[Retracted] An Integrated Development Model of Cultural and Creative Industry and Rural Tourism Industry Based on Data Mining
Abstract
In the later stage of industrialization or postindustrialization era, the driving force of human social and economic development mainly comes from technological innovation, cultural creativity, and the development of creative industries, high-tech industries, and service industries. The cultural and creative industries meet the needs of the postindustrial era and the era of knowledge economy. This shows the importance of culture, knowledge, and technology in the rapid economic development. This paper introduces data mining technology and obtains a data mining method system suitable for this study. It mines and analyzes data related to cultural and creative industries and rural tourism industries. It finally obtained that the degree of integration of the two industries in the past six years was 0.498, 0.496, 0.487, 0.498, 0.499, and 0.5, respectively.
1. Introduction
Compared with industrial diversification, industrial integration is a development process that follows the intersection and penetration of independent industries. When industry boundaries blur or disappear, new industries eventually emerge. Rural tourism is a significant part of the tourism industry. It has the potential to provide many innovative elements to the cultural and creative industries, as well as to create a large-scale creative space and boost their originality. After years of rapid expansion, China’s rural tourism industry has reached a snag. It is necessary to reexamine the growth of rural tourism and to improve the overall quality of rural tourism. The cultural and creative industries have grown rapidly with government support, but this is not enough. Rural tourism provides an innovative, high-value-added permeability, strong influence, and high-tech content to the cultural and creative industries. It is the power of rural tourism’s long-term growth.
For data mining, relevant scientists have done the following research. Xu et al. take a broader perspective on privacy issues related to data mining and study various methods that help protect sensitive information. They reviewed game theory methods and found that these methods were proposed to analyze interactions between different users in data mining scenarios [1]. Jalal and Ali proposed a document classification method. This can cluster text documents of research papers into meaningful categories that contain similar fields of science. The method they propose is based on the fundamental focus and scope of target categories, each of which contains many topics [2]. The purpose of Chaurasia and Pal is to study the performance of different classification techniques. They used data mining techniques to develop accurate breast cancer prediction models, comparing three classification techniques [3]. Yan and Zheng build on a number of basic signals from financial reports and use a supervised approach to assess the impact of data mining on fundamental differences. Even after accounting for data mining, a number of fundamental signals are significant predictors of overall stock returns [4]. Hong et al. proposed a new method for creating flood sensitivity maps by combining fuzzy evidence weights and data mining techniques. Their method is one-of-a-kind in that it uses a dual-purpose fuzzy algorithm [5]. Lei et al. investigate the use of data mining algorithms and advanced network analysis to identify important features of accidents. They use a community discovery algorithm to cluster the data, which reduces natural heterogeneity. Then, on each cluster, they used a correlation rule learning algorithm to find significant patterns [6]. Under various uncertainties, Parvizimosaed et al. introduce a new multilayer SEMS architecture for resource optimization. Data extraction, pattern recognition, and online decision making are just a few of the things it can do [7]. Huang et al. are working on a fast data mining algorithm for computing fuzzy conceptual approximations in dynamically fuzzy decision systems with moving objects and features. According to the results of trials on six UCI date sets, the dynamic proposed method is clearly more efficient than the combination of the static method and the two benchmark methods [8]. According to Pourghasemi et al., fluvial erosion is a significant source of sediment in many areas. It also aids in the redistribution of eroded soil on slopes. Data mining techniques were used to map the erosion susceptibility of rivers. On the other hand, their calibration and validation procedures must be thoroughly investigated [9]. Wu and Peng proposed a data mining method for short-term wind energy prediction to solve the dynamics of training patterns and improve prediction accuracy. According to simulation results, the prediction accuracy is better than other existing methods for short-term wind energy prediction [10]. Mishra et al. presented a comprehensive overview of data collection methods and statistical techniques for time series data used in rainfall forecasting. They also contrasted and compared the various methods. They also proposed some potential future algorithms for implementing efficient time series data exploration techniques [11]. Marozzo et al. project’s goal is to show how cloud-based software technologies can be used to design and implement scalable data analytics workflows. It explains how to create and deploy a cloud-based data mining framework. It is a data analysis framework that incorporates a visual workflow language, a parallel execution model, and software services. [12]. A data mining method was proposed by Zheng et al. The wind data can be efficiently preprocessed and filtered using this method, which uses only the total active power of the wind farm and the corresponding wind speed values. It examines the characteristics of raw wind data and divides all data into monthly categories using statistical methods based on the magnitude of the characteristic [13]. Ravi K and Ravi V proposed a method for extracting features from a set of texts. Then, using the text-data mining paradigm, they proposed a novel framework for automatic sarcasm detection in news and customer reviews. The proposed method performed admirably on one dataset and showed promise on two others [14]. Marco admired how data mining techniques (correlation analysis) were used to better understand household travel survey usage patterns. Correlation rules can demonstrate the substitutability of private cars and public transportation from an economic standpoint. This effect, on the other hand, was not observed between public transportation and nonmotorized modes like cycling and walking. These methods provide some research references. The study has not been recognized by the public due to the short time and small sample size of the relevant research.
