Effects of Breed, Age, Body Condition Score, and Nutritional Status on Follicular Population, Oocyte Yield, and Quality in Three Cameroonian Zebus Cattle Bos indicus
Abstract
This study was aimed at investigating the effects of breed, age, body condition score, and nutritional status on follicular dynamics, quality, and oocyte yield in Cameroonian zebus cattle Bos indicus (Gudali and Red and White Fulani). A total of 95 cows were investigated for breed, age, body condition score, and nutritional status. Blood samples and ovaries of these cows were collected during slaughtering. Follicles on each ovary were counted and measured using electronic digital calipers and then classified into three categories: small (<3 mm), medium (3 – 8 mm), and large (> 8 mm) diameter. The oocytes were retrieved by slicing each ovary into a Petri dish containing collected medium. The oocytes recovered were examined under a stereoscope (x 10) and classified into four groups based on the morphology of cumulus oophorus cells and cytoplasmic changes. From these ovaries, 3888 follicles were counted with an average population of 27.81 ± 6.88 follicles per cow. The average numbers of small, medium, and large follicles per cow were 17.26 ± 1.36 (62.06%), 9.64 ± 1.00 (34.66%), and 0.52 ± 0.32 (1.86%), respectively. A total of 1822 oocytes were harvested with an average of 19.11 ± 0.89 oocytes per cow. Oocytes graded I, II, III, and IV were 7.03 ± 2.30 (36.65%), 4.53± 2.01 (23.61%), 3.19 ± 0.85 (16.63%), and 4.43 ±1.62 (23.09%), respectively. This study also showed that ovarian weight, number of follicles, and oocytes’ yield of right ovary were higher than left ones (P < 0.05). Younger and normal cows (BCS = 3) presented higher (P < 0.05) number of follicles and oocytes. Urea and cholesterol levels were higher in Gudali and White Fulani cows (P < 0.05). This study indicated that ovaries of zebus harvested in slaughterhouse are an important source of follicular population, oocytes yield, and quality. Right ovaries are heavy and offer more numbers of follicles and oocytes than the left ones. BCS is the best indicator of nutritional status of cows. Important follicle populations are obtained from cows aging 6-9 years with BCS = 3.
1. Introduction
The livestock sector is a major component of the agricultural economy of Cameroon and contributes to about 1.643 billion USD to the national investment budget [1]. Zebus (Bos indicus) is the main cattle breed found in Cameroon and represents about 10% of the global livestock [2]; there are also 2% of Bos taurus and exotic breeds [3]. However, the total bovine productivity remains low in the country and is not enough to satisfy the demand of the population as recommended by Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) [4]. Several factors like poor genetic make-up and nutritional and reproductive pathologies have been identified as responsible items for these limitations in cattle productivity [5]. To solve these problems, assisted reproductive technologies (ARTs) such as artificial insemination (AI), in vitro embryo production (IVEP), multiple ovulation, and embryo transfer (MOET) have been developed to overcome reproductive inefficiency and accelerate genetic gain [6] and thereby reduce the generation intervals in farm animals. AI was introduced in Africa in 1935 and was spread throughout sub-Saharan Africa due to many improvement projects [7]. In Cameroon, AI is used on local breeds with exotic semen (Holstein and Brahman), which contributes to the improvement of cattle genetic potential [8]. However, AI is rarely used and certain cattle breeders artificially inseminate their local zebu cattle with imported semen in an unregulated manner, thereby causing dispersion and dilution of protected genotype [9]. Additionally, AI raises just male reproductive potential. IVEP and embryo transfer (ET) are reproductive techniques that supplement AI in the genetic improvement of local cattle breeds [10]. IVEP permits the preservation of genetic potential of subfertile or dead animals [11] by the creation of a gene bank with oocytes recovered from slaughterhouses [12] for the improvement of livestock productivity [13].
Ovaries collected from the abattoir are the attainable and most abundant source of primary oocyte for large scale production of embryo through in vitro maturation (IVM) and in vitro fertilization (IVF) [14]. IVEP is widely used in the world and has allowed the production of high genetic embryos from oocytes collected from the ovaries of live cows or cows slaughtered in order to promote the growth of the specific species [15]. This method involves several steps: IVM of oocytes, IVF of oocytes with capacitated sperm, and in vitro culture of embryos up to blastocyst stage. The first and the most important step in IVEP is the selection of viable oocytes for IVM. The follicular population, oocytes yield, and quality of local breeds cattle are commonly poor and many factors such as breed, age, weight, BCS, season, and physiological, nutritional, and pathological status of females have been reported as the cause of results’ variations [5, 16]. Dietary energy restriction has been shown to suppress episodic release of LH in cattle [17]. A high frequency mode of pulsatile LH secretion is important for the final phase of maturation of ovarian follicles [18]. Previous investigations reported mainly the biochemical and hormonal profiles related to female cows’ reproduction [19]. The nutritional influence includes proteoenergetic rate, vitamins, and traces’ elements necessary to maintain different reproductive processes such as follicular growth and oocyte yield and quality, as well as age [20].
To our knowledge, few studies have reported the effects of environmental and genetic factors on follicular population, oocyte yield, and quality in tropical zebu cattle. Therefore, it is in this context that this study was carried out with the main objective of evaluating the effect of breed, age, BCS, nutritional status on the follicular population, the oocyte yield, and quality of local zebu cows. This has been achieved by determination of follicular population and oocytes quality and establishes the relation between some characteristics of cows, the nutritional status of animals, the impact of energy and protein parameters, and phosphorus on the follicular population, quality, and oocyte yield.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The study was carried out in Bafoussam, West region of Cameroon (latitude 5°46′ N and longitude 10°40′E), characterized by Sudano Guinean climate, an average annual precipitation of 2000 mm with a short dry season (November to February) and long rainy season (March-October). The samples were collected at the Bafoussam municipal slaughterhouse from November 2017 to February 2018 and analyzed in the Animal Physiology and Health Laboratory of the University of Dschang.
2.2. Animal Selection
The study was conducted on a total of 95 cyclic cows of different breeds: Gudali (33) and White (30) and Red (32) Fulani. Cows were originated from North West region and were randomly selected. BCS and age of cows were determined as described by Natumyana et al. [21] and Moussa Garba et al. [22], respectively.
2.3. Blood Collection
Blood sample was collected from the jugular vein of each cow immediately after slaughter in 10 mL dry vacutainers. After collection, blood samples were transferred to the laboratory at 4°C and centrifuged at 2700 rpm for 15 min and the sera obtained were stored in aliquots at -20°C for analysis.
