SWCNT-Based Biosensor Modelling for pH Detection
Abstract
Different forms of CNT delivery have been discovered with several biomedical functions during past decades. The mechanisms of the cellular uptake of CNTs are mainly maintained due to the chemical nature, the cell type, and the features of the molecules, which are used to functionalize the nanotube exterior. Since single-wall carbon Nanotube (SWCNT) has unique chemical and physical properties, it is a great applicant for pH sensing. In addition, ion sensitive FET (ISFET) base on nanostructured SWCNT have covered a new method to help genetic investigators restructure metabolic pathways in cells, recognize the progression of disease, and expand diagnostics and therapeutics. Particularly, because PH sensing is very crucial for the constancy of enzymes, it is essential to extend the cost efficient types of this sensing. In this research, the conductance changes of the CNT-based ISFET device with different pH values can be modelled by ion concentration of the solution. In addition, the electrical current of channel is imagined as a function of pH levels, which can be controlled by a control factor (α). Thus, ISFET based nanostructured SWCNT is proposed focusing on the area of electrical detection of hydrogen ions of the electrolyte membrane. Besides, electrical detection of hydrogen ion applications is suggested to be used by modelling the delivery of SWCNT sheets. In the end, after comparing the proposed model and experimental data, it has been reported that there is a good compatibility between them.
1. Introduction
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) can be imagined as a sheet of carbon atoms turned up into a pipe with a diameter of nanometres [1–3]. There are two major types of CNTs including single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) and multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs). SWCNTs are made from numerous concentric layers of turned graphene as shown in Figure 1. SWCNTs are particularly described by a high feature proportion [4]. Furthermore, their multipurpose physicochemical features facilitate the noncovalent and covalent beginning of several biosensing and biomedicine functions of appropriate entities [5].
Therefore, the development of their distinctive thermal, optical, electrical, and spectroscopic properties in a biological framework is expected to bring about great progress in the treatment of disease and the discovery of biomolecules such as antigen–antibody, cells, DNA, and other biomolecules [6].
Principally, SWCNTs can be used to avoid dispersing proteins of CNTs without destroying or damaging the nanotube construction. In general, physical entrapment or adsorption can help to gather the proteins [7]. Enhanced solvability of CNTs in organic or aqueous flushes is a main factor in biological functions [7]. Many researchers attempted to investigate useful approaches in which CNTs are functionally connected to biomolecules as identifying factors [8]. In general, this process can take place by covalent functionalization and noncovalent approach [9]. For instance, in carbon nanotube-based ISFET, the conductance of the CN-based ISFET is dependent on pH changes to pH [10]. Similarly, diarylethenes can be considered as a bridge that is able to conversely change nonconjugated conditions to conjugated conditions. The molecular bridge can have two functions, transporting electrical current and sensing/identification through biological occurrences such as DNA hybridization and protein/substrate binding [6].
2. Structure and Detection Mechanism of SWCNT-Based pH Sensor
The homogeneous and transferable SWCNT-based bendable ISFET sensor is an adaptable biological and chemical sensor, which creates in vivo functional capable device due to the biocompatible characteristic of polymer substrate [11]. The assemblage of nanomaterials on cut-price, clear, and bendable substrate via layer-by-layer (LbL) bottom-up structure is useful and proposes a new concept of industrialized procedure [12]. As demonstrated in the proposed structure (Figure 2), the dissolved Cr-Au films were used as electrical contacts on the top of the nanotubes and a certain amount of CNT is deposited into the sensor.
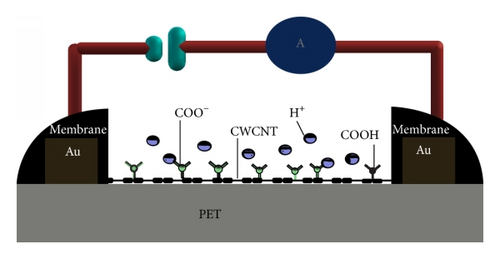
In fact, when π electrons in one-dimensional CNTs are transferred on the surfaces, the transporters move on the surface of the device [13]. Consequently, the ecological perturbations occurring in the areas surrounding carbon surfaces have a strapping impact on the conductance of CNTs.