The introduction of data mining technology is the paper’s innovation. It looked at tourists’ age and educational backgrounds, their occupational structure and family income, rural tourism travel information and tourism attractions, tourism motivation and travel mode, and rural tourism per capita expenditure and revisit rate. It finally received the comprehensive development level and integration coordination degree, and it proposed some ideas for integrating the cultural and creative industries with rural tourism.
2. The Integrated Development Method of Cultural and Creative Industry and Rural Tourism Industry
2.1. Data Mining
Data mining is part of the information discovery process. Data mining refers to algorithms that search for hidden information in large amounts of data. Data mining is the extraction of useful information that was previously unknown but is hidden in an incomplete, large, and ambiguous dataset. Information extraction from data is an important computational technique. Extracting data from a database is called data mining and data processing. It can be used in the process to search for relationships between concepts, taxonomy, bias, chance analysis, descriptive and evolutionary analysis, and visual results.
Therefore, data mining can be understood as a database-based search process. This search refers to the exploration and organization of large amounts of data. Its purpose is to find out valuable hidden events and information. This search process is the use of prediction, artificial intelligence, statistical science, and technology. Figure 1 shows the knowledge discovery process.
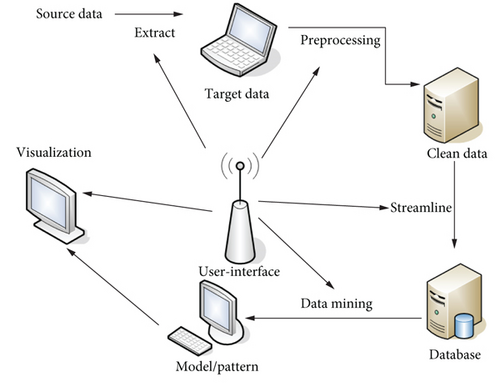
The type of data can be structured, semistructured, or even heterogeneous. Methods of discovering knowledge can be mathematical, nonmathematical, or inductive. The knowledge that is finally discovered can be used for information management, query optimization, decision support, and maintenance of the data itself. The object of data mining can be any type of data source, and it can be a relational database. This class contains data sources for structured data. It can also be data warehouse, text, multimedia data, spatial data, time series data, and Web data. Such data sources contain semistructured data or even heterogeneous data.
- (1)
A concept or description of a particular category of data that exploits data relationships between concepts and categories or dependencies. It accurately and clearly describes the concept through the description and characteristics of the data and then summarizes its characteristics. Data differentiation is to construct a dataset of several comparison classes and classify the data to be mined by querying
- (2)
Predictive modeling is used to predict server load, server downtime, or estimate sales, etc. and builds models for target variables in the form of explanatory variables. Prediction is divided into classification and regression. Classification is used to predict discrete target variables, and regression is used for continuous target variables. Both prediction goals are to train and derive a model that minimizes the user-defined error between the predicted value and the actual value of the variable
- (3)
Association analysis is used to describe the characteristics of strong associations in the data. Such as it can be used to determine which items are likely to be bundled together and generate recommendations. The discovered patterns are generally represented in the form of entailment rules or feature subsets
- (4)
Cluster analysis is to divide the dataset into meaningful or valuable groups. Cluster analysis is very similar to classification analysis. The difference is that the number of classes is not known before clustering, and the class labels need to be derived from the data. Therefore, cluster analysis belongs to unsupervised classification
- (5)
Anomaly detection, based on the analysis of the dataset, is to obtain some abnormal data or abnormal data that is obviously different from other data. Algorithms in this area are often used in network security and rare disease inspections
Figure 2 shows the data mining steps.