2.4. Ovary Collection and Handling
After slaughter, the left and right ovaries were excised and placed in separate conical tubes containing physiological normal saline solution (0.9%) supplemented with antibiotics (0.5 mg / mL of penicillin–streptomycin sulfate) and transported immediately (within 1 h) to the laboratory in sterile thermos at 34 – 36°C.
2.5. Determination of Ovaries Weight
In the laboratory, all ovaries were dissected free and weighed using an electronic scale (Mettler PC 2000).
2.6. Determination of Ovaries Size and Follicular Population
Then ovaries were washed (5-6 times) with warm saline fortified with antibiotics (0.5 mg / mL penicillin-streptomycin sulfate) and transferred into the laminar flow. The cortical follicles in each ovary were measured using electronic digital calipers, counted, and then classified according to their diameters (Φ) into three categories: small (Φ < 3 mm), medium (3 ≤ Φ ≤ 8 mm), and large (Φ > 8 mm) follicles [23].
2.7. Oocyte Recovery
Oocytes were collected using slicing technique [24] in the separate Petri dishes containing collection medium (physiological normal saline solution 0.9%). The collected oocytes were graded as excellent (I), good (II), fair (III), and poor (IV) quality under the stereo microscope (x 10) according to their cumulus and cytoplasmic distribution [25, 26]. The index (overall quality) was calculated using the following formula I= [(GI x 1 + GII x 2 + GIII x 3 + GIV x 4) / total number of oocytes recovered] with I = index and G = grade as described by Duygu et al. [27] and Kouamo et al. [26]. Index values that trend to one reflected good quality oocytes.
2.8. Biochemical Analysis
Serum sample was analysed to determine the concentration of total cholesterol, urea, phosphorus, total protein, and albumin. Total globulins were calculated by subtracting albumin from total protein [28]. All biochemical parameters were determined by colorimetric methods using an automated chemistry analyzer (Lab Max Plenno, Labtest, Lagoa Santa, Brazil) and using commercially available reagents.
2.9. Statistical Analysis
The collected data were analysed using SPSS version 20.00. Analysis of variance 2 ways and Duncan test statistics were used to clarify the differences between means. The level of significance was recorded at 5%. The normality of data was tested using the Shapiro-Wilk Test.
3. Results
3.1. Follicular Population
From 190 ovaries collected, 3888 follicles were counted on their surface. The average follicular population per cow was 27.81 ± 6.88. Depending on the size, the average numbers of small (Φ < 3mm), medium (3 ≤ Φ ≤ 8 mm), and large (Φ> 8 mm) follicles per cow were 17.33 ± 1.36 (62.32%) 9.75 ± 1.00 (35.06%), and 0.61 ± 0.32 (2.20%), respectively.
When considering Table 1, we can observe that the number of small follicles was significantly (P < 0.05) higher in Gudali and White Fulani cows than in Red Fulani. However, taking into account the BCS, we observed that the number of small follicles was significantly higher in Red Fulani cows of BCS=3 than in White Fulani and Gudali. This was a trend irrespective of the breed as well, where cows with BCS of 3 presented overall significantly higher number of small follicles than other BCSs. From Table 2 one may infer, considering total number of follicles, Gudali cows presented significantly higher follicular population than both Fulani breeds. The overall number of follicles was significantly higher in cows of BCS of 3, irrespective of breed and ovary. Additionally, the number of follicles in the right ovary of White Fulani cows was significantly higher in cows with BCS of 3 than cows with BCS of 1-2 or 4-5.
| Size of follicle | Breed | BCS | Average ± SD | P-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1-2) n=27 | (3) n=49 | (4-5) n=19 | ||||
| Total of small follicle | Gudali n=33 | (8)17.75 ± 0.70 αx | (15)18.73 ± 0.93 αy | (9)17.78 ± 0.68 αx | 18.22 ± 0.50β | 0.64 |
| White Fulani | (10)17.20 ± 1.08 αx | (17)19.06 ± 0.70 αy | (4)16.00 ± 1.29 αx | 18.10 ± 0.57β | 0.11 | |
| n=30 | ||||||
| Red Fulani | (9)15.78±0.57 αx | (17)16.53±0.58 αx | (6)16.17±0.30 αx | 16.25±0.35α | 0.67 | |
| n=32 | ||||||
| Average ± SD | 16.89 ± 0.49 x | 18.08 ± 0.44v | 16.89 ± 0.45 x | 17.26±0.46 αx | __ | |
| P-value | 0.27 | 0.03 | 0.18 | __ | __ | |
| Total of medium follicle | Gudali | (8)10.25 ± 0.75 αx | (15)10.07 ± 0.77 αx | (9)9.89 ± 0.53 αx | 10.06± 0.42β | 0.95 |
| n=33 | ||||||
| White Fulani n=30 | (10)8.30 ± 1.04 αx | (17)8.71 ± 0.86 αx | (4)9.75 ± 0.75 αx | 8.71 ± 0.58α | 0.76 | |
| Red Fulani | (9)10.33±0.70 αx | (17)10.53±0.52 αx | (6)9.50 ± 0.61 αx | 10.28±0.35β | 0.57 | |
| n=32 | ||||||
| Average ± SD | 9.56 ± 0.52 x | 9.76 ± 0,42 x | 9.74 ± 0.34 x | 9.68 ± 0.42 αx | __ | |
| P-value | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.89 | __ | __ | |
| Total of large follicle | Gudali | (8)0.63± 0.18 αx | (15)0.53± 0.13 αx | (9)0.44± 0.24 αx | 0.53 ± 0.10α | 0.81 |
| n=33 | ||||||
| White Fulani n=30 | (10)0.50 ± 0.16 αx | (17)0.59± 0.15 αx | (4)0.50±0.28 αx | 0.56 ± 0.10α | 0.91 | |
| Red Fulani | (9)0.33±0.16 αx | (17)0.35± 0.11 αx | (6)0.33 ± 0.21 αx | 0.34 ± 0.08α | 0.99 | |
| n=32 | ||||||
| Average ± SD | 0.48 ±0.09 x | 0.49±0.07 x | 0.42±0.13 x | 0.46 ± 0.09 αx | __ | |
| P-value | 0.51 | 0.43 | 0.91 | __ | __ | |
- x, y, and z: being on the same line, values affected with the same letter do not differ significantly (P > 0.05).