In the current paper, the interaction between CNTs and solution with different pH causes considerable alterations in conductance of nanotube network field-effect transistors (NTNFET) device by electrostatic gating method [14]. In the previous studies, the proposed recognition methods of carbon-based materials were electrostatic gating, transporter mobility modifying, and Schottky obstruction results [15–18]. Electrostatic gating which is influenced by adsorbed charge type has been approved to describe the conductance amend of carbon nanotube transistors [19]. In contrast, the conductivity of the NTNFET tools has an effect on increasing the number of transporters in the channel. The similarity of CNTs with different hydrogen ion concentrations is due to nucleic acid base π stacking on the nanotube surface. It causes the hydrophilic molecular part indicating the exterior and a steady hybrid with individual CNTs to be shaped by covering around the bonds through the fragrant interfaces between CNTs sidewalls and nucleotide bases [20, 21]. In the present paper, the model of ISFET tools is planned as detectors of pH sensing. The suggested model imitates the behaviour of ISFET tool to differentiate between wild-type (wt) and mutant (mut) alleles [22]. Different pH rates, as a function of entrance voltage, are replicated using pH-sensing factor. In the end, a study has been reported evaluating/comparing the offered model and experimental data in [10].
3. I-V Characteristic of Perfectly Symmetric SWCNT
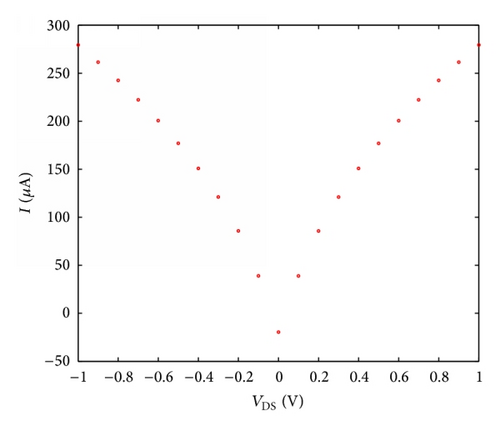
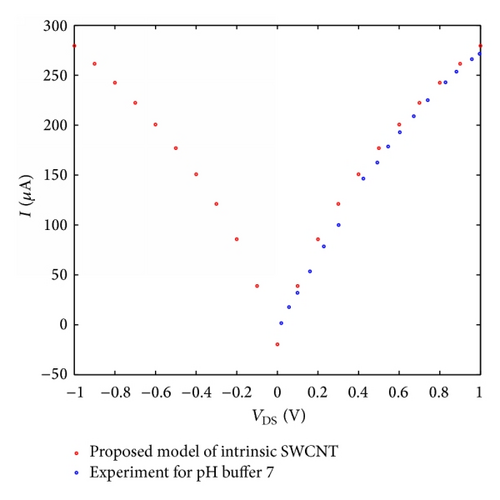
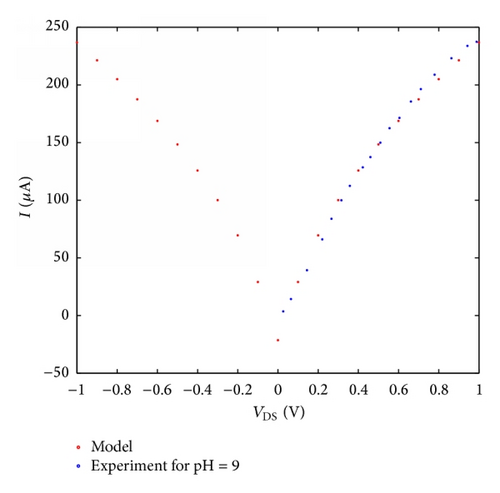
There is a positive relationship between planned model for pH sensor based SWCNT and experimental result which is reported from [31].
4. Proposed Model for SWCNT-Based ISFET
Different rates of pH buffer have been inserted in the chamber to permit attachment to SWCNT surfaces to be saturated. As it is represented in Figure 4, by affecting the gate voltage in the electrolyte membrane, it is obviously declared that the conductance of FET-based CNT demonstrates different behaviour and after that the I-V feature of ISFET tool will be converted. The different layers of CNT have been observed by considering the current versus the voltage, which is recognized from transferring characteristic curve.