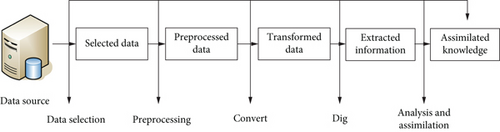
Cluster analysis technology is an important technology and method in the process of data mining. It is also a crucial link in the data mining process. This makes it an important research direction in data mining related fields. The process of clustering is to classify objects into a certain class according to their characteristics or to classify objects with similar properties into a class. A collection of data objects that are similar to each other in the same category is called a cluster, and all objects in the same cluster have a strong similarity. The essence of cluster analysis is to use an effective clustering algorithm to obtain classes of data. It divides data with large differences into different clusters, so that the generated clusters are a collection of one type of data objects. Cluster analysis does not require knowledge guidance, and it directly obtains meaningful data classification from the data, which is a kind of unsupervised learning. Cluster analysis technology generally starts from the data to classify, and there is no fixed classification standard. Clustering results often vary by clustering method. The same dataset may present different clustering results if different clustering methods are used.
Clustering algorithm, also known as cluster analysis, is one of the most famous methods in data mining. Cluster analysis uses various methods to identify the categories of data in each part of the dataset. It is an unsupervised data mining method. Its purpose is to integrate data with high similarity into multiple clusters for data analysis, as well as pattern recognition, image segmentation [15], text summarization, etc. By executing the clustering algorithm in multiple loops, the sum of the internal similarity of each cluster reaches the maximum. The optimal division of the data global is thus determined.
S2: The minimum distance from the candidate data point to the center point.
N: The number of objects in the dataset,
k: The final number of clusters,
a: Algorithm parallelism,
ouv: The degree of membership in the cluster,
mu: Dimensional measurement data,
savg: Average distance,
nu: The number of objects,
tl: Last update time,
S(g, tl): Grid density,
tb- Current time,
m: Number of matches,
bu: Number of data objects,
au: Mean vector,
a: The mean vector of the entire dataset,
ε: Weights of categorical attributes in the class.
It is related to data mining and also involves privacy issues. For example, an employer could try to cut insurance spending by accessing medical records to screen out those with diabetes or serious heart disease. However, this practice can lead to ethical and legal issues. For the mining of government and commercial data, issues such as national security or commercial secrets may be involved. This is also a challenge for confidentiality.
2.2. Cultural Creativity and Rural Tourism
Rural tourism mainly includes the following three parts: First, it takes place in rural areas; second, it is based on the unique natural and cultural landscapes of rural areas; and third, the target market group is urban residents, meeting tourists’ desire to return to nature and experience rural life. Since ancient times, China has established its country with agriculture, preserved a large number of farming cultures, preserved the original ecological folk culture, and accumulated profound cultural connotations. Rural tourism in rural areas can enjoy beautiful pastoral scenery, experience the simple folk culture, and appreciate the unique farming culture. And these are part of “rurality.” The key to defining rural tourism is whether it is rural. Rurality is the core of rural tourism and the key to distinguish rural tourism from other tourism. The quaint village buildings, the simple folk culture, and the original ecological agricultural products constitute the unique landscape of the rural area. Rurality has become the biggest attraction for tourists to rural areas.
Compared with other tourism activities, rural tourism can enable tourists to experience unique rural scenery and rural culture in the process of tourism. The essence of tourism is experience. Tourists in rural tourism mainly come from cities, and these tourists mainly fall into two categories. One is a native city dweller who is curious about life in the countryside. The second is residents who grew up in the countryside and lived in the city, trying to find memories that are gradually fading. Urban residents living in high-pressure, fast-paced cities pursue a slow-paced, close-to-nature rural life. They hope to experience the folk customs in rural areas, eat, live, and work with farmers, so as to increase their knowledge and enrich their travel interests. The number of rural tourists and the proportion of the main travel modes of rural tourism in recent years are shown in Figure 3.
