MELD score < 18 rule out 28-day ACLF development among inpatients with hepatitis B-related previous compensated liver disease
Tingting Qi
Hepatology Unit, Department of Infectious Diseases, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorCongyan Zhu
Hepatology Unit, Department of Infectious Diseases, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
Hepatology Unit and Department of Infectious Disease, Zhuhai People's Hospital, Zhuhai, China
Search for more papers by this authorJiapeng Wang
Hepatology Unit, Department of Infectious Diseases, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
Department of Infectious Diseases, Tianjin First Central Hospital, Tianjin, China
Search for more papers by this authorBeiling Li
Hepatology Unit, Department of Infectious Diseases, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorZuxiong Huang
Department of Hepatology, Mengchao Hepatobiliary Hospital of Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, China
Department of Hepatology, Affiliated Infectious Disease Hospital of Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorZhibin Zhu
The Forth Department of Hepatology, The Third People's Hospital of Shenzhen, Affiliated with Guangdong Medical College, Shenzhen, China
Search for more papers by this authorMinghan Tu
Department of Hepatology, The Ninth Hospital of Nanchang, Nanchang, China
Hepatology Unit, Zengcheng Branch, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorGuohong Deng
Department of Infectious Diseases, Southwest Hospital, Third Military Medical University (Army Medical University), Chongqing, China
Search for more papers by this authorXin Zheng
Department of Infectious Diseases, Institute of Infection and Immunology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorYan Huang
Department of Infectious Diseases, Hunan Key Laboratory of Viral Hepatitis, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, China
Search for more papers by this authorZhongji Meng
Department of Infectious Diseases, Hubei Clinical Research Center for Precise Diagnosis and Treatment of Liver Cancer, Taihe Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan, Hubei, China
Search for more papers by this authorXianbo Wang
Center of Integrative Medicine, Beijing Ditan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
Search for more papers by this authorZhiping Qian
Department of Liver Intensive Care Unit, Shanghai Public Health Clinical Centre, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
Search for more papers by this authorHai Li
Department of Gastroenterology, Ren Ji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
Shanghai Institute of Digestive Disease, Key Laboratory of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Chinese Ministry of Health (Shanghai Jiao Tong University), Shanghai, China
Search for more papers by this authorYanhang Gao
Department of Hepatology, The First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China
Search for more papers by this authorFeng Liu
Department of Infectious Diseases and Hepatology, The Second Hospital of Shandong University, Jinan, China
Search for more papers by this authorJia Shang
Department of Infectious Diseases, Henan Provincial People's Hospital, Zhengzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorYu Shi
The State Key Laboratory for Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Diseases, The First Affiliated Hospital of School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Collaborative Innovation Center for Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Disease, Hangzhou, China
National Clinical Research Center of Infectious Disease, Hangzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorXiaobo Lu
Infectious Disease Center, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi, China
Search for more papers by this authorShaoyang Wang
Department of Infectious Diseases, Fuzhou General Hospital of Nanjing Military Command, Fujian, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Hai Li
Department of Infectious Diseases, Affiliated Hospital of Logistics University of People's Armed Police Force, Tianjin, China
Correspondence
Jinjun Chen, Hepatology Unit, Department of Infectious Diseases, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China, Hepatology Unit, Zengcheng Branch, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China.
Email: [email protected]
Hai Li, Department of Gastroenterology, Ren Ji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Jinjun Chen
Hepatology Unit, Department of Infectious Diseases, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
Hepatology Unit, Zengcheng Branch, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
Correspondence
Jinjun Chen, Hepatology Unit, Department of Infectious Diseases, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China, Hepatology Unit, Zengcheng Branch, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China.