- α, β, and ɤ: being on the same column, values affected with the same letter do not differ significantly (P > 0.05).
| Mean weight of ovaries | Breed | BCS | Average ± SD | P-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1-2) n=27 | (3) n=49 | (4-5) n=19 | ||||
| Mean weight of right ovary (g) | Gudali n=33 | (8) 4.39 ± 0.29 βy | (15)4.40± 0.30 βy | (9) 3.98± 0.32 αx | 4.27 ± 0.18β | 0.04 |
| White Fulani n=30 | (10)2.75± 0.29 αx | (17)3.84± 0.32 αx | (4) 4.28± 1.08 αy | 3.52 ± 0.24α | 0.07 | |
| Red Fulani n=32 | (9)2.76 ± 0.26 αx | (17)3.72± 0.36 αx | (6)4.08± 0.29 αxy | 3.52 ± 0.22α | 0 .09 | |
| Average ± SD | 3.24 ± 0.21 x | 3.97 ± 0.19 xy | 4.06 ± 0.23 y | 3.75 ± 0.21α | __ | |
| P-value | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.92 | __ | __ | |
| Mean weight of left ovary (g) | Gudali | (8) 3.69± 0.39 αx | (15)3.76± 0.38 αx | (9)3.55± 0.30 αx | 3.68 ± 0.21α | 0.92 |
| n=33 | ||||||
| White Fulani n=30 | (10)2.75± 0.29 αx | (17)3.40± 0.30 αx | (4)4.57± 1.10 αy | 3.35 ± 0.21α | 0.09 | |
| Red Fulani n=32 | (9) 2.76± 0.26 αx | (17)3.02± 0.23 αx | (6) 3,19± 0,17 αx | 3.91 ± 0.14α | 0.21 | |
| Average ± SD | 3.00 ± 0.16 x | 3.38 ± 0.17 x | 3.60 ± 0.24 x | 3.32 ± 0.19α | __ | |
| P-value | 0.1 | 0.25 | 0.01 | __ | __ | |
| Total mean weight of ovaries (g) | Gudali | (8) 4.04 ± 0.28 βy | (15)4.08± 0.29 βx | (9) 3.77± 0.18 αx | 3.97 ± 0.16α | 0.02 |
| n=33 | ||||||
| White Fulani n=30 | (10)2.82± 0.14 αx | (17)3.62± 0.24 αx | (4) 4.42± 0.62 αy | 3.43 ± 0,18α | 0.07 | |
| Red Fulani n=32 | (9) 2.64± 0.10 αx | (17)3.37± 0.26 αx | (6) 3.63± 0.18 αx | 3.21 ± 0.16α | 0.07 | |
| Average ± SD | 3.12 ± 0.16 x | 3.79 ± 0.13 x | 3.83 ± 0.15 x | 3.58 ± 0.14 αx | __ | |
| P-value | 0.00 | 0.20 | 0.02 | __ | __ | |
- x, y, and z: being on the same line, values affected with the same letter do not differ significantly (P > 0.05).
- α, β, and ɤ: being on the same column, values affected with the same letter do not differ significantly (P > 0.05).
Table 3 showed that the number of follicles in right ovary and the total number of follicles in Gudali were significantly higher than in Fulani cows (P < 0.05) when breed was considered independently of BCS. But when only BCS was considered, the number of follicles in the right ovary and the total number of follicles were significantly higher in cows with BCS = 3 than cows with BCS = 1-2 and 4-5 (P < 0.05).
| Number of follicles | Breed | BCS | Average ± SD | P-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1-2) n=27 | (3) n=49 | (4-5) n=19 | ||||
| Number of follicles on right ovary | Gudali n=33 | (8)14.63± 0.96 αx | (15)15.40± 0.51 αx | (9)15.44± 0.66 αx | 15.94 ± 0.38β | 0.53 |
| White Fulani n=30 | (10)12.90± 0.43 αx | (17)14.47± 0.37 βx | (4)12.75± 0.75 αx | 13.75 ± 0.29α | 0.02 | |
| Red Fulani n=32 | (9)13.11± 0.65 αx | (17)14.24± 0.38 αx | (6)12.83± 0.47 αx | 13.75 ± 0.29α | 0.11 | |
| Average ± SD | 13.48± 0.40 x | 14.67 ± 0.25 y | 13.58 ± 0.41 x | 13.91 ± 0.35 αx | __ | |
| P-value | 0.18 | 0.14 | 0.13 | __ | __ | |
| Number of follicles on left ovary | Gudali | (8)14.25± 0.59 αx | (15)13.60± 0.55 αx | (9)13.78± 0.94 αx | 13.81 ± 0.38α | 0.80 |
| n=33 | ||||||
| White Fulani n=30 | (10)13.50± 0.58 αx | (17)13.94± 0.81 αx | (4)13.50± 1.25 αx | 13.74 ± 0.49α | 0.93 | |
| Red Fulani n=32 | (9)13.22± 0.36 αx | (17)13.12± 0.38 αx | (6)13.00± 0.36 αx | 13.13 ± 0.21α | 0.94 | |
| Average ± SD | 13.63 ± 0.30 x | 13.53 ± 0.34 x | 13.47 ± 0.50 x | 13.54 ± 0.38 αx | __ | |
| P-value | 0.39 | 0.65 | 0.81 | __ | __ | |
| Total number of follicles | Gudali | (8)28.63± 0.99 αx | (15)29.33± 0.75 αx | (9)28.11± 1.04 αx | 28.81 ± 0.51β | 0.61 |
| n=33 | ||||||
| White Fulani n=30 | (10)26.00± 0.84 αx | (17)28.41± 0.77 αx | (4)26.25± 1.54 αx | 27.35 ± 0.56α | 0.12 | |
| Red Fulani n=32 | (9)26.44± 0.74 αx | (17)27.41± 0.45 αx | (6)26.00± 0.77 αx | 26.88 ± 0.36α | 0.27 | |
| Average ± SD | 26.93 ± 0.52 x | 28.33 ± 0.39 y | 27.05 ± 0.65 x | 27.43 ± 0.52 αx | __ | |
| P-value | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.31 | __ | __ | |
- x, y, and z: being on the same line, values affected with the same letter do not differ significantly (P > 0.05).
- α, β, and ɤ: being on the same column, values affected with the same letter do not differ significantly (P > 0.05).
