Reform of University English Teaching and Examination Based on Stratified Teaching Method and Mobile Computing
Abstract
Teachers should change the traditional mode of teaching with the same content, schedule, and method, take note of individual differences among university students, implement hierarchical teaching, and use mobile computing platforms to improve teaching quality, in light of the “polarization” phenomenon that university students are currently experiencing in English learning. The hierarchical teaching mode, as a new type of teaching mode, has the potential to improve the quality and efficiency of English reading instruction in junior high schools. The stratified teaching method, as a teaching mode that can effectively demonstrate the principles of teaching university students according to their intelligence and graded guidance, plays a very important role in improving university students’ English learning level and learning enthusiasm. Teachers must abandon the traditional teaching mode, actively apply the hierarchical teaching method to English reading instruction, and design teaching content that is reasonable in relation to the physical realities of university students in order to contribute to the improvement of junior high school English instruction and the reading ability of university students. To continue to adapt to the development and needs of today’s society, university English teaching should implement hierarchical teaching, cultivate university students’ interest in learning in a variety of ways, and constantly strengthen the exploration and implementation of classroom teaching models.
1. Introduction
At present, it is common for university students of various learning levels to be placed in the same class, and the problem of grade differentiation within the class is also very prevalent, which has a negative impact on teachers’ teaching and university students’ development [1]. The importance of English has increased as a result of the digitization of social life and economic globalization. Traditional teaching methods can easily cause university students to lose interest in learning [2]. Teachers must change their teaching methods [3] in order to effectively improve the reading ability and grades of university students. Under the influence of traditional teaching methods, university students’ English learning frequently falls short of expectations. As a result, the hierarchical teaching model can be used in English classes [4].
At present, the classroom teaching of secondary vocational schools is carried out in accordance with the unified requirements of the syllabus and textbooks, and the same is true for English teaching [5]. With the continuous deepening of national teaching reforms, relevant departments have set the teaching requirements and teaching goals that universities need to achieve in English teaching and have made certain requirements for hierarchical teaching, thereby making a certain degree of hierarchical teaching in university normative guidance. There is a stratification of English proficiency levels in the teaching process due to differences in reading habits, vocabulary accumulation, reading interest, and motivation among university students [6]. In today’s world, English is the most widely used language in a variety of fields. Many countries make English a required course in basic education, and many employers make it one of the requirements for employment [7]. Teachers must establish reasonable levels for university students and then develop different teaching plans that take into account the development of university students at all levels so that all university students’ reading levels can be effectively cultivated and improved, and the effect of junior high school English reading teaching can be improved [8]. University students, as we all know, differ in character, ability, and knowledge, so there will be even more differences in the learning process. The number of university students with learning disabilities is rising, and the polarization phenomenon is intensifying, leading to a significant drop in interest in learning English. With the deepening of teaching reform in recent years, the hierarchical teaching model, which has the characteristics of teaching university students in accordance with their intelligence and hierarchical guidance, has also been universally recognized by a large number of universities and has been widely promoted and applied in English teaching [9]. Teaching university students in accordance with their intelligence is the earliest embodiment of hierarchical teaching. Hierarchical teaching is no longer a new topic. As early as two thousand years ago, Confucius put forward the principles of “teaching in accordance with their intelligence” and “teaching without class.” Many objective conditions constrain the existing class teaching system, which frequently employs a “one size fits all” teaching method and a teaching model based on teacher explanations that cannot meet the needs of all university students, resulting in a lack of motivation for top university students and a lack of support for potential university students. English “layered teaching” has a psychological foundation. Vygotsky, an educational psychologist, believes that learning content should be relevant to the learner’s experience. Therefore, for different levels of university students, the main body of the learning material should be distinct. A hierarchical teaching method, also known as a task-based teaching model, is used in this article. The cultivation of talents in higher education should also emphasize comprehensiveness so that the university students we educate will be more competitive in the future economic wave. The most important of these are good countermeasure teaching and teaching reform in English subjects. The investigation of the actual teaching situation revealed that there are numerous reasons for university students’ low reading levels. One of the most important reasons is that university students differ in many ways, particularly in terms of reading ability. To reverse this passive teaching situation and enable all university students to develop, it is necessary to break the traditional organizational form of classroom teaching, so as not to suppress university students with strong foundations or abandon university students with weak foundations, implement “layered teaching,” which is based on university students’ actual English proficiency [10].