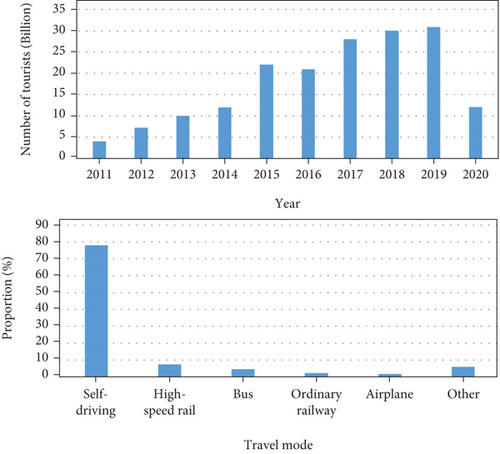
In order to realize the integration of urban and rural areas, change the status quo of poverty and backwardness in some areas, and build a moderately prosperous society in an all-round way, the government attaches great importance to the development of rural areas. Often, the poorer the region, the more ecological the natural scenery, the more simple the human landscape, and the richer the tourism resources. However, the lack of tourism services is an obstacle to the development of rural tourism in poor rural areas. If the government introduces incentive policies to encourage the development of local tourism in rural areas, the resource gains will become economic gains. This will promote rural economic development and growth of related industries. This can increase the income of residents in poverty-stricken areas and lead them out of poverty and become rich.
Tourism is an entertainment and leisure activity and a consumption activity that pursues the spiritual level. With the increase of people’s disposable income, residents have begun to carry out various forms of leisure tourism activities such as city outings, intercity tours, interprovincial tours, and outbound tours. While the number of travel destinations is increasing, tourists are no longer satisfied with fancy tourism. They need to enhance the experience and culture of tourism activities. At present, rural tourism products are constantly being upgraded. It has gradually transitioned from activities such as public sightseeing and farm picking to participatory, curious, and experience-based rural tourism products. The unique rural folk customs are favored by tourists. The diversification, individualization, and quality of rural tourism have become the focus of tourists. Tourists tend to pursue spiritual enjoyment. Only in-depth development of rural tourism products can meet the tourist needs of tourists. For example, it can add creative elements to traditional villages, traditional handicrafts, folk experiences, and national song and dance performances to increase the connotation and quality of rural tourism. These cultural and creative industries are in line with the spiritual needs of urban tourists, and the transformation of tourist consumption has become the driving force for the integrated development of the two industries.
The connotation and scope of rural tourism are very wide, involving many aspects of rural areas. It includes natural and human landscapes, such as beautiful pastoral scenery, agricultural production tools, farming culture, characteristic dwellings, folk customs, festival culture, and entertainment activities. The content of rural tourism in each region is different. As far as China is concerned, because of different natural environments, different cultural habits arise. This in turn affects the development of rural areas and diversifies rural areas in China. It is precisely because of the diversified development of rural areas that it can better attract tourists. At the same time, various high-quality resources of rural tourism can be developed into tourist resources that tourists like. It revitalizes idle resources and enriches the content of rural tourism. Rural tourism is extensive in both content and form.
Cultural and creative industries are defined as new industries that combine high-tech industries with knowledge economies, individual creativity, and innovation, with the core combining economy and culture. Knowledge, industry, culture, and innovation are rapidly developing and spreading in this economic era. It began to integrate into a variety of fields, and new forms of cultural innovation rural tourism emerged as a result of the integration of culture and innovation with tourism. It is the form of cultural and creative industries, as shown in Table 1.
| Forms of cultural and creative industries | Cultural and creative products | Propagation mode | Feature |
|---|---|---|---|
| Network and audio visual products | Computer software; TV works; radio works, etc. | Internet and audiovisual means | Spread widely |
| Publication | Books, newspapers, periodicals, text ads | Bookstores, newspapers | Tradition |
| Artwork or art performance | Art galleries, museums; handicrafts, antiques, calligraphy, and painting | Performance facilities: pavilion and stage | Vivid |
| Design drawings, models, or samples | Architectural design, fashion design, industrial product design | Productive demand | Sell ideas directly |
There are three levels of content in creative tourism: First, unlike traditional sightseeing tourism, tourists gain spiritual pleasure by participating in or experiencing the tourist destination’s folk customs, art, and way of life. The second is tourists’ ability to explore or improve a specific aspect of the tourism process. The third option is to engage in activities related to tourism destinations’ cultural and creative industries, such as participating in the planning of creative tourism destinations or filming of creative tourism destinations. Creative tourism is not just a combination of “creativity” and “tourism,” but two elements that have been integrated and have become inseparable. On the one hand, creative tourism is a subset of cultural tourism, which includes things like art, performances, festival folk customs, and folk handicrafts. Creative tourism, on the other hand, is a part of the cultural and creative industries. “Creativity” is at the heart of creative tourism.