When age was considered independently of breed, cows aging 6 to 9 years presented significantly higher number of follicles on right ovary (P < 0.05). But when considering breed, the number of follicles on right ovary and the total number of follicles of Gudali were significantly higher than Fulani cows (P < 0.05) (Table 4).
| Number of follicles | Breed | Age | Average ± SD | P-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (3-5) n=21 | (6-9) n=52 | (10-15) n=22 | ||||
| Number of follicles on right ovary | Gudali | (5)13.80±0.86 αx | (20)15.15 ± 0.49 βx | (7)15.14 ± 0.85 αy | 14.94 ± 0.38β | 0.04 |
| n=33 | ||||||
| White Fulani | (9)12.67± 0.50 αx | (16)14.19± 0.4 αx | (6)14.17± 0.54 αAy | 13.74 ± 0.29α | 0.06 | |
| n=30 | ||||||
| Red Fulani | (7)13.71± 0.68 αβx | (16)14.38± 0.35 βx | (9)12,33± 0.50 αx | 13.66 ± 0.30α | 0.01 | |
| n=32 | ||||||
| Average ± SD | 13.29 ± 0.37 x | 14.62 ± 0.25 y | 13.73 ± 0,44 x | 13.88 ± 0.35 αx | __ | |
| P-value | 0.37 | 0.24 | 0.01 | __ | __ | |
| Number of follicles on left ovary | Gudali | (5)13.60± 0.67 αx | (20)14.00± 0.44 αx | (7)13.43± 1.21 αx | 13.81 ± 0.38α | 0.82 |
| n=33 | ||||||
| White Fulani | (9)14.22± 0.86 αx | (16)13.63± 0.80 αx | (6)13.17± 0,70 αx | 13.71 ± 0.49α | 0.76 | |
| n=30 | ||||||
| Red Fulani | (7)13.14± 0.34 αx | (16)13.06± 0.35 αx | (9)13.22± 0.40 αx | 13.13 ± 0.21α | 0.95 | |
| n=32 | ||||||
| Average ± SD | 13.71 ± 0.41 x | 13.60 ± 0.31 x | 13.27 ± 0.43 x | 13.52 ± 0.38 αx | __ | |
| P-value | 0.54 | 0.48 | 0.97 | __ | __ | |
| Total number of follicles | Gudali | (5)28.40± 1.12 αx | (20)29.00± 0.66 αx | (7)28.57± 1.25 αx | 28.81 ± 0.51β | 0.89 |
| n=33 | ||||||
| White Fulani | (9)26.78± 1.14 αx | (16)27.69± 0.84 αx | (6)27.17± 0.87 αx | 27.32 ± 0.56α | 0.78 | |
| n=30 | ||||||
| Red Fulani | (7)26.86± 0.63 αx | (16)27.50± 0.46 αx | (9)27.78± 0.79 αx | 26.88 ± 0.36α | 0.13 | |
| n=32 | ||||||
| Average ± SD | 27.19 ± 0.58 x | 28.13 ± 0.39 x | 27.05 ± 0.59 x | 27.45 ± 0.52 αx | __ | |
| P-value | 0.53 | 0.22 | 0.14 | __ | __ | |
- x, y, and z: being on the same line, values affected with the same letter do not differ significantly (P > 0.05).
- α, β, and ɤ: being on the same column, values affected with the same letter do not differ significantly (P > 0.05).
3.2. Oocyte Number
The overall average oocyte was 1822. The mean oocyte recovered per cow was 19.11 ± 0.89. The oocyte quality grades I, II, III, and IV per cow were 6.83 ± 0.68 (35.74%), 4.47 ± 0.38 (23.39%), 3.35 ± 0.31(17.53%), and 4.30 ± 0.32 (22.50%), respectively. The cultivable oocyte for IVEP (grades I and II) was 11.3 ± 1.04 (59.13%) (Figure 1).
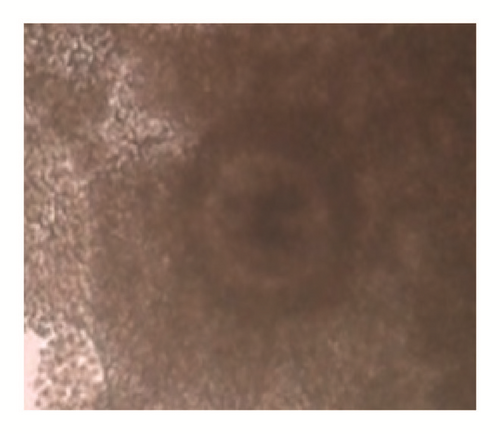
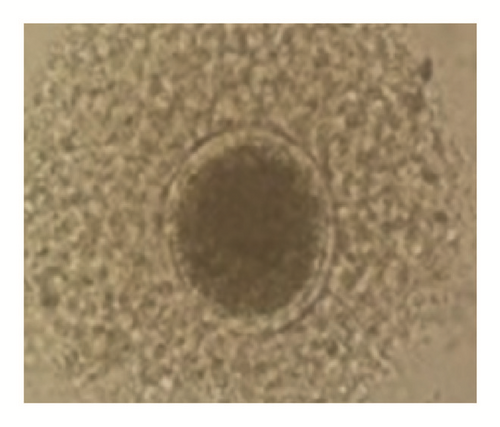
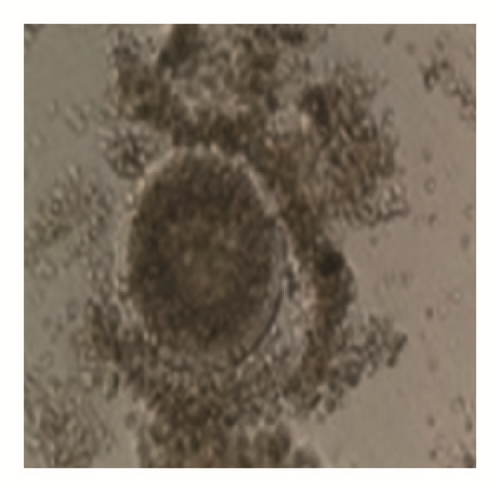

When breed was considered, independently of BCS, the number of grade III oocytes was significantly higher in Gudali zebu (P < 0.05). However when BCS was considered independently of breed, it appeared that cows with BCS = 3 presented a number of class II oocytes and the total number of classes I and II oocytes was significantly higher than cows with BCS located between 1-2 and 4-5 (P < 0.05) (Table 5). In addition, the total number of oocytes was significantly higher in Gudali and White Fulani zebu (P < 0.05) than in Red Fulani and the number of oocytes in right ovaries was nonsignificantly higher than left ovaries (P > 0.05) (Table 6).