Using the hierarchical teaching model to realize English teaching is not only convenient for teaching but also can meet the needs of university students and has a great stimulating effect on university students’ learning enthusiasm. The hierarchical reading of the task-based teaching model draws attention to the reading learning of different university students, enhances the reading interest and hobbies of university students at different levels, enhances the ability of university students to use reading strategies, improves the reading ability of most university students, and obtains the greatest benefit from reading classes, so as to optimize the teaching of English reading and make the reading classroom more effective [11].
2. Related Work
Reference [12] suggests a method of combining large classes, small classes, and individual teaching, in which two or more parallel classes are combined for class; small class research, discussion of large class teaching materials, individual teaching, primarily by university students independent work, part of the job is designated, and part of the job is optional. This teaching method is still in its early stages of development. Reference [13] proposes the concept of “layered and progressive teaching,” which holds that university students can be classified into several levels or types based on the different characteristics and levels of their learning abilities. This concept theoretically explains the implementation, the viability of stratified instruction. In the 1990s, the first experiment was carried out in Shanghai. The practice of stratified teaching was carried out in reference [14]. Different schools in different places discuss the benefits and drawbacks of stratified teaching in other schools and learn stratified teaching theory at home and abroad and put in some practice time, as well as propose some new ideas that are appropriate for our school. The development of hierarchical teaching is proposed in reference [15]. The recent development zone theory proposed by former Soviet educator Vygotsky is one of the important theoretical foundations. Treat them with respect so that they have genuine and equal access to education and the opportunity to grow as much as possible [16]. “In order to boost university students’ learning motivation, teachers should assign moderately difficult tasks that are appropriate for their current grades and abilities.” Reference [17], also known as the “flexible schedule system,” is thought to have been founded in 1868 by American educator Harris in St. Louis. “The implementation of differential teaching means that teachers change the speed, level, or type of teaching to adapt to learners’ learning needs, learning styles, and learning,” according to American scholar Diane Heck Si in his book Differential Teaching One by One Helps Every Student Get Success. Teachers and interests do not allow all university students to be held to the same standard. Reference [18] suggests that American scholar Tomlinson pointed out in his book Differential Teaching in Multiple Intelligences Classrooms that “the core idea of differential teaching is to differentiate between individual university students. Regarded as a component of teaching, teaching designs differentiated teaching content, processes, and results from university students’ different levels of preparation, interest, and style and ultimately promotes all university students to get their due development on the original level.” Reference [19] puts forward the regional teaching reform experiment of “layered and progressive teaching,” which makes “resolving the contradiction between the uniformity of teaching requirements and the possible differences of university students’ actual learning” as a strategy, which is helpful for real teaching strategy that faces all university students, comprehensively improves their quality, and is recognized by the majority of educators. Use the new and old knowledge to explore and realize the goal of the activity in the set scenario. Reference [20] proposes that from the perspective of education “tasks are activities or behaviors that people carry out after learning, understanding, and experiencing language.” Reference [21] proposes to define tasks from the perspective of language learning: a task is careful series of teaching activities organized to promote language teaching. These activities have their own specific goals, appropriate content, unique learning procedures, and various results. Task-based learning, according to reference [22], is a 20th century concept. Prabhu (1987) proposed it from the standpoint of teaching in the 1980s. The goal is to allow university students to learn a language by completing tasks with it, i.e., using specific tasks as motivation or motivation to complete the task. It reflects the results of teaching by displaying task results as a learning process. In the book Task-Based Learning Framework, reference [23] proposes the framework of task-based teaching, which includes pretask, during task, and posttask. A hierarchical teaching model, according to reference [24], can promote better teaching. University students are divided into groups based on their academic performance and growth potential. University students with similar assessments are placed in the same class or group, while those with larger differences are placed in a different class or group. Go to different classes or groups so that the disparity between educated people in each group is minimized. In the hierarchical teaching mode, according to reference [25], teachers must take into account the individuality and differences of university students and design classroom activities and lessons accordingly. Different types of educated people are educated according to their individual circumstances in the process of guiding learning so that all university students can learn in the most appropriate teaching environment for them. The “differential teaching theory,” as stated in reference [26], is as follows. Differential instruction: the personality of university students can be fully developed and their needs can be effectively met based on the differences between university students in the class and on the basis of university students’ knowledge and ability.