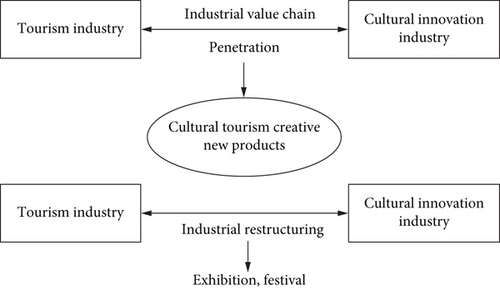
The advancement of technology has made the industrial categories continue to be refined, and industrial integration has gradually become an economic development trend. As the categories of industries become more and more detailed, both traditional and emerging industries are constantly changing, and there are more or less certain connections between industries. The boundaries between industries began to blur, and the industrial structure became increasingly complex. This requires the integration of related industries in order to maximize the use of resources. Most scholars believe that the theory of industrial integration is a dynamic process. It is not achieved overnight but requires a process of integration. The process is that the two industries are not related to each other, the boundaries are clear, the connections are increasing, the boundaries are blurred, and finally a brand new industry is formed. According to relevant theories, there are three main ways of industrial integration. The first is through the penetration and integration of new technologies; the second is the extension and integration of industries; and the third is the reorganization and integration within the industry.
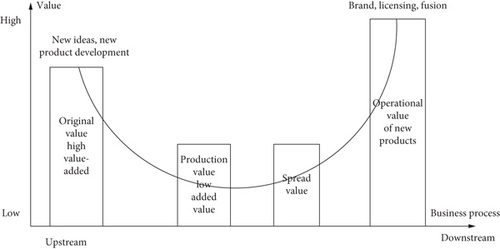
At this stage, many countries and regions attach great importance to the development of cultural and creative industries in their own countries and regions. The fundamental reason is to take a fancy to the driving effect of the cultural and creative industries on related industries and the promotion effect on the overall image of the country and region. Figure 4 shows the value performance of cultural and creative industries.
According to the division method of technology boundary, product boundary, organizational boundary, and market boundary, the boundary of rural tourism is to develop rural tourism relying on rural tourism resources. This has formed a wealth of rural tourism products and services. It then manages rural tourism, plans rural tourism, and sells rural tourism products. This in turn forms the tourism market and tourism groups and constitutes a complete industrial chain.
According to the same division method, the boundary of cultural and creative industries is to rely on cultural resources to produce. It produces different types of cultural and creative products and services and markets the resulting cultural products and services. This in turn forms consumer groups for cultural products and cultural markets and constitutes a complete industrial chain.
3. Experiment of the Integrated Development of Cultural and Creative Industry and Rural Tourism Industry
The phenomenon of industrial integration first appeared in the information technology industry. Tourism is an entertainment and leisure activity, and a consumption activity that pursues the spiritual level. To promote the integration of the two industries of cultural innovation and rural tourism, we must first have a sufficient understanding of the information and data of these two industries. Figure 5 shows the data mining method system designed in this paper.
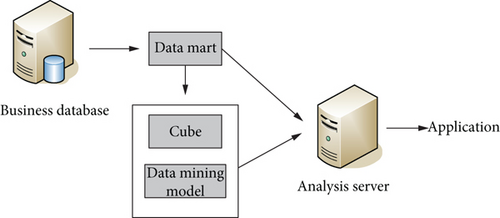
It uses high technology and creative wisdom to enhance the cultural connotation and value function of tourist attractions. It can extend the value chain of the tourism industry and drive the development of related tourism. The reorganization in the form of fusion is mainly to dismantle the value chain of the original industry, so that any changes in the activities of the value chain will cause the chaotic state of the value chain. This further dismantles the basic links with added value in the original industry, creates new value paths, and integrates emerging industries. If the new value chain includes the basic functions of creating value in different industries, then the new integrated industry is the same in every industry. But it will also create new business models that help the industry grow. The schematic diagram of fusion is shown in Figure 6.
With the development of science and technology, under the influence of internal and external factors, the boundary between the two major industries has become blurred, and the phenomenon of industrial integration has appeared. Industrial integration will break the boundaries of the two major industries and gradually realize industrial integration from four levels. Figure 7 shows the integration process of rural tourism and cultural and creative industries.