Email: [email protected]
Hai Li, Department of Gastroenterology, Ren Ji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorTingting Qi
Hepatology Unit, Department of Infectious Diseases, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorCongyan Zhu
Hepatology Unit, Department of Infectious Diseases, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
Hepatology Unit and Department of Infectious Disease, Zhuhai People's Hospital, Zhuhai, China
Search for more papers by this authorJiapeng Wang
Hepatology Unit, Department of Infectious Diseases, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
Department of Infectious Diseases, Tianjin First Central Hospital, Tianjin, China
Search for more papers by this authorBeiling Li
Hepatology Unit, Department of Infectious Diseases, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorZuxiong Huang
Department of Hepatology, Mengchao Hepatobiliary Hospital of Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, China
Department of Hepatology, Affiliated Infectious Disease Hospital of Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorZhibin Zhu
The Forth Department of Hepatology, The Third People's Hospital of Shenzhen, Affiliated with Guangdong Medical College, Shenzhen, China
Search for more papers by this authorMinghan Tu
Department of Hepatology, The Ninth Hospital of Nanchang, Nanchang, China
Hepatology Unit, Zengcheng Branch, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorGuohong Deng
Department of Infectious Diseases, Southwest Hospital, Third Military Medical University (Army Medical University), Chongqing, China
Search for more papers by this authorXin Zheng
Department of Infectious Diseases, Institute of Infection and Immunology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorYan Huang
Department of Infectious Diseases, Hunan Key Laboratory of Viral Hepatitis, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, China
Search for more papers by this authorZhongji Meng
Department of Infectious Diseases, Hubei Clinical Research Center for Precise Diagnosis and Treatment of Liver Cancer, Taihe Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan, Hubei, China
Search for more papers by this authorXianbo Wang
Center of Integrative Medicine, Beijing Ditan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
Search for more papers by this authorZhiping Qian
Department of Liver Intensive Care Unit, Shanghai Public Health Clinical Centre, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
Search for more papers by this authorHai Li
Department of Gastroenterology, Ren Ji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
Shanghai Institute of Digestive Disease, Key Laboratory of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Chinese Ministry of Health (Shanghai Jiao Tong University), Shanghai, China
Search for more papers by this authorYanhang Gao
Department of Hepatology, The First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China
Search for more papers by this authorFeng Liu
Department of Infectious Diseases and Hepatology, The Second Hospital of Shandong University, Jinan, China
Search for more papers by this authorJia Shang
Department of Infectious Diseases, Henan Provincial People's Hospital, Zhengzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorYu Shi
The State Key Laboratory for Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Diseases, The First Affiliated Hospital of School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Collaborative Innovation Center for Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Disease, Hangzhou, China
National Clinical Research Center of Infectious Disease, Hangzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorXiaobo Lu
Infectious Disease Center, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi, China
Search for more papers by this authorShaoyang Wang
Department of Infectious Diseases, Fuzhou General Hospital of Nanjing Military Command, Fujian, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Hai Li
Department of Infectious Diseases, Affiliated Hospital of Logistics University of People's Armed Police Force, Tianjin, China
Correspondence
Jinjun Chen, Hepatology Unit, Department of Infectious Diseases, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China, Hepatology Unit, Zengcheng Branch, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China.
Email: [email protected]
Hai Li, Department of Gastroenterology, Ren Ji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Jinjun Chen
Hepatology Unit, Department of Infectious Diseases, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
Hepatology Unit, Zengcheng Branch, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
Correspondence