This article uses a layered teaching device, which can effectively mend university students’ learning enthusiasm, help university students build self-confidence, and make university students’ learning attitude significantly more positive. Moreover, in the hierarchical teaching model in the class, university students at different levels can have appropriate learning goals and can gain knowledge and learning fun from cooperative learning with classmates and rich learning materials. University students are more willing and good at autonomous learning.
3. Overview of Layered Teaching Method
3.1. The Connotation of Stratified Teaching
The hierarchical teaching model was first proposed in 1868 and has a history of more than a century of development, with its definition constantly evolving and updating. Currently, in the reform, university English teaching has faced unprecedented challenges. In order to address issues that arise in the classroom, some universities have started to use graded English classes [27]. Hierarchical teaching refers to the division of a class of university students into two or three levels based on intelligence and grade differences and the establishment of stratified teaching goals for them. Teaching takes into account the needs of university students at various levels, and they are taken into account as much as possible to strengthen classmates. There are also different levels of evaluation requirements for student performance. The English score management system is shown in Figure 1.

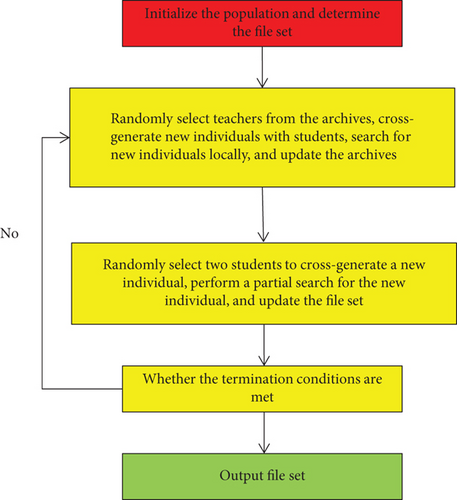
Let each student fully develop, this is the goal of applying the layered teaching model. Hierarchical teaching refers to “the teacher scientifically divides university students into groups of similar levels according to the university students’ existing knowledge, ability, and potential tendency and treats them differently.” These groups can be best achieved by teachers’ appropriate stratification strategies and interactions. “Good development and improvement” are affected by test-oriented education. University students have long been in a passive learning mode. Many university students have no interest in English. University English teaching is relatively boring. Many university students have no confidence in listening and speaking of English and have no motivation to learn. Teachers should stratify university students by combining their personalities, rather than using grades or subjective impressions of university students. This will have an impact on the rationality of stratification, and it will easily lead to rebellious psychology among university students, limiting the teaching effect. The stratified teaching model is not stratified for the sake of stratification, but rather to account for the differences in various aspects of university students. Teachers can stratify university students, teaching goals, teaching, homework, tutoring, and evaluation to create the most appropriate teaching environment for university students at each level. Hierarchical teaching is based on the objective existence of differences among university students, differentiatingly formulating guiding teaching goals, course content, teaching progress, changing teaching methods, and determining the evaluation system, so that each student can learn in the most appropriate learning environment. In the process, look for the best development [28]. The process of layered teaching method is shown in Figure 2.