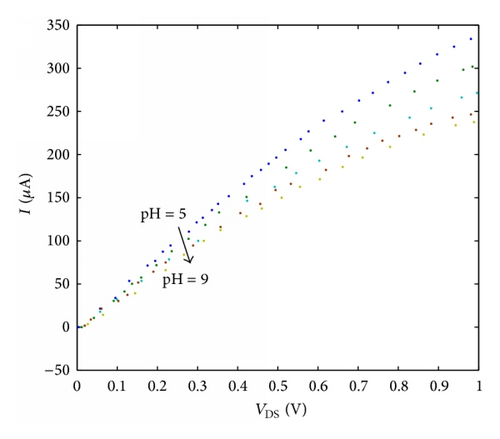
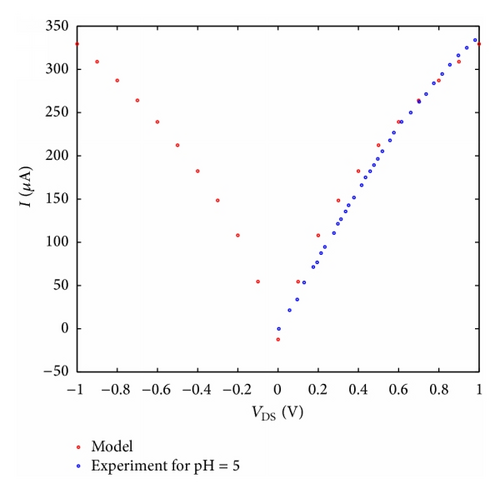
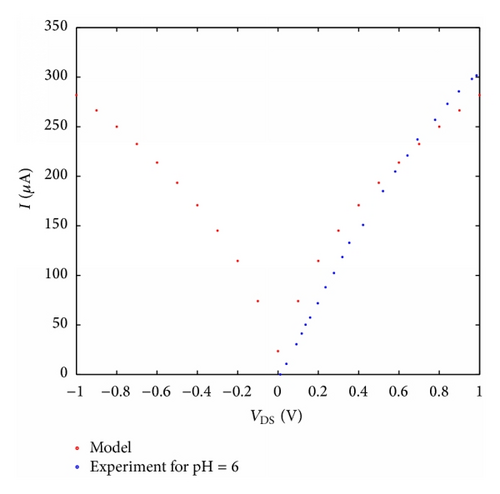
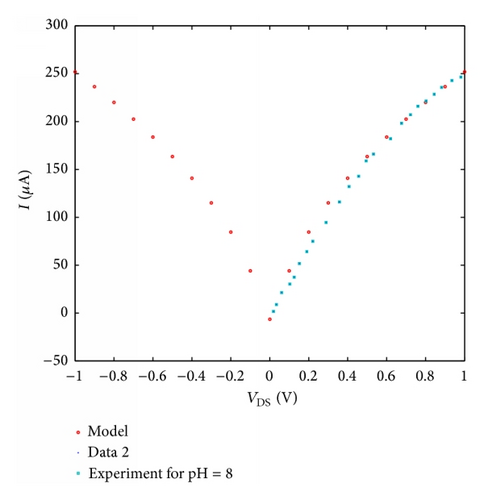
For instance, when pH buffer improves from 5 to 7, it is remarkable that the model is closer to the blue line and the conductance of nanotube will be reduced about 35 μs; in the same way we can evaluate other experimental data as well. It is actually shown that I-V characteristic curve can be managed by altering pH buffer through the pH feature. In addition, the planned model is powerfully estimated with experimental data [10].
According to Figure 6, the quantity of conductance will be saturated by rising the pH buffer from 8 to 9, probably holding the fact that the concentration of hydrogen ions is inadequate and the sensor transfer cure has been saturated. According to what is discussed above, one could strongly assert that the current versus gate voltage of SWCNT-based ISFET device with different pH values can be displayed by ion concentration of the solution. In addition, the current of its channel is assumed as a function of PH levels, which can be controlled by a control parameter (α). The number of carriers changing in the channel influences the conductance of the CNT-based FET devices. FET-based CNT with high sensitivity was applied to detect the pH changes, based on the conductance variations. The performance of CNT-based biosensor for pH = 5 to pH = 9 is evaluated and the analytical results of the proposed model for pH sensor with appropriate parameters are compared with the experimental which indicates a good agreement. It is evident in the figures that the points calculated and obtained from our model agreeably overlap the measurement data.
5. Conclusion
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) with considerable electrochemical properties as the leading materials in nanotechnology have attracted scientific attention. Due to its considerable features, single-walled CNT (SWCNT) can be employed as an electrochemical sensor. The rising potentials of nanostructured SWCNT-based ISFET in elevated responsive and useful emergence of single-base polymorphism as the key to the identification of genetic diseases and understanding of modified medicine can be confirmed. The PH sensing mechanism plays an important role in several aspects affecting the structure and activity of enzymes. As a pH sensor, pH buffer can present the gate voltage. In the current study, the gate voltage is presumed as a function of pH buffer of electrolyte membrane, which exemplifies pH-sensing factor. Measurements demonstrate that the conductance of SWCNT is considerably reduced when the pH buffer improves. As a pH sensor, the gate voltage can be displayed by ion concentration of different pH buffer, which demonstrates that pH sensing aspect presented model verifies the reported experimental data as well.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support from the Research University Grant of the Ministry of Higher Education (MOHE), Malaysia. Also thanks are due to the Research Management Center (RMC) of Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (UTM) for providing excellent research environment in which to complete this work.