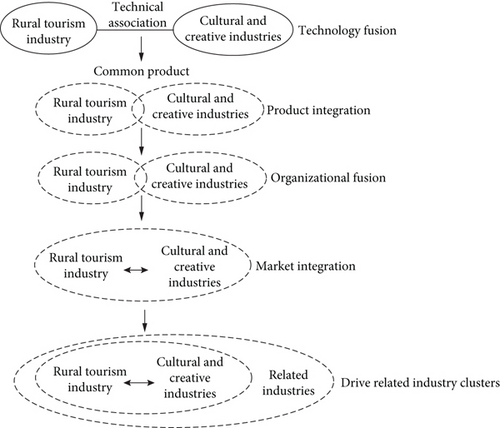
Each industry has its own production technology, and if there is technology, there will be technological boundaries. The two industries are technically related, and both industries have the technology of tangible and productized cultural resources, and can complement each other. In the early stage of industrial integration, the two major industries originally had clear boundaries and because of their technological relevance, appeared technology integration. Technology integration has become the first level of mutual integration and development between the two industries, and it is also the basic requirement for the integration of the two.
Cultural and creative industries have rich connotations and strong dissemination. Farming culture, ethnic minority songs and dances, traditional folk customs, and characteristic dwellings, etc. rely on their unique cultural content advantages and tourists’ curiosity, through creativity or technology, to excavate the originally hidden cultural resources and enrich the cultural connotation of rural tourism. Figure 8 shows the correlation data of tourists’ age and education.
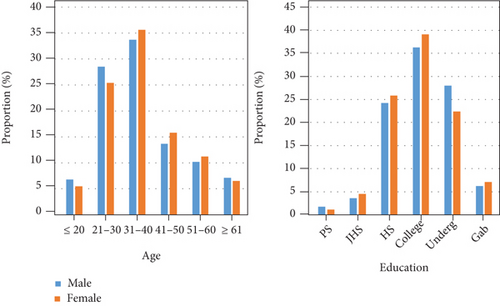
It can be seen that in the rural tourism market, the target customer group is mainly concentrated in the age group of 21-50. Tourists in this age group usually have a lot of work pressure, a fast pace of life, and a strong motivation for rural tourism. Tourists over 51 years old are also a very important target group for rural tourism because they have more leisure time and are more concerned about health. Tourists with college and undergraduate education are the main force of rural tourism, but there are fewer tourists with graduate degree and above. In the future, the development of rural tourism should be strengthened to attract tourists with higher education and further expand the rural tourism market.
Figure 9 shows the occupational structure and family income of tourists. It can be seen that in the occupational structure of rural tourists, workers account for the highest proportion, followed by civil servants and teachers. Tourists with a household income of more than 6,000 yuan have a strong demand for rural tourism.
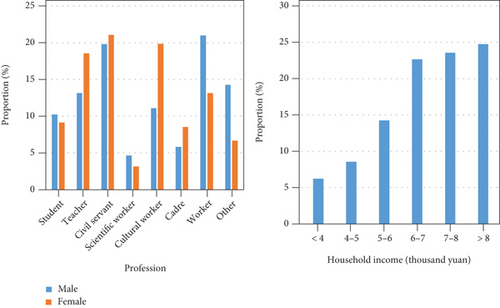
There are many sources of information for rural tourists to travel. The attractiveness of rural tourism to tourists is not solely dependent on one of the elements but is the result of the joint action of various attractions. Rural tourism travel information and tourism attraction are shown in Table 2.
| Information sources | Proportion | Tourist attraction | Proportion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recommended by relatives | 23.28% | Beautiful rural scenery | 75.4% |
| Broadcasting | 21.62% | Quiet and fresh environment | 67.6% |
| Outdoor advertising | 19.5% | Folk culture | 58% |
| Internet advertising | 20.74% | Wildlife | 36.4% |
| Newspapers and magazines | 8.41% | Country style | 25.4% |
| Travel agency recommendation | 3.54% | Agricultural labor | 21% |
| Other | 2.92% | Other | 18% |
The tourism motivation of rural tourists is relatively comprehensive. Tourists’ travel is often composed of a variety of motives, and rural tourism is greatly affected by emotional factors such as relatives and friends. The data related to travel motivation and travel mode are shown in Table 3.