Due to the limited teaching time and many knowledge points that need to be explained, the teaching method generally adopted by English teachers is to select classic articles for university students to read and listen to recordings and then expand the vocabulary. The teaching methods are rigid, making university students lose their learning interest. The key to applying this teaching method in teaching is that teachers should design corresponding learning tasks for each level of university students, and the difficulty of the tasks should be moderate to ensure that university students can achieve through hard work and avoid affecting their self-confidence. Teachers take note of the characteristics, interests, and expertise of university students and can help university students develop their individuality, explore various possibilities, and achieve comprehensive development. In general, the use of a layered teaching model is a step forward rather than a complete replacement for the original collective teaching method. Hierarchical teaching means that the school divides university students into groups based on student quality differences, establishes different teaching goals, creates different teaching content, and employs different teaching methods so that university students at all levels can learn. Learn to be useful, and eventually adapt to the various needs of society, in order to achieve the goal of talent development. Hierarchical teaching effectively avoids the teaching defects of the traditional teaching mode, as it is based on the principle of teaching university students according to their intelligence, with the main task of cultivating university students’ learning ability. It will aid in the resolution of a number of issues arising from the central government’s large-scale enrollment expansion. Adapt to the learning process and personality development of individual university students so that they can progress at all levels. Relevant professional knowledge will be incorporated on the basis of English knowledge according to the development of university students in the hierarchical teaching of University English, allowing university students’ English knowledge to be more targeted, reducing the student’s learning burden, and enabling university students to pass the knowledge of English. The acquisition has a more in-depth understanding of the meaning of the corresponding subject’s professional knowledge.
3.2. Theoretical Basis
3.2.1. The Theory of Teaching University Students in accordance with Their Intelligence
Teachers should adhere to the principle of “people-oriented,” according to the physical truth of university students, scientific and reasonable teaching goals, so as to avoid university students’ understanding of the goals or goals that are difficult to achieve, which will frustrate the enthusiasm of learning initiative. These all acknowledge the differences in student education, and conduct hierarchical teaching based on the differences. University students are different in physical and psychological aspects, such as intelligence, interest, hobbies, and other factors. This makes traditional class teaching activities more difficult for different university students to teach differently. In fact, there are not only differences between individual university students. There are differences and commonalities, which classify university students with similar learning characteristics into the same level. Teaching content also needs to be individually designed with university students of different levels. This is what is often said to teach university students in accordance with their intelligence. This is the key to ensuring that hierarchical teaching is of high quality. The adaptability of teachers is frequently reflected in their teaching. Teachers must be able to adapt to problems and change their teaching methods as needed, mobilize the classroom environment, and solve problems in the classroom creatively. Confucius, a Chinese educator, proposed the educational philosophy of “deepness, shallowness, benefit, and respect” more than two thousand years ago. “Teach university students in accordance with their intelligence and vary from person to person,” he advocated as a teaching principle. Zhang Zai is also of the opinion that “it is not difficult to teach others; however, you must give it your all. They are not to be confused with each other.” His ideas also emphasize the importance of teaching university students according to their intelligence levels. Following Confucius, Mencius, Dong Zhongshu of the Han Dynasty, Han Yu, and Liu Zongyuan of the Tang Dynasty were all practitioners who taught according to their intelligence. Later, in the Southern Song Dynasty, Zhu Xi popularized Confucius’ educational principle of “teach university students according to their intelligence.” Teachers should consider the personality characteristics and accepting abilities of university students when determining the teaching goals of cultivating university students. There are some distinctions among university students in each class, and some university students have exceptional comprehension and learning abilities. Recognize the differences in personality and abilities among university students by teaching them according to their intelligence. Advocate targeted education based on their personalities and expertise to promote the rational development of their advantages. In doing so, it not only takes care of the differences between individual university students but also avoids the indiscriminate one-shot end and improves the operational level of teaching. In teaching, university students should be placed in a dominant position, and they should be guided to discover interesting content, put forward interesting opinions, dig deeper into the connotation of the article, fully understand the essence of the article, and learn by analogy. Due to the wide range of information dissemination in today’s society, many university students tend to go to extremes in the acquisition and judgment of information. At this time, teachers are required to change teaching methods and teaching angles according to the physical truth to create a harmonious and equal teaching classroom for university students. When university students are tired, bored, and having other emotions, teachers should adjust the teaching mode in time to teach university students in accordance with their intelligence. The theory of teaching university students in accordance with their intelligence is based on the individual differences of university students. The hierarchical teaching that fully develops the university students’ personality is not only for all university students but also pays attention to the individual differences of university students. The achievable teaching content will eventually improve the learning ability and performance of all university students.
