Posttreatment Recurrence and Death Patterns in Patients with Advanced Esophageal Cancer
Abstract
Objective. To investigate into the clinical factors associated with posttreatment recurrence and death patterns in patients with advanced esophageal cancer. Methods. Clinical information of patients with recurrence/metastasis and death after radical resection of esophageal cancer at our hospital between January 1, 2005, and December 31, 2015, were retrospectively collected and followed up. Postoperative recurrence-free survival time, postrelapse survival time, and overall survival time were compared among the metabolic-associated, organ failure-associated, and anastomotic recurrence-associated mortality groups. Results. Five hundred and ninety-five qualified patients were retrieved, including 456 males and 139 females, with an average age of 58 ± 7.56 years. There were 57 cases of TNM-1 stage, 131 cases of TNM-2 stage, 365 cases of TNM-3 stage, and 42 cases of TNM-4 stage. There were 547 cases of squamous cell cancer and 48 cases of nonsquamous cell cancer. There were significant differences in age (p < 0.01), tumor location (p < 0.01), and lymph node metastasis (p = 0.04), recurrence type (p < 0.01) by one-way ANOVA, and recurrence-free survival (p = 0.02) and postrecurrence survival (p < 0.01) by Kaplan-Meier survival curve analysis among the three main death causes. Conclusions. Age, tumor location, and lymph node metastasis were significantly different among metabolic-associated, organ failure-associated, and anastomotic recurrence-associated mortality of recurrent EC patients.
1. Introduction
Esophageal cancer (EC) is one of the most common malignant upper gastrointestinal tumors and ranks the fourth cause of cancer-related mortality in China [1]. In 2017, there were 234,624 new cases of EC and 212,586 new deaths due to EC in China [2]. Risk factors of EC include smoking, heavy drinking, nitrosamine and certain mold/fungi, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and Barrett’s esophagus. In EC cases at early-mid clinical stages or above, surgery with postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy or radiotherapy is the most accepted treatment. However, after surgery and adjuvant therapy, 30%-40% of cases will still develop lymph node metastasis within 2 years, with poor treatment response and a median survival of 7 only months [1]. Previous studies have shown that postoperative lymph node metastasis and other related factors affect the postoperative recurrence and metastasis rates, but the characteristic patterns of recurrence, metastasis, and cancer-related death in patients with EC after radical resection and postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy or radiotherapy remain unclear. Therefore, we retrospectively collected patients with recurrence/metastasis after radical resection of esophageal cancer at our hospital and analyzed the relationship between patients’ clinical characteristics and their recurrence/metastasis patterns and death patterns, in order to provide evidence to clarify the disease process of advanced EC.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Population
The present study was approved by the ethics committee of our hospital. Patients’ information with posttreatment recurrence of EC [3] who were treated at our hospital from January 1, 2005, to December 31, 2015, was retrospectively collected. The following are the inclusion criteria: thoracic EC cases [4] and received esophagectomy, upper and lower stumps negative for cancer lesions, number of lymph nodes collected ≥16; and having complete postoperative adjuvant therapy information. The following are the exclusion criteria: those who suffered from other malignant tumors at the same time or after EC or those who were lost to follow-up for more than 6 months.
2.2. Follow-up Items
The requirement for follow-up within 2 years after operation included reexamination of chest and upper abdominal CT and esophagography every 3 (±1) months to determine the status of regional lymph nodes and anastomotic stoma, then every 6 months between 2-5 years after operation for similar items. According to the 8th edition of NCCN TNM staging standard for esophageal cancer [4], postoperative recurrence-free survival was defined as the time after surgery to the time of tumor recurrence or disease progression based on the pathology report during follow-up. Postrelapse survival time was defined as the time from the diagnosis of relapse to death. The definition of recurrence pattern is as follows: recurrence of anastomotic stoma refers to reexamination of new organisms and biopsy confirmed by biopsy; lymph node recurrence referred to reexamination of CT scan showing new enlarged lymph nodes with a short diameter greater than 1 cm. The definition of main death modes is as follows: metabolic disorder-related death was defined as death caused by chronic low serum protein, electrolyte imbalance, and other symptoms of cachexia; organ failure-related death was defined as death caused by clear diagnosis of heart, lung, liver, or multiple organ failure; anastomotic-related death was defined as death due to anastomotic-site fistula-induced infection or major bleeding. Adjuvant chemotherapy was defined as receiving at least once of platinum-containing combination chemotherapy after surgery.