| Travel motivation | Proportion | Travel mode | Proportion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enjoy the natural scenery | 76.49% | Accompanying family and relatives | 57.64% |
| Relieve stress | 68.21% | With friends and colleagues | 22.45% |
| Experience rural folk customs | 35.32% | Personal travel | 9.41% |
| Entertainment experience | 36% | Work reception | 6.58% |
| Agricultural production | 24.78% | Other | 3.92% |
Per capita rural tourism expenditure can best reflect the income of rural tourism destinations. The revisit rate of rural tourist destinations is not very high. It is mainly due to insufficient resource attractiveness and does not focus on innovation and has no sustained attractiveness. The per capita expenditure and revisit rate of rural tourism are shown in Table 4.
| Tourism expenditure per capita | Proportion | Tourists revisit | Proportion |
|---|---|---|---|
| <100 | 23.87% | Twice or less | 23.87% |
| 100-199 | 42.4% | Thrice | 25.67% |
| 200-299 | 14.28% | Four times | 16.78% |
| 300-399 | 10.04% | Five times | 11.97% |
| 400-499 | 6.87% | Six or more | 5.54% |
In order to more intuitively reflect the development status of the integration and coordination degree of the tourism industry and the cultural and creative industries, the integration and coordination degree intervals and grades are divided to obtain the comprehensive development level and integration and coordination degree. The results are shown in Figure 10.
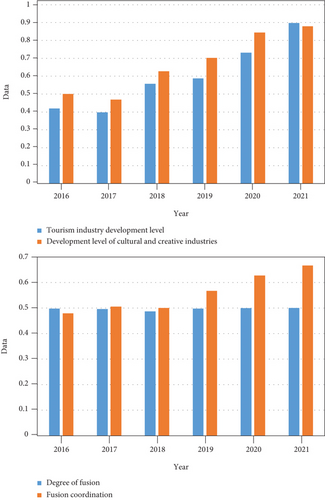
It can be seen that the level of fusion coordination has only reached the primary level of coordination. The sustainable development level of the tourism industry needs to be further improved. It needs to improve tourism infrastructure and improve service quality. This in turn makes the integration and coordination of the tourism industry and the cultural and creative industry system to a higher level.
The planning and development of creative rural tourism involves multiple departments. However, under the current fragmented administrative management system, the unified regulation and control ability of tourism administrative agencies is limited. It is unable to carry out macrodeployment and management of the creative rural tourism industry chain. In the specific development practice, due to the involvement of multiple administrative departments, coordination is difficult and there are many obstacles to implementation. This makes it impossible for the tourism administrative organ to designate a scientific and reasonable tourism plan, confusion of development ideas, random development methods, waste of resources, and repeated development. Due to the lack of scientific and rational planning, its agglomeration effect is limited. It has not established a cultural tourism industry demonstration area with regional characteristics and cultivated a composite creative rural tourism leading enterprise.
Rural tourism products are still designed and developed based on the development of primitive natural resources, and rural culture and tourism development are seriously out of touch. This is primarily due to a lack of integration between the rural tourism industry and the cultural and creative industries, as well as a lack of understanding of the rural cultural connotation and mutual promotion and interaction in a broad sense. Tourism’s soul is culture, and tourism is a major carrier of culture. The soul and core of the creative rural tourism industry should be rural culture with regional characteristics, but the reality is far from that. Traditional farming production tools and equipment have not received adequate attention in the development of farming culture due to the influence of agricultural mechanisation. Agricultural production has lost its original ecological flavour, and many items with a strong local flavour have long since vanished. Traditional weddings, funerals, festivals, folk art, and folk skills are not used to attract tourists in the development of folk culture. In short, there are not enough cultural elements in tourism development, and cultural characteristics are not well defined.
4. Discussion
There is a close relationship between cultural and creative industries and technology itself. On the one hand, the progress of science and technology can stimulate the inspiration of creativity, and on the other hand, it can turn creative ideas into reality. For regions, industries, and enterprises, talents are the primary productive forces for the development of regions, industries, and enterprises. Many social traditional concepts deeply affect people’s thinking. In order to have innovative ideas at the level of thinking, we must break the old thinking mode of the past and cultivate new thinking concepts. The integrated development of cultural tourism and creative industries is nurtured in an environment with innovative thinking. Applying new thinking to the tourism industry and cultural industry is not only a breakthrough in industrial boundaries but also an upgrade of industrial concepts. It should provide policy guidance and financial support for the introduction of high-level cultural and creative talents. In particular, it is necessary to introduce superior policies in terms of honor incentives, material treatment, working environment, and training to attract high-end cultural and creative talents. A scientific talent assessment mechanism is needed to ensure the quality and level of talents. Relying on the creative talent practice park, it attracts creative talents from all over the country to flow to the city. This provides intellectual support for the development of the creative rural tourism industry.