3.2.2. Nearest Development Area Theory
Former Soviet Union educator Vygotsky proposed the theory of the recent development zone. According to the theory, realistic teaching activities cannot maintain Xueniu’s current level of development. Teachers’ instruction should cause, inspire, and initiate a series of internal development processes for students so that they can use their own efforts to achieve a higher level of knowledge than they currently have. Traditional English instruction has failed to account for the differences and individuality among university students, and its flaws have become increasingly apparent. The “recent development zone” theory underpins hierarchical education. Every student is thought to have two stages of development. Teaching should focus on university students’ recent development areas, provide content with a certain level of difficulty, mobilize university students’ enthusiasm, play their potential, exceed their recent development area and reach the level of the next stage of development, and then proceed on this basis the creation of a growth zone. Teaching is a process of transforming potential levels into existing levels while also continuously creating new existing levels. The “recent development zone” is itself in a state of flux. The recent development zone is transformed into the current level of development when a certain stage of the teaching process is completed, resulting in the actualization of the potential level. The foregoing has resulted in the formation of a new recent development area that is higher than the original recent development area. Aside from differences in English proficiency, current university students differ greatly in terms of psychology and personality. As a result, traditional English is no longer capable of caring for university students. This necessitates that university students who share the same characteristics as a specific praying man be placed on the same level. This will not only take into account the differences in personality among university students but will also help them develop to their full potential. Individual differences are the only way to start teaching. Only by transforming the recent development zone into the current development level and continuously creating a higher-level recent development zone can the development of university students be promoted. Individual differences of university students include differences in current levels and differences in potential levels. Only from individual differences in university students start teaching and continue to create a higher level of recent development area for university students. To maximize the development of university students, teaching is the most effective step by step approach. Teaching can only be based on different individuals if university students’ individual differences are respected and hierarchical teaching is used. The “recent development zone” creates a “practical development level” by combining various tasks. The goal of teaching is to instill a love of learning in university students and to assist them in their overall development. The new development zone theory proposed by Vygotsky advocates aligns with the teaching philosophy. Start with the reality of university students at each level, taking into account their overall current and potential levels, assigning university students one development goal after another in accordance with their most recent development area, and continually mobilizing university students’ potential. Encourage them to keep working hard to progress to the next development zone, one by one, in order to achieve overall teaching improvement. The layer teaching mode is to find the nearest development zone close to the university students’ respective characteristics so that university students can see the hope of success, clarify the goal of hard work, and adopt educational methods suitable for the individual characteristics of university students, stimulating their enthusiasm and initiative in learning and gradually developing themselves, thereby improving teaching effects and learning quality. On the basis of respecting individual differences, implement hierarchical formulation of reading goals and hierarchical design of reading tasks. Targeting different university students and teaching university students in accordance with their intelligence reflect the strong pertinence in the implementation of hierarchical teaching, which can successfully help university students realize the most recent development area and promote the development of different university students’ potentials.
4. Reform of University English Teaching and Examination Based on the Stratified Teaching Method
4.1. Carry Out Layered Teaching
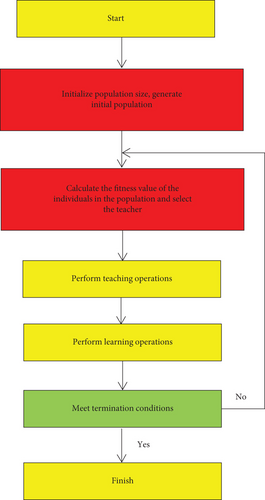
The reasonable stratification of university students should be based on the university students’ English foundation. Teachers can thoroughly understand the physical truth of the university students according to their classroom performance and test results and comprehensively consider the university students’ knowledge structure, learning interest, and learning ability, so as to achieve reasonableness of stratification. As a teacher, we should help university students formulate learning goals that are in line with actual academic conditions. On the one hand, we must consider objective conditions such as the school’s teaching management, teaching organization, teacher level, and teaching facilities. On the other hand, we must also consider many factors such as university students’ knowledge base, potential abilities, and parents’ wishes. In teaching, it is emphasized to give university students specific and clear monthly targets so that university students use specific daily targets as motivation and motivation for learning, and let university students see achievements and experience success in the process of completing tasks and achieving goals, so as to encourage university students’ enthusiasm for learning. The English optimization flowchart of the layered teaching method is shown in Figure 3.