2.3. Statistics
SPSS 24.0 software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, USA) was used to analyze the differences in survival time and survival rate of patients. The difference in median recurrence-free survival time between the two groups was analyzed by a t test, while the difference in median recurrence-free survival time between multiple groups was analyzed by one-way ANOVA, and the difference in survival rate was analyzed by a chi-square test. Correlation analysis was performed using Pearson’s correlation coefficient analysis. Differences in survival curves were analyzed using Log-Rank analysis within Kaplan-Meier survival curve. A two-tailed p value less than 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. General Conditions of Enrolled Patients
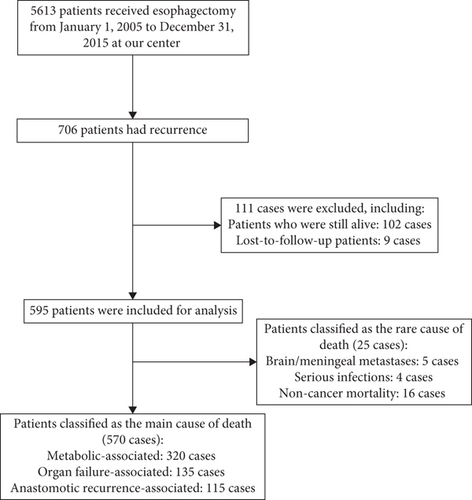
There were 5613 EC cases who received esophagectomy at our center from January 1, 2005, to December 31, 2015. Seven hundred and six patients had recurrence, and 595 cases were included for analysis, including 25 cases of rare causes of death and 570 cases of main causes of death (320 cases for metabolic-associated deaths, 135 cases for organs failure-associated deaths, and 115 cases of anastomotic recurrence-associated deaths, Figure 1). There were 456 males and 139 females, with an average age of 58 ± 7.56 years. There were 57 cases of TNM-1 stage, 131 cases of TNM-2 stage, 365 cases of TNM-3 stage, and 42 cases of TNM-4 stage. There were 547 cases of squamous cell cancer and 48 cases of nonsquamous cell cancer (Table 1).
| Number | Rate% | |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||
| Male | 456 | 76.6 |
| Female | 139 | 23.4 |
| Age | 58 ± 7.56 | |
| Tumor location | ||
| Upper | 66 | 11.1 |
| Middle | 409 | 68.7 |
| Lower | 120 | 20.2 |
| Tumor size | 5 ± 2.05 | |
| TNM stage | ||
| 1 | 57 | 9.6 |
| 2 | 131 | 22 |
| 3 | 365 | 61.3 |
| 4 | 42 | 7.1 |
| Lymph node metastasis | ||
| Negative | 272 | 45.7 |
| Positive | 323 | 54.3 |
| Pathological types | ||
| Squamous cell cancer | 547 | 91.9 |
| Nonsquamous cell cancer | 48 | 8.1 |
| Differentiation grade | ||
| Well | 324 | 54.4 |
| Poor | 264 | 44.4 |
| Undifferentiated | 7 | 1.2 |
| Location of anastomoses | ||
| Neck | 90 | 15.1 |
| On the arch aor | 460 | 77.3 |
| Under the arch aor | 45 | 7.6 |
| R0 resection | ||
| Yes | 540 | 90.7 |
| No | 55 | 9.3 |
| Stump pathological grade | ||
| Normal | 540 | 90.7 |
| Atypical hyperplasia | 22 | 3.7 |
| Carcinoma | 33 | 5.6 |
3.2. Metastasis Characteristics of Died Patients due to Recurrence
In a detailed analysis of the cause of mortality in the metabolic-associated category, there were 190 cases of extensive lymph node metastasis, 45 cases of cachexia, 40 cases of bone metastasis, 29 cases of liver metastasis, and 16 cases of rare metastasis. In the organ failure-associated category, there were 106 cases due to respiratory failure, 21 cases due to multiple organ failure, 6 cases due to circulatory failure, and 2 cases of hepatic failure. In the anastomotic recurrence-associated category, there were 95 cases of hematemesis and 20 cases of fistula. There were also 5 cases of brain/meningeal metastasis, 4 cases of serious infections, and 16 cases of noncancer mortality (Table 2). Among the three main death causes, there were significant differences in recurrence type, recurrence-free survival, and postrecurrence survival among the three main death causes (p < 0.05 for all comparisons, Table 3).