It needs to inject more creative elements into the cultural industry and tourism industry. In the past, a lot of creative thinking came from folk traditions. But it is indeed a theoretical guide to form a complete process from creative thinking, creative design, and creative integration. This requires some specialized schools and scientific research institutions to complete. It uses its own unique natural and cultural resources to form a development path that combines production, education, and research in the creative industry.
Any product level is a process of leaping from low level to high level, and creative products are no exception. The spiritual soul of a creative product is the thought in the human brain. This creative thinking comes from people’s rich imagination and creativity. In the development and utilization of the tourism industry, the government constantly pays attention to the upgrading of the spiritual level of creative products and launches spiritual products that meet consumers’ pursuit of higher levels. This plays an important role in improving the level of creative products. Tourism enterprises need to give full play to their own advantages and condense the essence of the core level of creative products. It enhances the level of creative products and increases the added value of products. To a certain extent, this will help the transformation of primary tourism creative products to more advanced tourism creative products.
A good social environment can promote the development of the city. A good social environment refers to an inclusive, diverse, and creative atmosphere, as well as the acceptance of innovative talents. City’s acceptance of innovative talents directly affects the development of city’s emerging industries, as well as the development of city’s economy. In the era of creative economy, in order to improve their competitiveness, enterprises must consider introducing innovative technical talents. Only in this way can we promote the development of enterprises and achieve sound and rapid economic development in the region. To sum up, the creative economy theory can achieve economic growth, realize a virtuous cycle of economic development, and provide new impetus for sustainable economic growth. The theory of “creative economy” is also an important theory that needs to be considered for the sustainable development of rural tourism.
With the development of rural tourism, rural tourism has become a key development industry in most regions. The development of rural tourism can bring many benefits to the local area, such as economic growth and the improvement of people’s income level. However, if the development is at the expense of the environment, it will inevitably cause many problems such as the deterioration of the ecological environment and the disappearance of characteristic cultural resources. The development of rural tourism is in conflict with resource development and ecological environment. The development of rural tourism is faced with the dilemma of how to achieve sustainable development. The sustainable development theory can solve the problem of how to choose between rural tourism development and resource development. Rural tourism in the theory of sustainable development is no longer blindly developed and only pays attention to economic benefits but realizes the harmonious development of economy, society, and ecology under the guidance of this theory. Under the guidance of the theory of sustainable development, the economy, society, and life of rural tourism areas realize a virtuous cycle and then realize the sustainable development of rural tourism.
5. Conclusion
The information age has not only changed the way of life of human beings but also gave birth to the new economic phenomenon of industrial integration. With the development of science and technology, industries that were originally not closely related have begun to gradually converge. And the content of its integration is getting richer and wider and wider, and the process is getting faster and faster. The cultural and creative industries will also become one of the important forces to stimulate China’s economic growth and can inject fresh blood into the Chinese economy. In this paper, based on different properties, a schematic diagram of osmotic and recombinant fusions is obtained. This paper proposes to gradually realize industrial integration from four levels and obtains a schematic diagram of the integration process of rural tourism and cultural and creative industries. In this paper, a preliminary forecasting study is carried out. Given the limited data sources and academic level, there are inevitably omissions in the research. The analysis of the status quo analysis stage is not thorough enough, and it only shows the changes of relevant indicators and lacks internal judgment analysis. In the theoretical research stage, the grasp of the theory is not deep enough. Future research will surely develop towards the direction of multielement fusion. On the basis of the integration of rural tourism and cultural and creative industries, it will realize the integration and development of information industry, science and technology industry, and ecological industry.
Conflicts of Interest
The author does not have any possible conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgments
This paper is the stage achievement of the major project of applied research of philosophy and social sciences in Henan Universities (2020-YYZD-03)“Research on the development strategy, path and countermeasure of the deep integration of Henan Culture and Tourism Industry.”
Open Research
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.