| Oocyte quality | Breed | BCS | Average ± SD | P-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1-2) n=27 | (3) n=49 | (4-5) n=19 | ||||
| Grade I oocyte | Gudali | (8)6.63± 0.46 αx | (15)7.40± 0.61 αx | (9)6.89± 0.35 αx | 7.06 ± 0.32α | 0.60 |
| n=33 | ||||||
| White Fulani n=30 | (10)7.20± 0.86 αx | (17)7.24± 0.45 αx | (4)5.75± 1.03 αx | 7.03 ± 0.39α | 0.46 | |
| Red Fulani n=32 | (9)7.11± 0.61 αx | (17)6.29± 0.51 αx | (4)5.75± 1.03 αx | 6.56 ± 0.34α | 0.61 | |
| Average ± SD | 7.00 ± 0.39x | 6.96 ± 0.30x | 6.53 ± 1.35x | 6.83 ± 0.68αx | _ | |
| P-value | 0.83 | 0.28 | 0.49 | __ | _ | |
| Grade II oocyte | Gudali | (8)4.38± 0.75 αA | (15)5.93± 0.88 αA | (9)4.67± 0.66 αA | 5.19 ± 0.49α | 0.37 |
| n=33 | ||||||
| White Fulani n=30 | (10)3.40± 0.74 αx | (17)4.94± 0.55 αx | (4)4.50± 0.64 αx | 4.39 ± 0.40α | 0.23 | |
| Red Fulani n=32 | (9)3.44± 0.47 αx | (17)4.47± 0.55 αx | (6)4.67± 0.66 αx | 4.22 ± 0.35α | 0.38 | |
| Average ± SD | 3.70 ± 0,38 x | 5.08 ± 0.38 y | 4.63 ± 0.38 x | 4.47 ± 0.38 αx | __ | |
| P-value | 0.54 | 0.30 | 0.48 | __ | __ | |
| Grade III oocyte | Gudali | (8)3.63± 1.01 αx | (15)4.20± 0.47 αy | (9)4.11± 0.62 αx | 4.03 ± 0.39β | 0.82 |
| n=33 | ||||||
| White Fulani n=30 | (10)3.20± 0.51 αx | (17)2.94± 0.38 αx | (4)4.50± 0.64 αx | 3.23 ± 0.28α | 0.22 | |
| Red Fulani n=32 | (9)2.78± 0.32 αx | (17)3.29± 0.23 αAy | (6)3.33± 0.49 αx | 3.16 ± 0.18α | 0.43 | |
| Average ± SD | 3.19 ± 0.36 x | 3.45 ± 0.22 x | 3.95 ± 0.35 x | 3.53 ± 0.31 αx | __ | |
| P-value | 0.66 | 0.06 | 0.98 | __ | __ | |
| Grade IV oocyte | Gudali | (8)5.38± 0.84 αx | (15)4.13± 0.01 αx | (9)4.33± 0.64 αx | 4.50 ± 0.39α | 0.45 |
| n=33 | ||||||
| White Fulani n=30 | (10)3.50± 0.37 αx | (17)4.47± 0.40 αx | (4)4.00± 0.40 αx | 4.10 ± 0.29α | 0.33 | |
| Red Fulani n=32 | (9)4.67± 0.23 αx | (17)3.71± 0.47 αx | (4)4.00± 0.40 αx | 4.16 ± 0.29α | 0.28 | |
| Average ± SD | 4.44 ± 0.32 x | 4.10 ± 0.29 x | 4.37 ± 0.37 x | 4.30 ± 0.32 αx | -- | |
| P-value | 0.4 | 0.56 | 0.83 | __ | __ | |
| Total grades I and II oocyte | Gudali | (8)11.00± 0.68 αx | (15)13.33± 1.25 αy | (9)11.56± 0.93 αx | 12.25 ± 0.71α | 0.36 |
| n=33 | ||||||
| White Fulani n=30 | (10)10.60± 1.40 αx | (17)12.18± 0.83 αxy | (4)10.25± 1.65 αx | 11.42 ± 0.67α | 0.47 | |
| Red Fulani n=32 | (9)10.56± 0.86 αx | (17)10.76± 0.96 αx | (6)11.17± 1.27 αx | 10.78 ± 0.60α | 0.94 | |
| Average ± SD | 10.70 ± 0.60 x | 12.04 ± 0.61 y | 11.16 ± 0.65 x | 11.30 ± 0.62 αx | __ | |
| P-value | 0.95 | 0.24 | 0.77 | __ | __ | |
| Total grades II and IV oocyte | Gudali | (8)9.00± 1.64 αx | (15)8.33± 0.79 αx | (9)8.44± 1.16 αx | 8.53 ± 0.62α | 0.91 |
| n=33 | ||||||
| White Fulani n=3à | (10)6.70± 0.74 αx | (17)7.41± 0.69 αx | (4)8.50± 1.04 αx | 7.32 ± 0.46α | 0.81 | |
| Red Fulani n=32 | (10)6.70± 0.74 αx | (17)7.41± 0.69 αx | (4)8.50± 1.04 αx | 7.31 ± 0.38α | 0.61 | |
| Average ± SD | 7.63 ± 0.58 x | 7.55 ± 0.40 x | 8.32 ± 0.64 x | 7.83 ± 0.54 αx | ___ | |
| P-value | 0 .27 | 0.40 | 0.95 | ___ | ___ | |
- x, y, and z: being on the same line, values affected with the same letter do not differ significantly (P > 0.05).
- α, β, and ɤ: being on the same column, values affected with the same letter do not differ significantly (P > 0.05).
| Number of oocytes | Breed | BCS | Average ± SD | P-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1-2) n=27 | (3) n=49 | (4-5) n=19 | ||||
| Number of oocytes on right ovary | Gudali n=33 | (8)10.50± 0.82 αx | (15)12.13± 0.92 αy | (9)11.44± 0.94 αx | 11.53 ± 0.54α | 0.49 |
| White Fulani n=30 | (10)9.80± 0.87 αx | (17)10.76± 0.59 αxy | (4)10.75± 1.31 αx | 10.45 ± 0.45α | 0.63 | |
| Red Fulani n=32 | (9)9.78± 1.07 αx | (17)9.47± 0.90 αx | (6)10.83± 1.24 αx | 9.81 ± 0.60α | 0.71 | |
| Average ± SD | 10.00 ± 0.56 x | 10.73 ± 0.46 x | 11.11 ± 0.62 x | 10.61 ± 0.54 αx | __ | |
| P-value | 0.83 | 0.08 | 0.88 | __ | __ | |
| Number of oocytes on left ovary | Gudali | (8)9.38± 1.06 αx | (15)9.40± 0.74 αx | (9)8.44± 0.47 αx | 9.13 ± 0.44α | 0.64 |
| n=33 | ||||||
| White Fulani n=30 | (10)7.50± 1.38 αx | ((17)8.82± 0,81 αx | (4)8.00± 1.15 αx | 8.29 ± 0.64α | 0.65 | |
| Red Fulani n=32 | (9)8.22± 0.46 αx | (17)8.35± 0.54 αx | (6)8.50± 0.95 αx | 8.34 ± 0.35α | 0.96 | |
| Average ± SD | 8.30 ± 0.61 x | 8.84 ± 0.40 x | 8.37 ± 0.40 x | 8.50 ± 0.47 αx | __ | |
| P-value | 0.48 | 0.59 | 0.90 | __ | __ | |
| Total number of oocytes | Gudali | (8)20.00± 1.60 αy | (15)21.67± 1.49 αx | (9)20.00± 1.2 αx | 20.78 ± 0.86β | 0.64 |
| n=33 | ||||||
| White Fulani n=30 | (10)17.30± 1.93 αx | (17)19.59± 1.19 βx | (4)18.75± 2.46 αβx | 20.78 ± 0.86β | 0.86 | |
| Red Fulani n=32 | (9)18.00± 1.06 αxy | (17)17.76± 1.33 αx | (6)19.17± 2.21 αx | 18.09 ± 0.85α | 0.83 | |
| Average ± SD | 18.30 ± 0.92 x | 19.59 ± 0.79 x | 19.45 ± 0.98 x | 19.11 ± 0.89 αx | __ | |
| P-value | 0.49 | 0.13 | 0.88 | __ | __ | |
- x, y, and z: being on the same line, values affected with the same letter do not differ significantly (P > 0.05).