Realize detailed stratification based on various majors and develop their own teaching standards. We set a long-term goal of memorizing 1500 commonly used vocabulary, using 600 communicative oral sentences, and mastering general practical writing skills. Aiming at the fact that university students’ basic level is uneven, the management mode of “classification and hierarchical teaching according to the rules” is established in accordance with the three-dimensional goal of “knowledge and skills, process and methods, and emotional attitudes and values.” Teaching in a hierarchical structure is a dynamic process. In the classroom, the goal is to teach 10 words, 6 sentences, and 1 dialogue. Students at the university are only required to be calm in every class. Learn these materials thoroughly so that university students believe that learning English is not a difficult task. The initial stratification was done based on the results of the high school entrance examination at the time of enrollment. The aspiration form was filled out by university students in order to learn about their knowledge and abilities, as well as their desire for employment and further education. Encourage university students and parents to take the proper position beneath the boat by respecting their opinions. The process of improving one’s English learning ability is a gradual one. Therefore, teachers should carry out a comprehensive evaluation according to the university students’ learning process and academic performance and carry out the improvement of the teaching plan based on the university students’ learning situation. Its purpose is also to teach university students in accordance with their intelligence so that university students can build up confidence and strive for a happy development. Language is developed in application and practice. In response to the needs of professional learning and job hunting in vocational schools, it is necessary to strengthen their basic knowledge and improve their language learning ability. The implementation of hierarchical teaching mode can fully consider university students’ knowledge, ability level, and personal hobbies conducive to the development of university students’ personality.
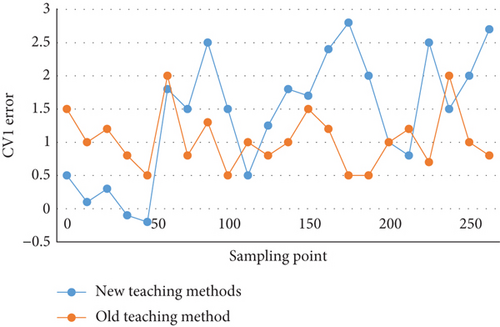
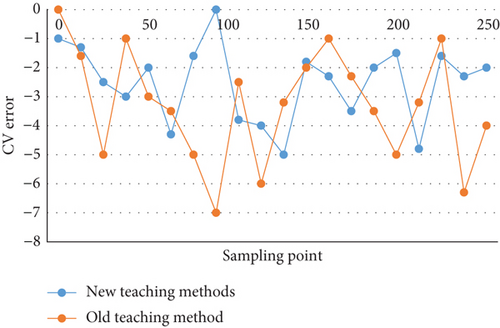
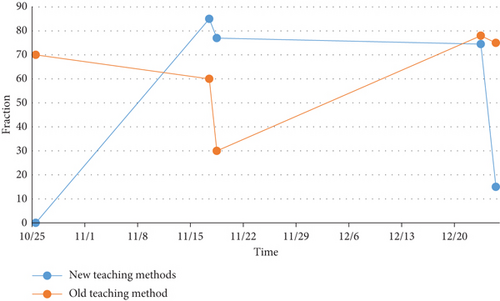
The modeling data in this section is obtained from the transfer function of the distillation tower WB model and the distillation tower OR model: step signal input with an amplitude of 1, and zero mean noise with an amplitude of 0.1 added. In 2 minutes, a total of 250 samples were taken. Figure 4 shows the simulation and actual value error diagram of the WB distillation column with the new and old teaching method. Figure 5 shows the simulation and actual value error diagram of the OR distillation column with the new and old teaching method.
