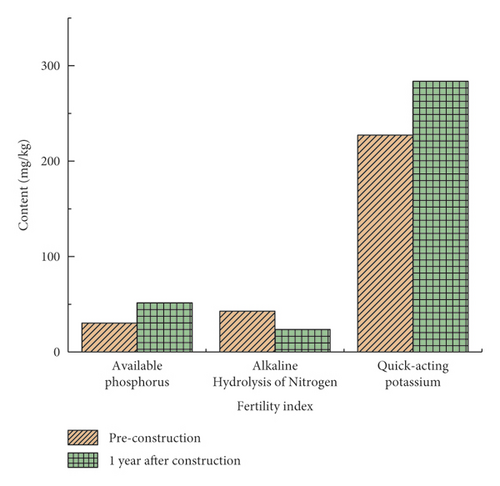
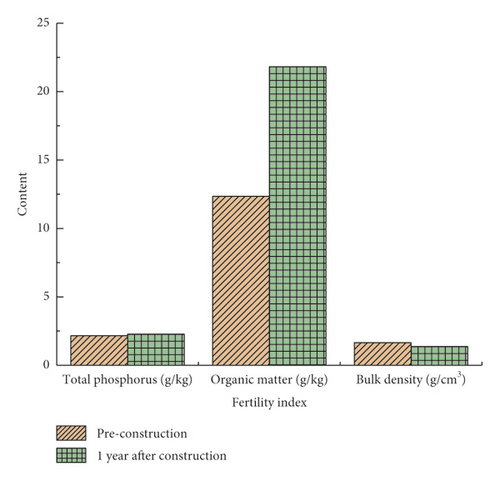
According to the changes of soil fertility indexes, the contents of soil available phosphorus, available potassium, and organic matter increase one year after construction, which is beneficial to improving soil fertility and the accumulation of nutrients. The results imply that the content of alkali hydrolyzable nitrogen is significantly reduced, that is, since, after the construction of vegetation concrete, herbaceous plants grow first, which do not have the ability of nitrogen fixation. The results showed that soil available nitrogen was significantly lost, and this phenomenon would be improved after legume shrubs such as big leaf pig excrement bean grew completely. Therefore, it is suggested to apply nitrogen fertilizer once a year after construction to supplement the content of alkali hydrolyzable nitrogen in the soil and ensure the nutrition needed for plant growth. The decrease of soil bulk density indicates that the degree of soil ripening increases and the soil porosity increases; it is beneficial to plant root growth.
According to continuous observation, vegetation concrete ecological slope protection for one year shows that some grass seeds had sprouted on the 5th day of maintenance. On the 8th day of concrete curing, the length of ryegrass leaves had grown to about 8 cm. Figure 7 shows the greening effect of carbonaceous rock slope after 60 days of maintenance, with a completely covered by herbaceous plants. Based on field investigation, the vegetation coverage rate of the slope is more than 95%. During the maintenance period, after three times of heavy rainfall scouring, no obvious erosion ditch and concrete spalling accrue, which could prove that the vegetation concrete matrix can resist the erosion of heavy rainfall and provide a good soil environment for plant growth.

Figure 8 shows the greening effect of the carbonaceous rock slope after 180 days. Through field investigation, it is found that after 6 months, the carbonaceous rock slope has been completely covered by vegetation, shrubs such as big leaf pig excrement bean grow gradually, herbs and shrubs coexist, and the species of ecological plants on the slope are gradually enriched. The restored slope can not only prevent and control soil erosion but also form a slope landscape compatible with the surrounding environment. The greening effect is very remarkable. After one year of construction, the plant communities on the slope are mainly composed of Leucaena leucocephala and Magnolia multiflora, which realizes maintenance-free. At the same time, it was found that although the growth rate was faster in the early stage, the ability of overwintering was poor. It would wither quickly in winter, and the survival rate was low in the next spring. It suggests that plant seeds should be selected reasonably according to sowing time and local climate conditions in the construction of vegetation concrete ecological slope protection. In the process of construction, triangle plum and other landscape plants can be planted on the slope platform, which has a certain antisulfur dioxide effect and can further improve the greening effect as an ornamental plant. Season or weather will have an impact on the application of this technology; mainly, seasons will affect the germination and growth of plants; different plant seeds for greening are chosen for different seasons. Weather mainly affects construction, which should be carried out after the rain. Construction is prohibited when raining takes into account construction safety and quality problems. Attention should be paid to timely spray maintenance after construction in summer. The technology requires a strict mix proportion of each component of vegetation concrete, and the dosage of each component should be strictly controlled during construction, ensuring the antierosion performance of ecological substrate and good soil ecological performance, and meeting the needs of slope ecological protection.

Through the application of vegetation concrete ecological protection technology in carbonaceous rock slope, it is found that vegetation concrete ecological slope protection technology has higher ecological benefits and lower maintenance costs than shotcrete and planting bags. Although the construction cost is slightly higher than the traditional earth spraying technology, the engineering characteristics of greening high and steep rock slopes are difficult to achieve by traditional hanging net soil spraying technology. Vegetation concrete provides a good soil condition for plants, with strong antierosion performance and a good greening effect. It can prevent rainwater from seeping into the slope, preventing the disintegration and softening of carbonaceous rock and resulting in an environmentally friendly slope. It can not only satisfy the surface sealing of slope but also realize the ecological restoration of the slope, which is in line with the development concept of the national green highway and is very suitable for ecological protection engineering of disintegrating rock slope such as carbonaceous rock.
7. Conclusions
- (1)
In the construction stage of applying the ecological slope protection technique of vegetation concrete on a carbonaceous rock slope, the cement content of vegetation concrete should be suitable for plant roots growth. Meanwhile, as the pH of carbonaceous rock is low and acidic, which is difficult for plants to grow, acid-resistant plants should be selected for slope greening.
- (2)
The protection mechanism of vegetation concrete ecological slope protection technique includes the surface sealing effect of vegetation concrete matrix and the environmental protection effect of plants. Plant ecological protection is mainly prominent in rainfall interception, splash erosion, and root reinforcement.
- (3)
Through analyzing the experiment of vegetation concrete, it can be concluded that the best greening effect can be obtained when the dosage of vegetation concrete greening additive ranges from 30 kg/m3 to 40 kg/m3. According to the observation of field application, the contents of available phosphorus, available potassium, and organic matter in vegetation concrete increased by 70.2%, 24.9%, and 76.8%, respectively, within one year after construction. Moreover, the content of alkali hydrolyzed nitrogen decreased by 44.8% and bulk density by 17.4%, while the content of total phosphorus changed a little. It suggested that within one year after the construction, one-time nitrogen fertilizer was applied to supplement the content of alkali hydrolyzable nitrogen in the soil enough to ensure the nutrition needed for plant growth.
- (4)
By observing the ecological protection of vegetation concrete on a carbonaceous rock slope, it can be found that the vegetation coverage rate of the slope can reach more than 95% after 60 days of construction. After three times of heavy rainfall, there is no obvious soil erosion phenomenon; moreover, the antierosion performance and slope greening effect are remarkable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by the Science And Technology Project of Guangxi “research and application of ecological slope protection technology in carbonaceous rock slope”(Grant: AD19110124).
Open Research
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of the study are available from the corresponding author upon request.