- α, β, and ɤ: being on the same column, values affected with the same letter do not differ significantly (P > 0.05).
When the age was considered independently of breed, cows aging 6 to 9 years registered significantly higher number of cultivable oocytes (grades I and II) than other groups (P < 0.05). Also, when breed was considered independently of age, the number of grades I and II oocytes’ quality was higher in Gudali than in White and Red Fulani (P < 0.05) (Table 7).
| Parameters | Breed | Age | Average ± SD | P-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [3-5] n=21 | [6-9] n=52 | [10-15] n=22 | ||||
| Grade I oocyte | Gudali | (5)6.20± 0.91 αx | (20)7.45±0.48 αx | (7)6.86± 0.45 αx | 7.13 ± 0,35α | 0,42 |
| n=33 | ||||||
| White Fulani n=30 | (9)6.67± 1.00 αx | (16)7.4± 0.51 αx | (6)6.00± 0.63 αx | 6.94 ± 0,41α | 0,40 | |
| Red Fulani | (7)6.43± 0.97 αx | (16)6.88± 0.55 αx | (9)6.33± 0.33 αx | 6.63 ± 0.35α | 0.78 | |
| n=32 | ||||||
| Average ± SD | 6.48 ± 0.55 x | 7.27 ± 0.29 x | 6.41 ± 0.26 x | 6.72 ± 0.36 αx | __ | |
| P-value | 0.95 | 0.68 | 0.46 | __ | __ | |
| Grade II oocyte | Gudali | (5)5.40± 1.03 αx | (20)5.35± 0.61 αx | (7)5.14± 0.73 αy | 5.31 ± 0.43α | 0.98 |
| n=33 | ||||||
| White Fulani n=30 | (9)4.44± 0.68 αx | (16)4.75± 0.53 αx | (6)3.00± 0.93 αx | 4.32 ± 0.39α | 0.24 | |
| Red Fulani | (7)4.00± 0.84 αx | (16)4.31± 0.54 ax | (9)4.33± 0.40 axy | 4.25 ± 0.33α | 0.93 | |
| n=32 | ||||||
| Average ± SD | 4.52 ± 0.46 x | 4.85 ± 0.33 x | 4.23 ± 0.40x x | 4.53 ± 0.39 αx | __ | |
| P-value | 0.55 | 0.44 | 0.12 | __ | __ | |
| Gudali | (5)4.20± 0.37 αx | (20)3.90± 0.37 αx | (7)4.71± 0.99 αx | 4.13 ± 0.32α | 0.60 | |
| n=33 | ||||||
| Grade III oocyte | White Fulani n=30 | (9)3.44± 0.60 αx | (16)3.25± 0.37 αx | (6)3.00± 0.57 αx | 3.26 ± 0.27α | 0.86 |
| Red Fulani | (7)2.86± 0.34 αx | (16)3.38± 0.31 αx | (9)2.89± 0.26 αx | 3.13 ± 0.18α | 0.43 | |
| n=32 | ||||||
| Average ± SD | 3.44 ± 0.30 x | 3.57 ± 0.20 x | 3.50 ± 0.39 x | 3.50 ± 0.29 αx | __ | |
| P-value | 0.27 | 0.38 | 0.10 | __ | __ | |
| Grade IV oocyte | Gudali | (5)5.80± 0.24 αy | (20)4.30± 0.44 αx | (7)5.29± 0.99 αx | 4.75 ± 0.39α | 0.33 |
| n=33 | ||||||
| White Fulani n=30 | (9)3.56± 0.29 αx | (16)4.31± 0.41 αx | (6)3.00± 0.57 αx | 3.97 ± 0.26α | 0.42 | |
| Red Fulani n=32 | (7)4.57± 0.71 αxy | (16)4.38± 0.37 αx | (9)2.89± 0.26 αx | 3.13 ± 0.18α | 0.74 | |
| Average ± SD | 4.43 ± 0.42 x | 4.33 ± 0.23 x | 3.50 ± 0.39 x | 4.08 ± 0.34 αx | __ | |
| P-value | 0.04 | 0.99 | 0.10 | __ | __ | |
| Total grades I and II oocytes | Gudali | (5)11.60± 1.50 αx | (20)12.80± 0.95 αx | (7)12.00± 1.11 αx | 12.44 ± 0.67β | 0,78 |
| n=33 | ||||||
| White Fulani | (9)11.11± 1.27 αx | (16)12.19± 0.91 αx | (6)9.00± 1.52 αx | 11.26 ± 0.21α | 0.21 | |
| n=30 | ||||||
| Red Fulani | (7)10.44± 1.74 αx | (16)11.19± 0.94 αx | (9)10.67± 0.62 αx | 10.83 ± 0.87α | 0.87 | |
| n=32 | ||||||
| Average ± SD | 11.00 ± 0.60 x | 12.12 ± 0.54 y | 10.64 ± 0.62 x | 11.25± 0.58 αx | __ | |
| P-value | 0.87 | 0.47 | 0.18 | __ | __ | |
| Total grades III and IV oocytes | Gudali | (5)10.00± 1.22 αy | (20)8.20± 0.57 αx | (7)10.00± 1.90 αx | 8.88 ± 0.56α | 0.31 |
| n=33 | ||||||
| White Fulani n=30 | (9)7.00± 0.75 αx | (16)7.56± 0.68 αx | (6)6.67± 1.11 αx | 7.23 ± 0.45α | 0.74 | |
| Red Fulani | (7)7.43± 0.92 αx | (16)7.75± 0.58 αx | (9)6.89± 0.35 αx | 7.74 ± 0.36α | 0.61 | |
| n=32 | ||||||
| Average ± SD | 7.86 ± 0.57 x | 7.87 ± 0.34 x | 7.82 ± 0.73 x | 7.84 ± 0.54 αx | __ | |
| P-value | 0.01 | 0.73 | 0.12 | __ | __ | |
- x, y, and z: being on the same line, values affected with the same letter do not differ significantly (P > 0.05).