4.2. Stimulate University Students’ Interest
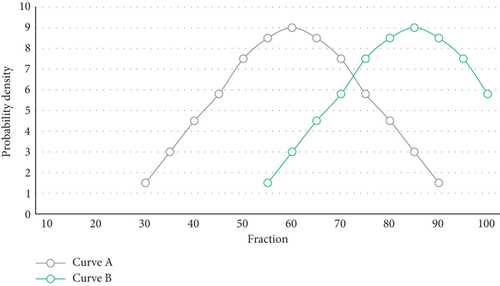
Teachers should consciously change the traditional teacher-based teaching model, abandoning the flaws and bad habits in English teaching in the past by optimizing classroom procedures and implementing new teaching methods in their English teaching activities. The teaching stratification is primarily aimed at teachers, who are responsible for instructing university students based on their intelligence. “Comprehensible language input” can encourage language learners to participate in language learning interactions, thereby promoting foreign language application and acquisition. Intuitive teaching can not only leave a lasting sensory impression on university students and pique their interest in learning, but it can also quickly form correct concepts for things so that they can be remembered as well as an initiative to promote the development of university students’ basic English knowledge and skills. A knowledgeable teacher instructs university students in order to improve the overall average score of the class. The score distribution of university students under different teachers’ teaching is shown in Figure 6, and the distribution curve of the score results obtained by university students is shown in Figure 7.
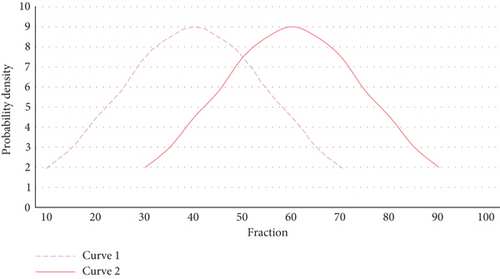
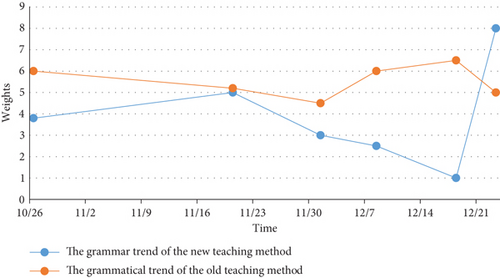
University students spend 5-10 minutes before class singing English songs, conversing in English, reciting English poetry, giving English speeches, performing English drama, and dubbing English films. Teachers should use different methods with university students of various levels and the same teaching content. The use of intuitive, vivid teaching methods appropriate for university students’ psychological development can increase university students’ interest in learning in the classroom. Allow university students to speak more in class to develop and improve their expressive skills, and allow university students to write more to develop and improve their writing skills. Teachers can also try to use writing to encourage students to learn and write to encourage students to listen. Using interactive activities in the classroom not only helps to activate the classroom atmosphere, but it also helps to stimulate university students’ interest in English learning and improves their oral expression, organization, and coordination skills. In second-language learning, the learner’s learning motivation and attitude are critical factors that have a direct impact on the learner’s foreign language acquisition. The results of the student examination show that, compared with the new layered teaching method, the trend of university students’ grammatical ability of the new and old teaching methods is shown in Figure 8.
Carrying out interactive activities, university students are concentrated, their understanding and absorption of English curriculum knowledge are at the optimal stage, and the efficiency of English learning has reached the best, which is beneficial for teachers to carry out English teaching activities. With a clear division of levels, university students at all levels have a clear learning goal. In the teaching process, we make full use of physical objects to organize classroom teaching, which is more vivid and lively, which is conducive to memory. Of course, there are many forms of intuitive teaching. In classroom teaching, you should choose an appropriate teaching method or a combination of various forms according to the physical truth. Teachers’ correct and clear explanations and heuristic questions and university students’ own exercises and summaries can also train university students to actively use a variety of thinking methods to analyze and solve problems. When university students are in university, there are English-related tests such as the university English application proficiency test and the public university English test four and six. These exams in themselves are motivating university students to study hard. After clarifying their goals through stratification, teachers should “teach university students in accordance with their intelligence,” that is, teach according to the requirements of university students at different levels in the course of teaching. University students’ interest in learning is formed and developed in learning practice. Teachers should change the obligatory concept of emphasizing “instillation” rather than “interest,” avoid the superficial teaching mode of emphasizing “knowledge” rather than “thinking,” and let university students gradually develop from “learning and answering” to “learning.” University students are diligent in thinking, active participation, hands-on practice, and other habits. Figure 9 shows the trend of student scores for the old and new teaching methods based on the student’s test scores.