| Cause of mortality | Number | Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Metabolic-associated | 320 | 53.8 |
| Extensive lymph node metastasis | 190 | 31.9 |
| Cachexia | 45 | 7.6 |
| Bone metastasis | 40 | 6.7 |
| Liver metastasis | 29 | 4.9 |
| Rare metastasis | 16 | 2.7 |
| Organ failure-associated | 135 | 22.7 |
| Respiratory failure | 106 | 17.8 |
| Multiple organ failure | 21 | 3.5 |
| Circulatory failure | 6 | 1 |
| Hepatic failure | 2 | 0.3 |
| Anastomotic recurrence-associated | 115 | 19.3 |
| Hematemesis | 95 | 15.9 |
| Fistula | 20 | 3.4 |
| Brain/meningeal metastases | 5 | 0.8 |
| Serious infections | 4 | 0.7 |
| Non-cancer mortality | 16 | 2.7 |
| Cause of mortality (n) | p value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolic-associated | Organ failure-associated | Anastomotic recurrence-associated | ||
| Recurrence type (n) | <0.01 | |||
| Anastomosis associated | 11 | 8 | 58 | |
| Local lymph node metastasis | 243 | 109 | 53 | |
| Distant lymph node metastasis | 66 | 18 | 4 | |
| Recurrence-free survival (months, mean ± SD) | 12 ± 17.28 | 14.5 ± 23.11 | 16 ± 32.34 | 0.02 |
| Post-recurrence survival (months, mean ± SD) | 10 ± 11.02 | 16 ± 13.31 | 11 ± 12.7 | <0.01 |
| Overall survival (months, mean ± SD) | 24 ± 21.27 | 32 ± 26.48 | 26 ± 36.36 | 0.10 |
3.3. Clinical Characteristics of Patients due to Different Death Causes
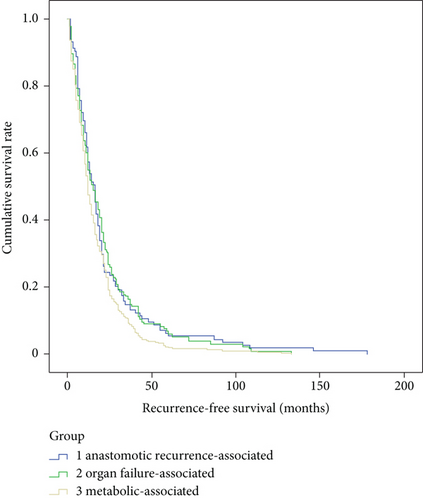
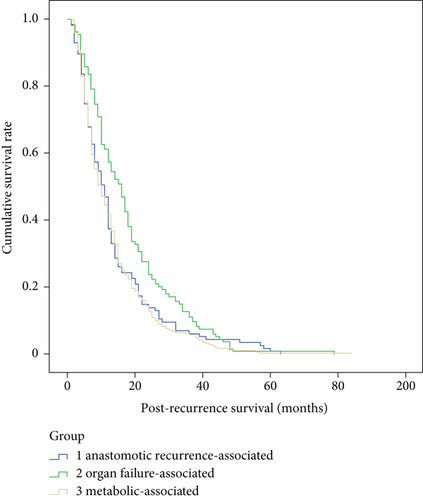
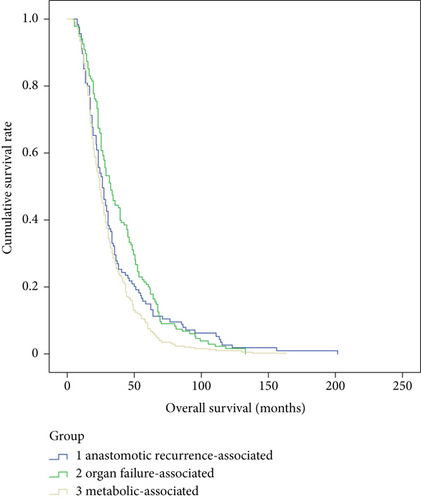
There were no significant differences in gender (p = 0.53), tumor size (p = 0.75), tumor stage (p = 0.86), pathological types (p = 0.83), differentiation grade (p = 0.18), location of anastomoses (p = 0.07), R0 resection (p = 0.92), or adjuvant therapy (p = 0.93), but there are significant differences in age (p < 0.01), tumor location (p < 0.01), and lymph node metastasis (p = 0.04) among the three main death cause groups, e.g., metabolic-associated, organ failure-associated, and anastomotic recurrence-associated (Table 4). According to the Kaplan-Meier survival curve, there were significant differences in recurrence-free survival (p = 0.02) and postrecurrence survival (p < 0.01), but not in overall survival (p = 0.10) among the three main death cause groups (Figures 2–4).