Jinjun Chen, Hepatology Unit, Department of Infectious Diseases, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China, Hepatology Unit, Zengcheng Branch, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China.
Email: [email protected]
Hai Li, Department of Gastroenterology, Ren Ji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorTingting Qi, Congyan Zhu and Jiapeng Wang equally contributed and share first authorship.
Jinjun Chen and Hai Li equally contributed and share corresponding authorship.
Abstract
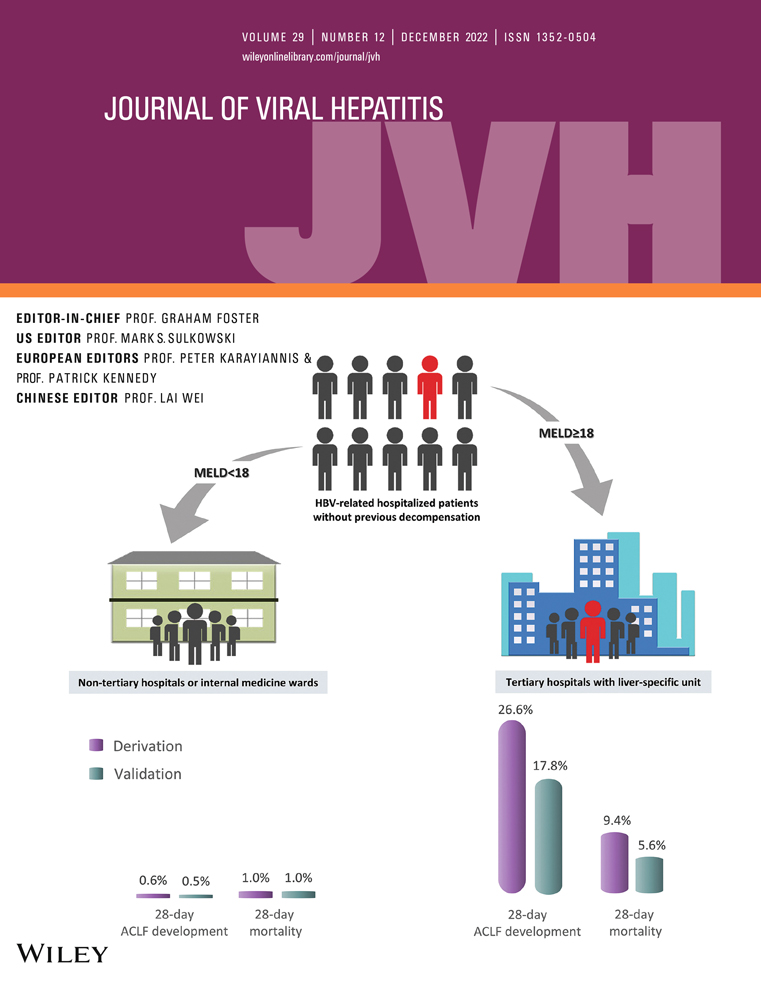
The acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) development is highly dynamic. Currently, no satisfactory algorithm identifies patients with HBV at risk of this complication. The aim of the study was to characterize ACLF development in hospitalized HBV-related patients without previous decompensation and to test the performance of traditional prognostic models in ruling out ACLF development within 28 days on admission we conducted a cohort study. Two multi-center cohorts with hospitalized HBV-related previous compensated patients were analyzed. Performances of MELD, MELD-Na, CLIF-C AD, and CLIF-C ACLF-D in ruling out ACLF development within 28 days were compared and further validated by ROC analyses. In the derivation cohort (n = 892), there were 102 patients developed ACLF within 28 days, with profound systemic inflammatory levels and higher 28-day mortality rate (31.4% vs. 1.0%) than those without ACLF development. The MELD score (cut-off = 18) achieved acceptable missing rate (missed/total ACLF development) at 2.9%. In the validation cohort (n = 1656), the MELD score (<18) was able to rule out ACLF development within 28 days with missing rate at 3.0%. ACLF development within 28 days were both lower than 1% (0.6%, derivation cohort; 0.5%, validation cohort) in patients with MELD < 18. While in patients with MELD ≥ 18, 26.6% (99/372, derivation cohort) and 17.8% (130/732, validation cohort) developed into ACLF within 28 days, respectively. While MELD-Na score cut-off at 20 and CLIF-AD score cut-off at 42 did not have consistent performance in our two cohorts. MELD < 18 was able to safely rule out patients with ACLF development within 28 days in HBV-related patients without previous decompensation, which had a high 28-day mortality.
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
The authors declare that they do not have anything to disclose regarding funding or conflict of interest with respect to this manuscript.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| jvh13747-sup-0001-FigureS1.tifimage/tif, 411.8 KB |
Figure S1 |
| jvh13747-sup-0002-FigureS2.tifimage/tif, 7.6 MB |
Figure S2 |
| jvh13747-sup-0003-FigureS3.tifimage/tif, 7.6 MB |
Figure S3 |
| jvh13747-sup-0004-TableS1.docxWord 2007 document , 14.3 KB |
Table S1 |
| jvh13747-sup-0005-TableS2.docxWord 2007 document , 18.4 KB |
Table S2 |
| jvh13747-sup-0006-TableS3.docxWord 2007 document , 18.6 KB |
Table S3 |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
REFERENCES
- 1Moreau R, Jalan R, Gines P, et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure is a distinct syndrome that develops in patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2013; 144(7): 1426-1437. 1437.e1-9, 1437.e9.
- 2Jalan R, Saliba F, Pavesi M, et al. Development and validation of a prognostic score to predict mortality in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure. J Hepatol. 2014; 61(5): 1038-1047.
- 3Bajaj JS, O'Leary JG, Reddy KR, et al. Survival in infection-related acute-on-chronic liver failure is defined by extrahepatic organ failures. Hepatology. 2014; 60(1): 250-256.
- 4Sarin SK, Choudhury A, Sharma MK, et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: consensus recommendations of the Asian Pacific association for the study of the liver (APASL): an update. Hepatol Int. 2019; 13(4): 353-390.
- 5Tang L, Covert E, Wilson E, Kottilil S. Chronic hepatitis B infection: a review. JAMA. 2018; 319(17): 1802-1813.
- 6Li H, Chen LY, Zhang NN, et al. Characteristics, diagnosis and prognosis of acute-on-chronic liver failure in cirrhosis associated to hepatitis B. Sci Rep. 2016; 6:25487.
- 7Shi Y, Yang Y, Hu Y, et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure precipitated by hepatic injury is distinct from that precipitated by extrahepatic insults. Hepatology. 2015; 62(1): 232-242.
- 8Wu T, Li J, Shao L, et al. Development of diagnostic criteria and a prognostic score for hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure. Gut. 2018; 67(12): 2181-2191.
- 9Tang X, Qi T, Li B, Chen J. Pre-acute-on-chronic liver failure in hepatitis B-related patients. J Hepatol. 2021; 74(2): 479-480.