- α, β, and ɤ: being on the same column, values affected with the same letter do not differ significantly (P > 0.05).
3.3. Biochemical Parameters
Biochemical analyses used in this study were classified in protein parameters (total protein, albumin, globulin, and urea), energy (total cholesterol), and traces element (phosphorus). When breed was considered independently of age, it showed that the levels of urea and cholesterol were significantly higher, respectively, in Gudali and White Fulani (P < 0.05). The levels of urea were significantly higher in Gudali cows aging 10-15 years and White Fulani aging 3-5 years (P < 0.05), whereas Gudali and White Fulani breeds presented significantly higher levels of cholesterol (P < 0.05). Meanwhile, Gudali cows aging 3 to 5 years and Red Fulani aging 6 to 9 years registered higher levels of phosphorous and albumin, respectively (P < 0.05).
Nevertheless, when age was considered independently of breed, the levels of urea and cholesterol were significantly higher in cows aging 3 to 5 and 6 to 9 years, respectively (P < 0.05). The levels of globulin were also significantly higher in older Red Fulani (10 -15 years) than other groups of age (P < 0.05). White Fulani and Gudali cows aging, respectively, 3 to 5 and 10 to 15 years, presented significantly higher levels of urea (P < 0.05). In addition, the total level of cholesterol was significantly higher in White Fulani cows aging 6 to 9 and 10 to 15 years (P < 0.05) (Table 8).
| Parameters | Breed | Age | Average ± SD | P-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (3-5) n=21 | (6-9) n=52 | (10-15) n=22 | ||||
| Total proteins (g / dl) | Gudali | (9)10.11±0.58 αx | (17)10.23 ±0.51 αx | (7)9.37± 0.49 αx | 10.00 ±0.31α | 0.56 |
| n=33 | ||||||
| White Fulani n=30 | (9)10.88 ±1.22 αx | (19)10.78 ±0.31 αx | (4) 9.25 ±1.31 αx | 10.62±0.4α | 0.47 | |
| Red Fulani n=32 | (3)10.00 ±00.00 αx | (16)9.93 ±0.46 αx | (11)11.63 ±1.27 αx | 10.58 ±0.55α | 0.34 | |
| Average ± SD | 10.45 ±0.60 x | 10.34 ±0.24 x | 10.43 ±0.69 x | 10.40 ±0.51 αx | __ | |
| P-value | 0.81 | 0.36 | 0.26 | __ | __ | |
|
Gudali | (9)2.77 ±0.146 αx | (17)2.76 ±0.10 αx | (7)2.25 ±0.16 αx | 2.64 ±0.08α | 0.09 |
| n=33 | ||||||
| White Fulani n=30 | (9)2.35 ±0.17 αβx | (19)2.78 ±0.09x βx | (4)2.25 ±0.25 αx | 2.65 ±0.08α | 0.02 | |
| Red Fulani n=32 | (3)3.00 ±0.00 αx | (16)2.68 ±0.11 αx | (11)2.36 ±0.15 αx | 2.58 ±0.09α | 0.12 | |
| Average ± SD | 2.70 ±0.10 x | 2.75 ±0,06 x | 2.30 ±0.09 x | 2.58 ±0.08 αx | __ | |
| P-value | 0.40 | 0.78 | 0.85 | _ | __ | |
| Globulin (g / dl) | Gudali | (9)7.33 ±0.55 αx | (17)7.35 ±0.48 αx | (7)7.65 ±0.42 αxy | 7.14 ±0.29α | 0.50 |
| n=33 | ||||||
| White Fulani n=30 | (9)8.00 ±1.19 αx | (19)7.84 ±0.29 αx | (4)6.50 ±1.19 αx | 7.71 ±0.39α | 0.51 | |
| Red Fulani n=32 | (3)7.00 ±0.00 αx | (16)7.06 ±0.43 αx | (11)8.72 ±1.25 αy | 7.68 ±0.54α | 0.33 | |
| Average ± SD | 7.60 ±0.57 x | 7.44 ±0.23 x | 7 .56 ±0.67 x | 7.53 ±0.49 αx | __ | |
| P-value | 0.82 | 0.38 | 0.26 | __ | __ | |
|
Gudali | (9)35.22 ±4.30 αx | (17)34.94 ±2.60 αx | (7)37.25 ±4.14 βy | 35.55 ±1.92β | 0.89 |
| n=33 | ||||||
| White Fulani n=30 | (9)39.44 ±3.66 βy | (19)32.89 ±1.62 αβx | (4)30.00 ±7.32 αx | 34.37 ±1.69α | 0.15 | |
| Red Fulani n=32 | (3)38.50 ±2.50 αxy | (16)33.25 ±2.13 αx | (11)34.81 ±3.05 αx | 34.20 ±1.64α | 0.71 | |
| Average ± SD | 35.45 ±2.51 y | 33.67 ±1.20 x | 34.62 ±2.34 x | 34.64 ±2.01 αx | _ | |
| P-value | 0.74 | 0.76 | 0.59 | _ | _ | |
| Total cholesterol (mg / dl) | Gudali | (9)148,77 ±18.07 αβy | (17)159.35 ±15.25 βxy | (7)125.25 ±14.62 αx | 148.52 ±9.68α | 0.38 |
| n=33 | ||||||
| White Fulani n=30 | (9)147.77 ±11.72 αx | (19)171.63 ±11.88 βy | (4)141.75 ±42.62 αy | 161.18 ±9.26β | 0.40 | |
| Red Fulani n=32 | (3)158.00 ±8.00 αx | (16)146.93 ±13.11 αx | (11)140.81 ±11.72 αy | 145.37 ±8.50α | 0.87 | |
| Average ± SD | 149.25 ±7.64 x | 160.01 ±7.72 y | 135.56 ±9.96 x | 148.27 ±8.44 αx | __ | |
| P-value | 0.95 | 0.43 | 0.76 | __ | __ | |
|
Gudali | (9)15.33 ±1.33 βx | (17)13.94 ±0.66 αx | (7)14.00 ±0.80 αx | 14.32 ±0.51α | 0.51 |
| n=33 | ||||||
| White Fulani n=31 | (9)14.77 ±0.81 αx | (19)13.79 ±0.58 αx | (4)13.50 ±1.19 αx | 14.00 ±0.43α | 0.54 | |
| Red Fulani n=32 | (3)12.77 ±1.00 αx | (16)15.37 ±0.74 αx | (11)13.45 ±0.84 αx | 14.14 ±0.43α | 0,12 | |
| Average ± SD | 14.75 ±0.71 y | 14.30 ±0.38 x | 13.65 ±0.51 x | 14.23 ±0.53 αx | ___ | |
| p-value | 0.43 | 0.18 | 0.89 | ___ | ___ | |
- x, y, and z: being on the same line, values affected with the same letter do not differ significantly (P > 0.05).