| Cause of mortality | p value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolic-associated | Organ failure-associated | Anastomotic recurrence-associated | ||
| Gender (n) | 0.53 | |||
| Male | 245 | 100 | 92 | |
| Female | 75 | 35 | 23 | |
| Age (year, mean ± SD) | 57 ± 7.01 | 59 ± 7.9 | 58 ± 7.94 | <0.01 |
| Tumor location (n) | <0.01 | |||
| Upper | 27 | 14 | 20 | |
| Middle | 221 | 103 | 67 | |
| Lower | 72 | 17 | 28 | |
| Tumor size (cm, mean ± SD) | 5 ± 1.89 | 5 ± 2.2 | 5 ± 2.32 | 0.75 |
| Tumor stage (n) | 0.86 | |||
| 1 | 34 | 13 | 8 | |
| 2 | 71 | 32 | 25 | |
| 3 | 199 | 79 | 69 | |
| 4 | 16 | 11 | 13 | |
| Lymph node metastasis (n) | 0.04 | |||
| Negative | 137 | 62 | 64 | |
| Positive | 183 | 73 | 51 | |
| Pathological types (n) | 0.83 | |||
| Squamous cell cancer | 295 | 125 | 108 | |
| Nonsquamous cell cancer | 25 | 10 | 7 | |
| Differentiation grade (n) | 0.18 | |||
| Well | 162 | 81 | 66 | |
| Poor | 157 | 51 | 47 | |
| Undifferentiated | 1 | 3 | 2 | |
| Location of anastomoses (n) | 0.07 | |||
| Neck | 42 | 17 | 26 | |
| On the arch | 249 | 115 | 79 | |
| Under the arch | 29 | 3 | 10 | |
| R0 resection (n) | 0.92 | |||
| Yes | 292 | 120 | 105 | |
| No | 28 | 15 | 10 | |
| Adjuvant therapy (n) | 0.93 | |||
| No | 134 | 55 | 46 | |
| Chemotherapy | 149 | 63 | 52 | |
| Radio/chemo | 37 | 17 | 17 | |
4. Discussion
Many biomarkers for EC have been reported [5–7]. However, some studies reported lymph node metastases patterns at the time of surgery [8, 9], and to attribute the recurrence/metastasis patterns and death patterns of advanced EC to patients’ clinical characteristics is still a big challenge. In this study, we retrospectively collected 595 cases who died due to recurrence of EC and analyzed the recurrence and death patterns. We found that metabolic-associated causes (53.8%) accounted for the majority of death, followed by organ failure-associated (22.7%) and anastomotic recurrence-associated (19.3%) causes.
Compared with a recent study by Sohda et al. [10], which contained 307 EC cases (197 nonrecurrence cases and 110 recurrence cases) from Japan, more EC-recurrent patients (n = 595) were enrolled in our study. Their findings that 92% recurrent were observed in less than 2 years after radical esophagectomy have a similar trend as our findings, which was much higher than the 30-40% by Chinese surveillance [1]. The difference between their and our findings might be due to the difference in the composition of pathological types (squamous cell: 83.4% in their study vs. 91.9% in our study), age (mean: 65.2 years old in their study vs. 58 years old in our study) [11, 12] and living environment and habits [13–15]. They also found that patients with lymph node metastasis survived significantly longer than those metastasized to other organs and patients after surgical or additional postoperative chemotherapy lived longer than those who received other treatments. Due to the difference in study design, we could not validate the above two findings in our cohort of EC patients.
In another study by Yang et al. [16], 95 recurrent EC patients was analyzed. Among them, 4 (4.2%) were local-only, 40 (42.1%) were regional-only, 44 (46.3%) were hematogenous-only, and 7 (7.4%) were combined recurrences, while in our study, we included all dead patients and divided the recurrence pattern into metabolic-associated, organ failure-associated, and anastomotic recurrence-associated groups, which was more detailed and cause-attributable. They also found that cervical lymph nodes were the most frequent sites of regional recurrence, whereas the lung was the most hematogenous recurrence site. Their median recurrence-free interval was 12.1 months (versus 12 months in the metabolic-associated group, 14.5 months in the organ failure-associated group, and 16 months in the anastomotic recurrence-associated group in our study). In their study, tumor in the upper esophagus, larger tumor length, and positive lymph nodes were independent risk factors for recurrence. In contrast, we found that age, tumor location, and positive lymph nodes were significantly different among the three main death cause groups. Again, our findings among the dead patients drew a much closer picture of the death pattern based on more enrolled dead cases. It is also interesting to note that some clinical conditions, such as hepatitis, HPV, inflammation, or hypoxia, might affect the development or recurrence of EC [17–20].
In conclusion, based on our relative large enrolled number of patients, age, tumor location, and lymph node metastasis were significantly different among metabolic-associated, organ failure-associated, and anastomotic recurrence-associated mortality of recurrent EC patients.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study were supplied by the Institutional Ethnics Committee of the Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University under license and so cannot be made freely available. Requests for access to these data should be made to Dr. Jidong Zhao (e-mail: [email protected]).