- 10Trebicka J, Fernandez J, Papp M, et al. The PREDICT study uncovers three clinical courses of acutely decompensated cirrhosis that have distinct pathophysiology. J Hepatol. 2020; 73(4): 842-854.
- 11Gu WY, Xu BY, Zheng X, et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure in China: rationale for developing a patient registry and baseline characteristics. Am J Epidemiol. 2018; 187(9): 1829-1839.
- 12Qiao L, Wang X, Deng G, et al. Cohort profile: a multicentre prospective validation cohort of the Chinese acute-on-chronic liver failure (CATCH-LIFE) study. BMJ Open. 2021; 11(1):e037793.
- 13Hou J, Wang G, Wang F, et al. Guideline of prevention and treatment for chronic hepatitis B (2015 update). J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2017; 5(4): 297-318.
- 14Xu X, Duan Z, Ding H, et al. Chinese guidelines on the management of ascites and its related complications in cirrhosis. Hepatol Int. 2019; 13(1): 1-21.
- 15Terrault NA, Lok A, McMahon BJ, et al. Update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B: AASLD 2018 hepatitis B guidance. Hepatology. 2018; 67(4): 1560-1599.
- 16Garcia-Tsao G, Abraldes JG, Berzigotti A, Bosch J. Portal hypertensive bleeding in cirrhosis: risk stratification, diagnosis, and management: 2016 practice guidance by the American association for the study of liver diseases. Hepatology. 2017; 65(1): 310-335.
- 17Runyon BA. Introduction to the revised American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases practice guideline management of adult patients with ascites due to cirrhosis 2012. Hepatology. 2013; 57(4): 1651-1653.
- 18Colecchia A, Ravaioli F, Marasco G, et al. A combined model based on spleen stiffness measurement and Baveno VI criteria to rule out high-risk varices in advanced chronic liver disease. J Hepatol. 2018; 69(2): 308-317.
- 19Gustot T, Fernandez J, Garcia E, et al. Clinical course of acute-on-chronic liver failure syndrome and effects on prognosis. Hepatology. 2015; 62(1): 243-252.
- 20Choudhury A, Kumar M, Sharma BC, et al. Systemic inflammatory response syndrome in acute-on-chronic liver failure: relevance of 'golden window': a prospective study. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017; 32(12): 1989-1997.
- 21Gustot T, Stadlbauer V, Laleman W, Alessandria C, Thursz M. Transition to decompensation and acute-on-chronic liver failure: role of predisposing factors and precipitating events. J Hepatol. 2021; 75(Suppl 1): S36-S48.
- 22Mehta G, Gustot T, Mookerjee RP, et al. Inflammation and portal hypertension - the undiscovered country. J Hepatol. 2014; 61(1): 155-163.
- 23Berzigotti A, Seijo S, Arena U, et al. Elastography, spleen size, and platelet count identify portal hypertension in patients with compensated cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2013; 144(1): 102-111.e1.
- 24Abraldes JG, Bureau C, Stefanescu H, et al. Noninvasive tools and risk of clinically significant portal hypertension and varices in compensated cirrhosis: the "anticipate" study. Hepatology. 2016; 64(6): 2173-2184.
- 25Macdonald S, Andreola F, Bachtiger P, et al. Cell death markers in patients with cirrhosis and acute decompensation. Hepatology. 2018; 67(3): 989-1002.
- 26Lei JH, Peng F, Chen Z, Xiao XQ. Is HBV viral load at admission associated with development of acute-on-chronic liver failure in patients with acute decompensation of chronic hepatitis B related cirrhosis? BMC Infect Dis. 2019; 19(1): 363.
- 27de Franchis R. Expanding consensus in portal hypertension: report of the Baveno VI consensus workshop: stratifying risk and individualizing care for portal hypertension. J Hepatol. 2015; 63(3): 743-752.
- 28Augustin S, Pons M, Maurice JB, et al. Expanding the Baveno VI criteria for the screening of varices in patients with compensated advanced chronic liver disease. Hepatology. 2017; 66(6): 1980-1988.
- 29Cales P, Buisson F, Ravaioli F, et al. How to clarify the Baveno VI criteria for ruling out varices needing treatment by noninvasive tests. Liver Int. 2019; 39(1): 49-53.
- 30Wang H, Wen B, Chang X, et al. Baveno VI criteria and spleen stiffness measurement rule out high-risk varices in virally suppressed HBV-related cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2021; 74(3): 584-592.
- 31Choudhury A, Jindal A, Maiwall R, et al. Liver failure determines the outcome in patients of acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF): comparison of APASL ACLF research consortium (AARC) and CLIF-SOFA models. Hepatol Int. 2017; 11(5): 461-471.