- α, β, and ɤ: being on the same column, values affected with the same letter do not differ significantly (P > 0.05).
4. Discussion
The mean weight of ovaries (3.50 ± 0.64 g) of this study was similar to those obtained by Naturmanya et al. [21] (4.60 ± 2.3 g) and Kouamo et al. [14] (4.60 ± 1.82 g) in Cameroon, respectively, on Ankole and Mbororo or Bokolo cow, but lower than that of Holstein breed 5-15 and 10-19 g recorded by Pierson and Ginther [29]. The difference could be due to the phase of estrus cycle, physiological status, or breed. In fact, ovary with corpus luteum and follicles, being in pregnancy stage, increases in size and weight [30, 31]. The different weight between right and left ovaries in this study was also reported by Rajakoski [32]. This confirmed the higher physiological activity that occurs in the right ovary. Indeed, the finding of Pierson and Ginther [28] and Ginther et al. [31] showed that there is great follicle activity on right ovary and consequently ovulations are more regular at this side. In addition, density of blood vessels that facilitates blood supply and the presence of primordial follicles are very important on right ovary than on the left one.
The average number of follicles obtained per cow (13.9± 3.44) was comparable to that reported by Carvalho et al. [33] in Nellore zebu (16.7 ± 1.6) and Kouamo et al. [14] in Gudali Cameroonian zebu (16.75 ± 0.8), but lower than the number reported by Fassi et al. [16] (22.98± 8.41) in Morocco zebu. Meanwhile, the mean numbers of medium and large follicles were similar to the findings of Acar et al. [34] and Kouamo et al. [35] on different breed of Cameroonian zebu (Gudali, Bokolo). These fluctuations may be related either to breed [36, 37] or to the livestock’s management. Fassi [16] reported that the Blonde Moroccan local breed presents fewer follicles (18.96 ± 1.3) in their ovaries than Holstein (25.19 ± 1.63) and their crossbreed (24.71 ± 1.69). Cow parity could be the cause of variation in ovarian dynamics [37]. A high number of small size follicles counted on the surface of ovaries may be due to the high numbers of reserve follicles recruited. Indeed, at the onset of the estrus cycle in cow, numerous reserve follicles are continuously recruited to develop, but only one reaches until the stage of De Graafian follicle which will ovulate [38].
The oocyte yield per ovary recorded in this work is in accordance with the findings of Kouamo et al. [14, 28] (10.94 ± 0.43 and 5.07 ± 4.19), respectively, on Cameroonian zebu Mbororo and Bokolo cattle, but lower to 66 oocytes obtained by Carolan et al. [39]. The mean acceptable oocytes for IVM (grades I and II oocyte quality) (5.68 ± 1.81) are in the interval of 30 to 60% oocytes as recommended by Natumanya et al. [21] and were higher than those obtained by Kouamo et al. [35] (2.95 ± 2.76), but lower than (9.6 ± 0 .4) that reported by Wang et al. [22] in China in Holstein cow. Several factors such as nutrition [40, 41] and harvesting techniques [36] may explain this divergence. In fact, the slicing technique leads to oocyte recovery at the surface of ovaries and in the cortex. In addition, certain oocytes lost by the aspiration or puncture methods can be recovered by slicing and could increase the quantity of retrieved oocytes [19].
The fact that the BCS had a significant effect on the number of follicles, oocyte yield, and quality supports the effect of nutrition on reproductive process, particularly at the ovarian level [36, 42]. Indeed, cows with BCS = 1- 2 had less ovarian follicles during the luteal phase and tend to produce less follicles [43] because the number of follicles that leave the ovarian reserve depends on individuals BCS [44].
The effect of age on follicular population and oocyte recovery recorded in this work was also obtained by Kouamo et al. [14] and Lucyna and Zdzislaw [45] who showed that follicular population and fertility decline with age in all species. Contributing factors such as hormones, apoptosis of cells, and senility may be the best factors responsible for this deflation of ovarian stock [46]. The cows less than 10 years old remain the best choice to increase the population of good embryos.
The decrease number of oocytes’ quality (grades I and II) with the decreasing of BCS in the presence of higher level of cholesterol as observed in this work is also reported by Nibart [47]. In fact higher level of plasmatic cholesterol leads to low oocytes yield whereas low viable embryo is the consequence of low cholesterol level due to the fat cow syndrome [48].
The low oocyte yield of cows with BCS = 1-2 obtained in this study may be related to the level of energy in the diet. It is proved that energy balance and the ability to mobilize fat reserves have an important role in reproductive function and especially on ovarian dynamics. In fact, Delacharie [49] showed that BCS influenced significantly not only follicular population and growth, but also oocytes production and quality. While cows with BCS ≥ 3 were the best donors of cultivable oocyte (grades I and II oocytes), BCS had a positive influence on the follicular population as reported by Alves et al. [25]. Moreover, nutrition related metabolic and hormonal changes may affect not only follicular development and growth, but also the oocyte quality [49]. Therefore, cows BCS ≤ 2 have fewer developing follicles during the luteal phase of estrus cycle and tend to produce fewer during the follicular phase than cows with BCS ≥ 3 [45].
This study presents a significant increase of the level of urea and cholesterol with BCS = 3. Rodriguez et al. [50] showed a positive correlation between the level of cholesterol and oocyte yield, suggesting that energy balance and BCS play an important role in reproductive function and especially on ovarian level.
5. Conclusion
This study showed that the ovaries of local zebu cows raised in Cameroon were a good and nonexpensive source of oocyte for IVEP. The females’ oocyte donors with BCS of 3 could be the best choice to improve IVEP and selected cows should be well fed to preserve oocyte yield and quality.
Ethical Approval
Experimental protocols used in this study were approved by the Ethics committee of the Department of Animal science, FASA, University of Dschang, Cameroon, and strictly conformed with the internationally accepted standard ethical guidelines for laboratory animal use and care, as described in the European Community guidelines, EEC Directive 86/609/EEC, of the 24th November, 1986.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors certify that no conflicts of interest exist.
Open Research
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.