4.3. Establish Scientific Teaching Evaluation
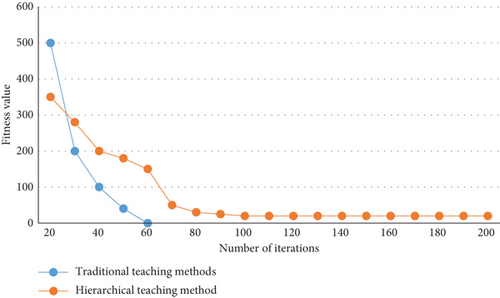
The importance of hierarchical evaluation in hierarchical teaching cannot be overstated. The process of improving one’s English learning ability is a gradual one. As a result, teachers should conduct a comprehensive evaluation based on the learning process and academic performance of university students, as well as improve the teaching plan based on the university students’ learning situation. The traditional practice of using test scores as the standard of summative evaluation to measure university students is being replaced by English hierarchical teaching. Only university students should be allowed to master the fundamentals of English learning. A strong foundation has been established. It is possible to improve their English learning abilities by allowing their university students to learn on their own and use the language independently. At the present stage, the evaluation method of junior high school English course teaching is relatively single and one-sided, and it does not reflect the actual learning situation of university students. The hierarchical evaluation is a comprehensive evaluation of university students’ performance in classroom learning and performance in practical activities, daily learning, and face-to-face results. The convergence curve of traditional teaching method and hierarchical teaching method is different. The convergence curve of the old and new teaching methods is shown in Figure 10.
The goal of hierarchical teaching is to determine the requirements for university students at various levels based on the syllabus’s requirements and the reality of the student’s cultural foundation. Every university student has something to learn, something to be strong about, and something to accomplish. For teaching evaluation, lecturers should consider the developmental and scientific nature of the material, as well as the motivation of university students, so that university students are encouraged to learn and can devote themselves more actively to teaching. To represent the parameter index distribution model of English proficiency evaluation, create a high-dimensional feature distribution space and restrict the main index parameters of English teaching ability, such as teacher level, teaching facility investment, and policy relevance level.
Teachers should use different evaluation standards for university students at various levels in order to boost their confidence in learning. “There are no university students who cannot teach well; there are only teachers who cannot teach well,” as the saying goes. We will undoubtedly be able to improve the level of English teaching in vocational high schools if we comprehend the psychological characteristics of university students and teach university students in accordance with their intelligence. Following the stratified teaching of English, the teacher focuses on the personality traits of university students, cultivates and improves their own humanistic qualities, and establishes the correct educational concept. Gradually, your teaching experience grows. Slowly learn how to deal with a variety of teaching issues, and his relationship with university students is pleasant. Teaching self-assurance is on the rise, as is personal educational efficacy.
5. Conclusions
As the saying goes, “there are no university students who cannot teach well, only teachers who cannot teach well.” As long as we grasp the psychological characteristics of university students and teach university students in accordance with their intelligence, we will definitely be able to improve the level of English teaching in vocational high schools. All in all, in order to improve the quality of university English teaching, teachers must have a deep understanding of the physical truth of university students, fully understand and respect the differences between them, and rationally design hierarchical teaching content according to the university students’ cognitive level and understanding ability. Hierarchical teaching plays an extremely vital role in the teaching of English reading in junior high schools. Through hierarchical teaching, we can find more effective solutions to help university students improve the quality and efficiency of learning and make outstanding contributions to the future development of university students and the improvement of comprehensive abilities. The use of hierarchical teaching in the process of English teaching in universities can effectively reflect the principles of teaching university students in accordance with their intelligence and graded guidance and has a beneficial effect on improving university students’ English proficiency, learning ability, and cognitive ability.
Conflicts of Interest
The author does not have any possible conflicts of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.




